Extensions to Mendel Unit 4 Genetics
advertisement

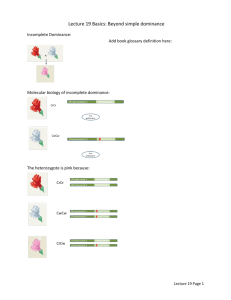
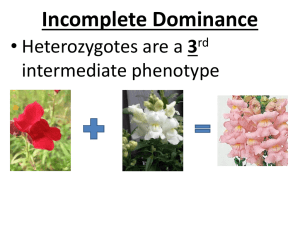
Extensions to Mendel Unit 4 Genetics Color Blindness • X-Linked Recessive Condition X Xc X XX XXc Y XY XcY Physiology of Color Blindness • Defective Cone Cells which detect color • Shift the wavelengths of light so the signal sent to the brain is the wrong color. • L, M and S wavelengths (Long, Medium and Short) • Mixture of abnormalities with cones (missing…) Most Common- M Cone The eye • Rods and Cones are on the cells of the retina Are You Color Blind? Everyone can see these shapes People who are colorblind cannot see the circle. Example: Find the Red Crayon Key Questions 1) Can a female inherit colorblindness from dad? Yes - nearly 100% 2) Does this mean that she will be colorblind? No - need to factor in the other X chromosome from mom 3) Why? It’s a recessive XcX-Normal vision XcXc-colorblind 4) Can a male inherit color blindness from dad? No, a male only inherits the Y chromosome from dad Exceptions to Mendelian ratios: 1 Incomplete or Codominance - Two or more alleles exist, but none is dominant to the other/s 2 Multiple alleles for a single gene 3 Epistasis - interactions b/t more than one gene 4 Sex-linkage - locus of a gene is on a sex chromosome 5 Sex influenced or limited expression is influenced or limited by gender (hormones…) Incomplete Or Codominance • Incomplete or codominance - Two or more alleles exist, but none are dominant to the other • Incomplete dominance results in blending of the parental traits • Example: In some flowers red crossed with white results in pink F1 generation RED + Incomplete Or Codominance In the F2 generation a 1:2:1 ratio results of red to pink to white • F2 results shown below CRCR CWCW F2 Generation 1:2: C R CW CR CW CR CR CR CR CW CW CRCW CWCW Epistasis 1 2 A B C pathway produces a red pigment, C, in flowers and that A is a colorless precursor and B is a yellow intermediate A If X 1 B 2 C the gene for enzyme 1 was knocked out, the flower would be colorless Epistasis (cont.) A If 1 B X 2 C the gene for enzyme 2 was knocked out, the flowers would be yellow Epistasis If both genes were knocked out, the flowers would be colorless A X 1 B X 2 C 1F1n2F2n X 1F1n2F2n Confusing 1F2F 1F2n 1n2F 1n2n F1F2F2F1F1F2F2n1F1n2F2F1F1n2F2n F F 1 1 2 1F2n 1F1F2F2n1F1F2n2n1F1n2F2n1F1n2n2n 1n2F 1F1n2F2F1F1n2F2n1n1n2F2F1n1n2F2n F1n2F2n1F1n2n2n1n1n2F2n1n1n2n2n n n 1 1 2 1F1n2F2n X 1F1n2F2n Mendelian- 9:3:3:1 1F2F 1F2n 1n2F 1n2n F1F2F2F1F1F2F2n1F1n2F2F1F1n2F2n F F 1 1 2 1F2n 1F1F2F2n1F1F2n2n1F1n2F2n1F1n2n2n 1n2F 1F1n2F2F1F1n2F2n1n1n2F2F1n1n2F2n F1n2F2n1F1n2n2n1n1n2F2n1n1n2n2n n n 1 1 2 1F1n2F2n X 1F1n2F2n Epistatic 1F2F 1F2n 1n2F 1n2n F1F2F2F1F1F2F2n1F1n2F2F1F1n2F2n F F 1 1 2 1F2n 1F1F2F2n1F1F2n2n1F1n2F2n1F1n2n2n 1n2F 1F1n2F2F1F1n2F2n1n1n2F2F1n1n2F2n F1n2F2n1F1n2n2n1n1n2F2n1n1n2n2n n n 1 1 2 A 9:4:3 Ratio A biochemical pathway like this one = 9:4:3 ratio as long as there are two alleles each of which behaves in a simple dominant/recessive way The 9:4:3 ratio is really a 9:(3+1):3 ratio Other possible phenotypic ratios for a dihybrid cross involving epistasis are below: – 9:7 = 9:(3+3+1) – 12:3:1 = (9+3):3:1 – 12:4 =(9+3):(3+1) – 10:3:3 = (9+1):3:3 – 10:6 = (9+1):(3+3) – 13:3 = (9+1+3):3 A ratio made up of some combination of 9:3:3:1 is generally a good hint that epistasis is at work