Science SCI.III.5.2 Grade: 6
advertisement

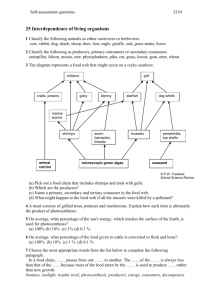
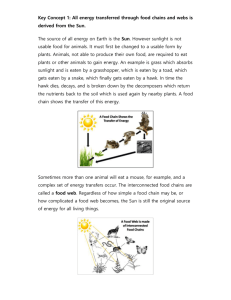
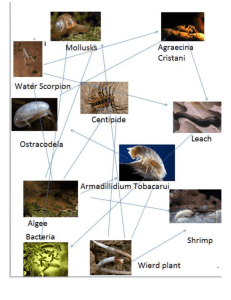
Science SCI.III.5.2 Grade: 6 Strand III: Using Scientific Knowledge in Life Science Standard 5: Ecosystems - All students will explain how energy is distributed to living things in an Ecosystem Benchmark 2: Describe how organisms acquire energy directly or indirectly from sunlight. Constructing and Reflecting: SCI.I.1.1 - Generate scientific questions about the world based on observations. SCI.I.1.6 - Write and follow procedures in the form of step-by-step instructions, formulas, flow diagrams, and sketches. SCI.II.1.1 - Evaluate the strengths and weaknesses of claims, arguments, or data. SCI.II.1.2 - Describe limitations in personal knowledge. SCI.II.1.3 - Show how common themes of science, mathematics, and technology apply in real-world contexts. SCI.II.1.5 - Develop an awareness of and sensitivity to the natural world. Vocabulary / Key Concepts Context • sunlight • plants • food • photosynthesis • producers • consumers • food webs See III.2.MS.3 Photosynthesis and food use Selected food webs, including humans Knowledge and Skills Students will demonstrate how energy flows through simple food chains and food webs. Students will recognize that sunlight is the direct source of energy for all producers. Producers, such as green plants and algae, make their own food through the process of photosynthesis. Consumers cannot make their own food. They must consume other organisms to obtain energy. All organisms can serve as energy sources (food) for other organisms. Resources Coloma Resources: Power Plant Other Resources • Field Detectives – AIMS • Exploring Environments – AIMS • Project Wild – Western Regional Environmental Education Council, Inc. – “Owl Pellets” • Invasive Species – many lesson opportunities – all interactive • Michigan Teacher Network Resources • Bill Nye: Caves, Deserts, Forests, Lakes, Ponds, Ocean Life, Rivers, Streams, Wet Lands. • Science Explosion: Ecosystems Videoconferences Available For more information, see www.remc11.k12.mi.us/dl or call Janine Lim 471-7725x101 or email jlim@remc11.k12.mi.us III.5.MS.2 Food Webs from the Bronx Zoo/Wildlife Conservation Society Photosynthesis from Camden Children's Garden Circle of Life from the Columbus Zoo Space Farming from NASA Johnson Space Center Food Chains and Webs from the Toledo Zoo 6th Grade Science Curriculum Technology Resources III.5.MS.2 Describe how organisms acquire energy directly or indirectly from sunlight. Vernier Probes available: Light Sensor, Temperature Probe Instruction Assessment Focus Question: How does energy move through a food web? Coloma Required Assessment: Discover the Wonder (Module F F24-55) • Optional Assessment (similar to Module F test) Students will select a presentation format (concept map, poster, or 3-D display) and design a food web. • • In small groups, students draw a picture of a double cheeseburger and list the contents in a table (include all possible items on a typical burger, including condiments). They will identify the contents as coming from a plant or animal. They will draw a food chain showing how the various contents can be traced back to the sun. Each group will present their food chain to the class and discuss similarities and differences. The class will discuss the following questions: - What is the primary energy source? - Why is sunlight so important? - What organisms are the producers? - What organisms are the consumers? - How do producers and consumers acquire energy? - Does the sun’s energy stop at the consumer level? - What will happen to your leftovers? Extension: Analyze owl pellets to identify members of a food chain. The food web should: • Use arrows that represent the direction and flow of energy from one organism to another. • Identify the role each organism plays in its food web (producer, consumer, decomposer). (Give students rubric before activity.) Scoring Rubric Criteria: Completeness of illustration: Apprentice -Shows none or limited flow of energy through the food web. Basic - Shows most of the energy flow correctly through the food web. Meets - Illustrates the correct flow of energy through the food web. Exceeds - Extends connections to include other organisms outside of the food web. Criteria: Correctness of identification: Apprentice -Identifies few producers, consumers, and decomposers. Basic - Identifies some producers, consumers, and decomposers. Meets - Identifies all producers, consumers, and decomposers. Exceeds - Identifies all producers, consumers, and decomposers and extends to include identification of organisms outside of the primary food web. Teacher Notes: Refer to Benchmarks concerning photosynthesis: Benchmark III.1.2: Explain why and how selected specialized cells are needed by plants and animals. Benchmark III.2.3: Describe evidence plants make and store food. “All organisms, including the human species, are part of and depend on two main interconnected global food webs. One includes microscopic ocean plants, the animals that feed on them, and finally the animals that feed on those animals. The other web includes land plants, the animals that feed on them, and so forth. The cycles continues indefinitely because organisms decompose after death to return food material to the environment.” (BSL) Focus Question • How does energy from the sunlight transfer through the food web?