Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Two Independent Samples
advertisement
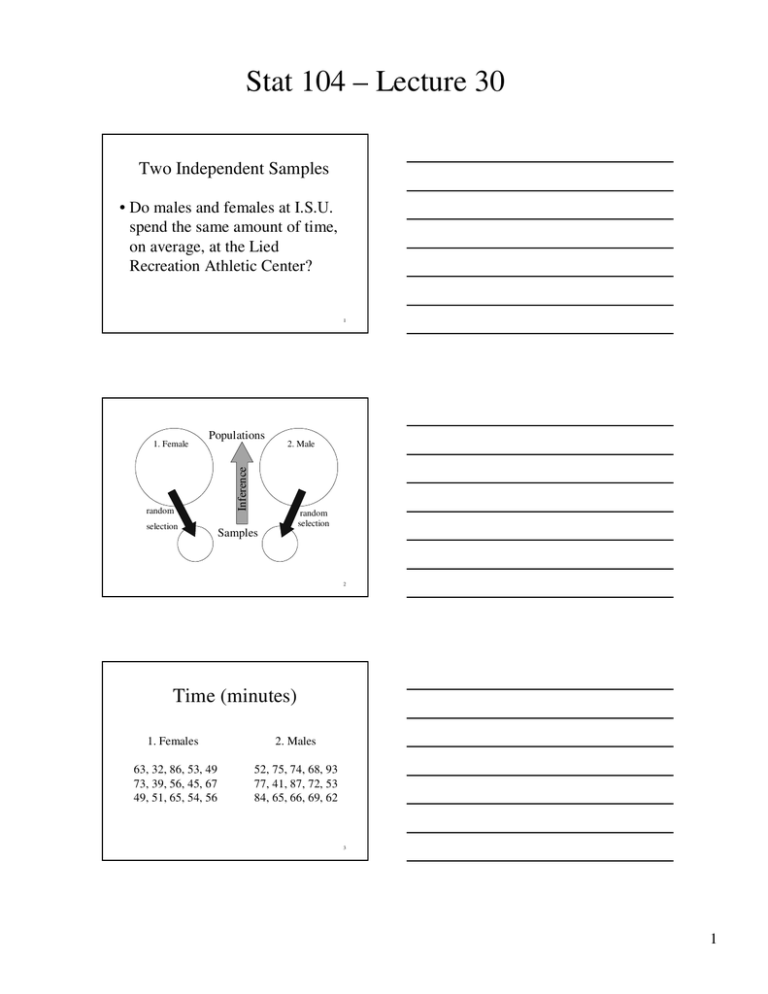
Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Two Independent Samples • Do males and females at I.S.U. spend the same amount of time, on average, at the Lied Recreation Athletic Center? 1 Populations random selection 2. Male Inference 1. Female random selection Samples 2 Time (minutes) 1. Females 2. Males 63, 32, 86, 53, 49 73, 39, 56, 45, 67 49, 51, 65, 54, 56 52, 75, 74, 68, 93 77, 41, 87, 72, 53 84, 65, 66, 69, 62 3 1 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Time (minutes) Sex=F Mean Std Dev Sex=M 55.87 Mean 69.20 13.527 Std Dev 13.790 n 15 n 15 4 Comment • This sample of I.S.U. females spends, on average, 13.33 minutes less time at the Lied Recreation Athletic Center than this sample of I.S.U. males. 5 Confidence Interval: μ 1 ( y1 − y2 ) ± t * − μ2 s12 s22 + n1 n2 t* from Table T, df = smaller of (n1 − 1, n2 − 1) 6 2 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Finding t* • Use Table T. • Confidence Level in last row. • df = smaller of (n1 – 1, n2 – 1) = 14. 7 Table T df 1 2 3 4 M 2.145 14 Confidence Levels 80% 90% 95% 98% 99% 8 s12 s22 + = n1 n2 (13.527)2 + (13.792)2 15 15 = 24.88 = 4.988 9 3 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Confidence Interval: μ 1 ( y1 − y 2 ) ± t* − μ2 s12 s 22 + n1 n2 (55.87 − 69.2) ± 2.145(4.988) − 13.33 ± 10.70 − 24.03 to − 2.63 10 Interpretation • We are 95% confident that I.S.U. females spend, on average, from 2.63 to 24.03 minutes less time at the Lied Recreation Athletic Center than I.S.U. males do. 11 Test of Hypothesis: μ 1 − μ2 • Step 1: Set – up. H 0 : μ1 = μ2 or H 0 : μ1 − μ2 = 0 H A : μ1 ≠ μ2 or H A : μ1 − μ2 ≠ 0 12 4 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Test of Hypothesis: μ 1 − μ2 • Step 2: Test Criteria. – Times are normally distributed. – Population standard deviations not known. – t-test statistic. – α = 0.05 13 Test of Hypothesis: μ 1 − μ2 • Step 3: Sample evidence. t= ( y1 − y 2 ) − 0 s12 s 22 + n1 n 2 14 Time (minutes) Sex=F Mean Std Dev n Sex=M 55.87 Mean 69.20 13.527 Std Dev 13.790 15 n 15 15 5 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 (13.527)2 + (13.792)2 s12 s22 + = n1 n2 15 15 = 24.88 = 4.988 16 Test of Hypothesis: μ 1 − μ2 • Step 3: Sample evidence. t= ( y1 − y2 ) − 0 = (55.87 − 69.20) 4.988 s12 s22 + n1 n2 t = −2.672 17 Table T Two tail probability 0.20 0.10 0.05 0.02 P-value 0.01 df 1 2 3 4 M 14 1.345 1.761 2.145 2.624 2.672 2.718 18 6 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 Test of Hypothesis: μ 1 − μ2 • Step 4: Probability value –The P-value is between 0.01 and 0.02. 19 Test of Hypothesis: μ 1 − μ2 • Step 5: Results. – Reject the null hypothesis because the P-value is smaller than α = 0.05 – The difference in mean times is not zero. Therefore, on average, females and males at I.S.U. spend different amounts of time at the Lied Recreation Athletic Center. 20 Comment • This conclusion agrees with the results of the confidence interval. • Zero is not contained in the 95% confidence interval (–24.03 mins to –2.63 mins), therefore the difference in population mean times is not zero. 21 7 Stat 104 – Lecture 30 JMP • Data in two columns. –Response variable: • Numeric – Continuous –Explanatory variable: • Character – Nominal 22 JMP Starter • Basic – Two-Sample t-Test –Y, Response: Time –X, Grouping: Sex 23 Oneway Analysis of Time By Sex 100 90 Time 80 70 60 50 40 30 F M Sex Means and Std Deviations Level F M Number 15 15 Mean 55.8667 69.2000 Std Dev 13.5270 13.7903 Std Err Mean 3.4927 3.5606 Lower 95% 48.376 61.563 Upper 95% 63.358 76.837 t Test F-M Assuming unequal variances Difference -13.333 t Ratio Std Err Dif 4.988 DF Upper CL Dif -3.116 Prob > |t| Lower CL Dif -23.550 Prob > t Confidence 0.95 Prob < t -2.67326 27.98961 0.0124 0.9938 -15 -10 0.0062 -5 0 5 10 15 24 8