Types of Plants Non - Vascular Plants
advertisement
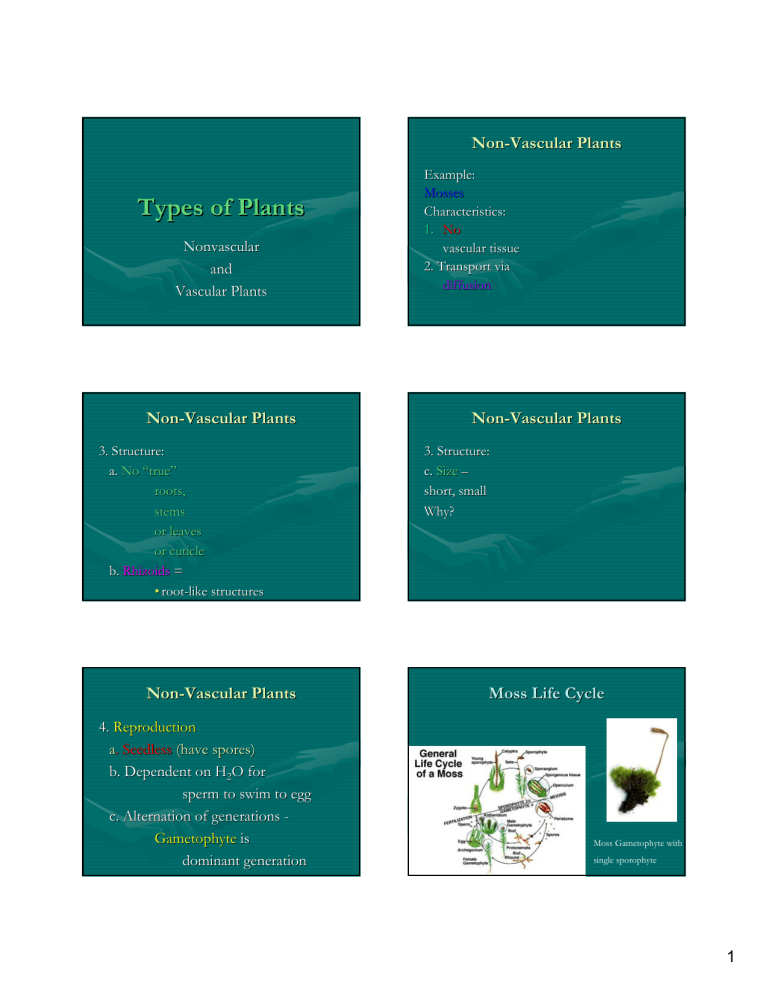
Non-Vascular Plants Types of Plants Nonvascular and Vascular Plants Non-Vascular Plants 3. Structure: a. No “true” true” roots, stems or leaves or cuticle b. Rhizoids = • rootroot-like structures Non-Vascular Plants 4. Reproduction a. Seedless (have spores) b. Dependent on H2O for sperm to swim to egg c. Alternation of generations Gametophyte is dominant generation Example: Mosses Characteristics: 1. No vascular tissue 2. Transport via diffusion Non-Vascular Plants 3. Structure: c. Size – short, small Why? Moss Life Cycle Moss Gametophyte with single sporophyte 1 Non-Vascular Plants 5. Habitat – wetlands 6. Ecological Roles : • Habitat for animals • Fuel (peat) • Soil improvement (peat) What is Vascular Tissue? Definition: system of tubes for transport Location: in “true” true” roots, stems, leaves Examples: 1. Xylem – move nutrients & H2O UP from roots 2. Phloem – transports the products of photosynthesis in all directions Fern Structure • Size : can be taller than mosses Why? Vascular Plants 1. Seedless Vascular Plants Example: Ferns 2. Seed Plants Example: trees, flowering plants 1. Seedless Vascular plants : Ferns a. Structure • True roots, stems & leaves vascular tissue • Frond = blade (leaf) of fern • Cuticle on upper surface of frond (Waxy covering, prevents dehydration) • Have Stomata 1. Seedless Vascular plants : Ferns c. Reproduction i. Seedless (use spores) ii. Spores in sporangia (spore cases) iii. Sporangia clustered in Sori iv. Dependent on H2O for sperm to swim to egg 2 Fern Reproduction Fern Life Cycle v. Alternation of generations Sporophyte is dominant generation Ferns d. Habitat : moist areas e. Ecological Roles • Habitat • Food (Fiddleheads) • Fertilizer Vascular Plants 2. Seed Plants 1. Seeds in Cones 2. Seeds in Flowers = Flowering Plants 3