Science SCI.III.5.1 Grade: 4th
advertisement

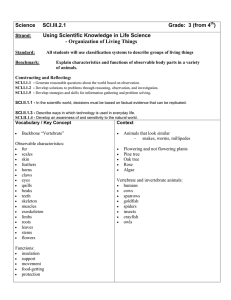
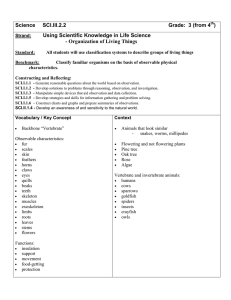
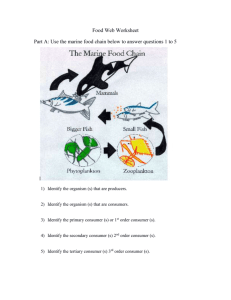
Science Strand: Should this go to 3rd with other Owl Study material? Grade: 4th Using Scientific Knowledge in Life Science - Ecosystems SCI.III.5.1 Standard: All students will explain how parts of an ecosystem are related and how they interact Benchmark: Identify familiar organisms as part of a food chain or a food web and describe their feeding relationships within the web. Constructing and Reflecting: SCI.I.1.1 - Generate reasonable questions about the world based on observation. SCI.I.1.2 - Develop solutions to problems through reasoning, observation, and investigation. SCI.I.1.3 - Manipulate simple devices that aid observation and data collection. SCI.I.1.5 - Develop strategies and skills for information gathering and problem solving. SCI.I.1.6 - Construct charts and graphs and prepare summaries of observations. SCI.II.1.1 - In the scientific world, decisions must be based on factual evidence that can be replicated. SCI.II.1.2 - Show how science concepts can be illustrated through creative expression such as language arts and fine arts. SCI.II.1.4 - Develop an awareness of and sensitivity to the natural world. Vocabulary / Key Concept Context Words describing parts of a food web: • producer • consumer • predator • prey • decomposer • habitat • community Food chains and food webs involving these common organisms: • rabbits • birds • snakes • grasshoppers • plants Knowledge and Skills All living things depend on each other to survive. The parts of a food chain or food web have special names that describe the feeding relationships with the web. Students will: • Identify and categorize producers – they make their own food (plants) • Identify and categorize consumers – they depend on producers or consumers for their food • Identify and categorize decomposers – they break down dead plants and animals and return nutrients to the soil • Identify and categorize predators – they hunt other animals and devour their prey • Identify and categorize prey – they are animals that are hunted for food • Define food chain • Define food web. Resources Coloma Resources: Need resources here Sarett Visit – Owls and other cool animals! The Owl Study has been moved to 3rd grade. These resources should move too???? Other Resources: Owl Cam – Web site with photos and narrative of nesting owls and their owlets. FACINATING! http://www.owlcam.com/index.htm “The Secret Life of Owls” – links to lots of resources on the Carolina site – lots of info to accompany a teaching unit about owls – evolution, diet, hunting, nesting, quicktime videos and more. http://www.carolina.com/owls/index.asp Carolina Biological – Tips – Owl Pellets – good information to accompany a pellet dissection. http://www.carolina.com/tips/98mar/tips398a.asp Barn Owl Pellet Interactive Study – students compare pellet dissection results with other students around the USA. http://www.carolina.com/owls/form.asp Owl Pellet Bone Chart – Carolina Biological – http://www.carolina.com/manuals/manuals8/Owl_Pel let_Bone_Chart.pdf Rat Skeleton Chart – Carolina Biological – http://www.carolina.com/owls/guide/ratskeleton.pdf Bird Skeleton Chart – Carolina Biological – http://www.carolina.com/owls/guide/birdskeleton.pdf Owl Pellet Student Study Manual http://www.carolina.com/manuals/manuals8/Owl_Pel let_Study_Kit_tm.pdf Resources (continued from column on right) Slide show – various bird beaks – with adaptation information – excellent photos. http://www.teachersdomain.org/35/sci/life/colt/birdfood/index.html Quicktime video – What sounds do Animals Make? – meshes nicely with the OwlCam sound clips http://www.teachersdomain.org/35/sci/life/colt/sound/index.html The Owl Pages – Lots of information about owls around the world - http://www.owlpages.com/ Teacher Domain – Characteristics of Living Things – lots of clips and images of various animals and adaptations! AWESOME http://www.teachersdomain.org/35/sci/life/colt/index.html Instruction Benchmark Question: How are parts of an ecosystem related and how do they interact? Focus Question: How are organisms linked together in a food chain or food web and what is the flow of energy in the chain or web? Owl Study Moved to 3rd grade Assessment Owl Study Moved to 3rd grade Teacher Notes: Explain how parts of an ecosystem are related and how they interact. It is important for students to learn about many ecosystems, but they need to begin with those that have the closest connection to them. Very young children think in terms of organisms that are around them such as pets, animals in zoos, and houseplants. At a young age, many children think humans help to feed wild animals. As they mature, children begin to understand the concept of populations of organisms in the wild. The concept of populations is most clearly understood in terms of food chains and food webs. In elementary school, students should be introduced to food chains and learn about some of the organisms involved. Early in this time, students may only be able to understand the relationship between two organisms. Later, students should be able to identify the organisms involved in both food chains and food webs and the feeding relationships that occur. Interestingly, children in elementary school may not believe that food can be a scarce resource in a food web. They think that all animals are more like people in that animals can change what they need to eat whenever they want according to what is available. Students in these grades should be able to describe all of the basic requirements needed for all living things to exist. As students progress through the upper elementary grades and go into middle school they should become more aware of different interactions between organisms, besides food. For example, there are mutually beneficial relationships like plants depending on animals for pollination. There are also competitive relationships in which different animals with similar environmental requirements compete for the same resources. In the middle school, students should be made aware of the relationships between organisms in which neither could survive without the other. By high school, students should be able to describe common ecological relationships between and among species and their environments. They should understand the difficult concepts of competition, territory, and carrying capacity among others.