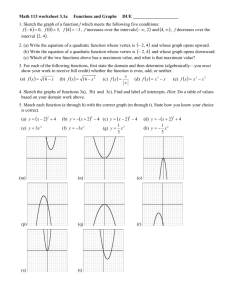
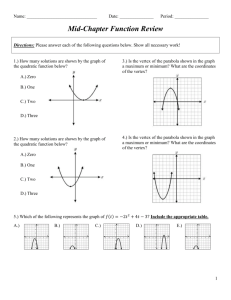
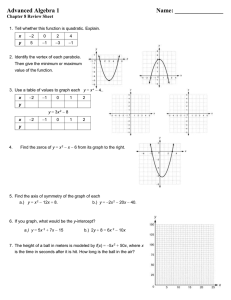
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models

3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models
Objectives:
1. Identify the vertex & axis of symmetry of a quadratic function.
2. Graph a quadratic function using its vertex, axis and intercepts.
3. Use the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function to
solve applied problems.
1
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Warmup:
1. Write the function in vertex form by completing the square.
x
2
+ 6
x
10 = 0
2
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
CU Succeed
Friday is the LAST day to register!!!!
3
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
General Form of a quadratic function: f(x) = ax
2
+ bx + c a ≠ 0
Standard Form of a quadratic function: f(x) = a(x h) + k a ≠ 0
Type of graph: Parabola
This form is easier to graph: Standard Form
How to change from general to standard form: Complete the Square
4
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Example #1: Find the vertex and line of symmetry by completing the square.
f(x) = 3x 2 + 12x + 4
Now you can pick out the vertex and axis of symmetry:
(Remember the axis of symmetry from the vertex form is .)
and
5
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
General Form:
We can also find the vertex from the general form by using the equation:
Then we substitute this value in for x and solve for y of the vertex.
From the general form, remember that
.
is also the equation for the axis of symmetry.
6
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Standard Form:
What does a , from the standard form, tell us?
If a > 0, the parabola opens up and the vertex is the minimum point.
If a < 0, the parabola opens down and the vertex becomes the maximum point.
7
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011
Example #2:
Find the vertex, axis of symmetry, and graph the parabola.
March 02, 2011
8
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
1) Using the general form 2) Using the standard form
Vertex:
Axis of Symmetry: x = 5 /
4
Vertex:
Axis of Symmetry: x = 5 /
4
9
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Having the vertex and knowing whether the graph opens up or down is really not enough to accurately graph the parabola. We should also locate the intercepts.
How many are possible? 0, 1, or 2
How can you find these intercepts?
Set the quadratic equal to "0" and solve for "x".
Use factoring, quadratic formula, or completing the square to solve for the xintercepts.
So the xintercepts
are 1 and
10
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Graph:
11
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
You can tell how many xintercepts there will be by using the discriminant: b
2
4 ac b
2
4 ac > 0, there are two real intercepts b 2
4 ac = 0, there is only one (double) real intercept b
2
4 ac < 0, there are no real intercepts
12
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Example #3:
Graph using vertex, axis of symmetry, y and xintercepts (if any).
13
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011
Example #4:
Write the quadratic function with V (3, 0)
and containing the point (6, 9).
March 02, 2011
14
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Quadratic functions are used in many mathematical models:
Revenue function: maximum
Cost function: minimum
15
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Example #5:
The manufacturer of Knuckle Draggin' Snowboards found that when the unit price is p dollars, the revenue R (in dollars) is:
What is the unit price needed to maximize the revenue?
What is the maximum revenue?
16
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Example #6:
A farmer has 600 yards of fencing for a rectangular garden.
Find the area of the garden as a function of the width x .
What value of x will maximize the area?
What is that area?
17
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Example #7:
The height of a softball (in feet) hit by a batter is given by the equation: where x is the horizontal distance from the batter (in feet).
What is the horizontal distance from the batter when the ball is at its maximum height?
Find the maximum height of the softball.
18
3.1 Quadratic Functions and Models 2011 March 02, 2011
Homework : page 164
(22, 29, 31, 33, 45,
49, 59, 63, 65, 72, 73,
77, 79, 81, 86, 100)
19