Chp. 15 pp. 363-379 Atom I.
advertisement

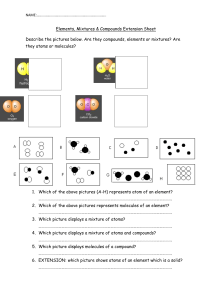
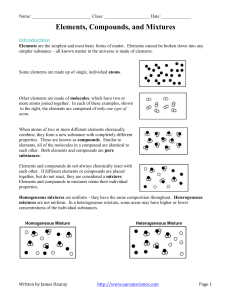
Chp. 15 pp. 363-379 Atom- the smallest component of an element having the chemical properties of the element Molecule- 2 or more atoms held tightly together I. II. III. Phases of Matter a. Easiest way to describe matter b. Solid- definite volume and shape c. Liquid- definite volume and indefinite shape d. Gas - indefinite volume and indefinite shape e. Submicroscopic level (can’t see) i. Solid-bonds between molecules are strong enough to hold them in a fixed position. ii. Liquid- molecules slip past one another like marbles in a bag iii. Gas- molecules bounce off one another Physical and Chemical Properties a. Physical properties- describe the physical attributes of a substance i. color ii. hardness iii. density iv. texture v. phase vi. Specific Heat Capacity- heat required to change the temp. of a unit mass of a substance by 1 (how fast things heat up) EX. Gold- yellowish, soft, dense at room temperature. b. Physical change i. Physical change- change in some physical property of a substance 1. Ex. Melting Ice, boiling water, freezing water a. All substances are still water (IT MAINTAINS IT’S CHEMICAL IDENTITY) b. Phase Changesi. Evaporation- Liquid to gas ii. Sublimation- solid to gas iii. Condensation- gas to liquid iv. Melting- solid to liquid v. Freezing- liquid to solid c. Chemical properties- the tendency of a substance to transform into another substance i. Chemical change- atoms rearrange and switch partners 1. Ex. Iron Rust Iron atoms break apart and combine with oxygen atoms 2. Ex: Grape juice Wine Sugar molecules rearrange to make alcohol molecules. b. Substances change (DO NOT MAINTAIN CHEMICAL IDENTITY) 3. Chemical change means there is a new chemical 4. Physical change means there are just new attributes to the same chemical 5. Hard because there is a change in appearance for both changes in many cases. Elements, Compounds and Mixtures a. Element- consisting of only one type of atom i. 118 elemental materials ii. 90 natural occurring elements iii. EX: H, O, C, B, He, O2, H2, b. Compound- atoms of different elements attached to one another i. EX: Sodium (Na) atoms and Chlorine (Cl) atoms Sodium chloride (NaCl) = Table Salt c. Chemical Formula- represents a compound i. EX: NaCl, H2O, MnO2 d. Mixtures- elements and compounds, compounds and compounds or mixture of elements i. EX: Sea Water = mixture of H2O and a variety of salts Air = Mixture of N2, O2, and other gases ii. Can separate mixtures by knowing the physical properties of the mixtures components. 1. Boiling pts. 2. Melting pts. 3. Color…