Algebra 2 Ch.8 Notes Page 51 P51 86 Natural Logarithms
advertisement

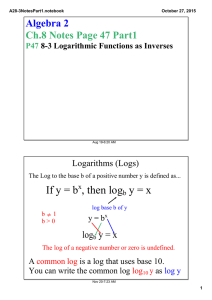
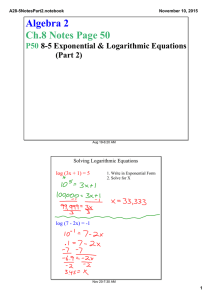
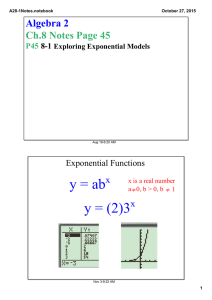
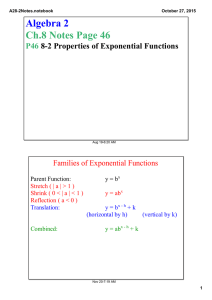
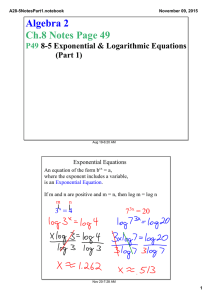
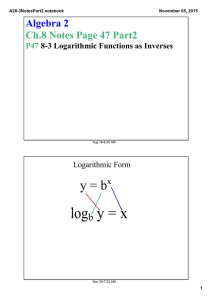
A28­6Notes.notebook October 27, 2015 Algebra 2 Ch.8 Notes Page 51 P51 8­6 Natural Logarithms Aug 19­6:20 AM The Natural Logarithmic Function If y = ex , then loge y = x , which is usually written ln y = x The natural log function is the inverse, y = ln x Nov 20­7:33 AM 1 A28­6Notes.notebook October 27, 2015 Simplifying Natural Logarithms The properties of common logs also apply to natural logs. Write as a Single Natural Logarithm 3 ln 6 ­ ln 8 3 ln x + ln y 1/4 ln 3 + 1/4 ln x Nov 20­7:33 AM Solving Natural Log Equations Remember the base of a Natural Log is e. ln (3x + 5)2 = 4 ln x = .1 ln (x+2) = 12 3 Nov 20­7:33 AM 2 A28­6Notes.notebook October 27, 2015 Solving Exponential Equations ex+1 = 30 7e2x + 2.5 = 20 Nov 20­7:33 AM Investment Example An investment of $100 is now valued at $149.18. The interest rate is 8%, compounded continuously. About how long has the money been invested? A = Pert Nov 20­7:34 AM 3 A28­6Notes.notebook October 27, 2015 Space Example A spacecraft can attain a stable orbit 300 km above Earth if it reaches a velocity of 7.7 km/s. The formula for a rocket's maximum velocity v in kilometers per second is v = ­.0098t + c ln R. The booster rocket fires for t seconds and the velocity of the exhaust is c km/s. The ratio of the mass of the rocket filled with fuel to its mass without fuel is R. Suppose R = 25, c = 2.8, and t = 100. Can the spacecraft attain a stable orbit 300 km above Earth? Nov 20­7:33 AM HW #53 8­6 P472 #1­4,7,10­12,14,15,17,18,20,24­26,29 Please put your name and class period at the top of the homework. Also include the homework number. Aug 19­6:25 AM 4 A28­6Notes.notebook October 27, 2015 Nov 20­7:31 AM 5