Java Syntax, Java Conventions, CSE 115 Conventions (Part 3) CSE 115 Spring 2006
advertisement

Java Syntax, Java Conventions,
CSE 115 Conventions (Part 3)
CSE 115
Spring 2006
February 6, 8 & 10, 2006
XX - References
Declaring an instance variable creates a
reference.
All references are initially null.
We assign a value to a reference using the
assignment operator
XXI – Assignment Operator
=
Takes the value on the right and assigns it
to the variable on the left:
_varName = new Object();
Review of Composition
Declare an instance variable
Create an instance of the subpart
Assign the instance to the instance
variable
Note that steps two and three above
actually happen in one line of code.
ClassA has a ClassB
public class ClassA {
private ClassB _classB;
public ClassB() {
_classB = new ClassB();
}
}
XXII – Sending Messages
Asking/telling an object to do something,
or asking it to perform one of its
capabilities.
Capabilities are methods inside our class
definition.
In code, we would be performing a method
call/method invocation.
Syntax of a Method Call
instanceName.methodName();
• Q: What is the name of the () and what
are the () used for in a method call?
Four Main Parts of a Method
Sender
Receiver
Return Type
Parameters
Describe the purpose of each of these and
what they correspond to in code.
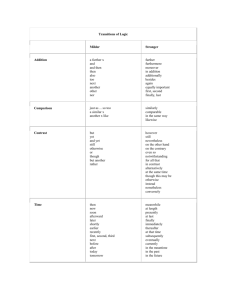
Cardinality
The number of a certain type of
relationship between objects.
An Applet can have 5 BouncingBalls. That
means there are 5 instances of the “has-a”
relationship present.
Association Relationship
“knows a” relationship
In UML, represented by an arrow ( → )
In code:
Declare an instance variable of the associate.
In constructor, accept a parameter whose type
is the same as that of the associate
Assign the value of the parameter to the
instance variable
Dog knows a Tree
public class Dog {
private Tree _tree;
public Dog(Tree tree) {
_tree = tree;
}
}