Open Data and Open Code for S&T Assessment
advertisement
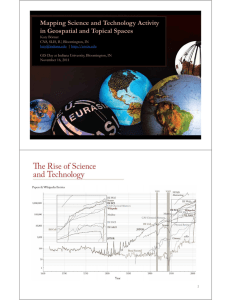
Open Data and Open Code for S&T Assessment Dr. Katy Börner Cyberinfrastructure for Network Science Center, Director Information Visualization Laboratory, Director School of Library and Information Science Indiana University, Bloomington, IN katy@indiana.edu With special thanks to Kevin W. Boyack, Micah Linnemeier, Russell J. Duhon, Patrick Phillips, Joseph Biberstine, Chintan Tank Nianli Ma, Angela M. Zoss, Hanning Guo, Mark A. Price, S Scott W Weingart i Northwestern Institute on Complex Systems (NICO) Annual Conference Northwestern University, IL September 3, 2009 Overview Science of Science Studies Science of Science Cyberinfrastructure (http://sci.slis.indiana.edu): (http //sci slis indiana ed ) Scholarly Database (SDB) (http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu) that provides free access to 23 million scholarly records Sci S i2 Tool T l which hi h reads d SDB data d andd supports the h id identification ifi i off activity i i bursts, the extraction and display of co-author/inventor/investigator networks, and topical analysis, among others. Mapping Science Exhibit Overview Science of Science Studies Science of Science Cyberinfrastructure (http://sci.slis.indiana.edu): (http //sci slis indiana ed ) Scholarly Database (SDB) (http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu) that provides free access to 23 million scholarly records Sci S i2 Tool T l which hi h reads d SDB data d andd supports the h id identification ifi i off activity i i bursts, the extraction and display of co-author/inventor/investigator networks, and topical analysis, among others. Mapping Science Exhibit Computational Scientometrics: Studying Science by Scientific Means Börner, Katy, Chen, Chaomei, and Boyack, Kevin. (2003). Visualizing Knowledge Domains. In Blaise Cronin (Ed.), Annual Review of Information Science & Technology, Medford, NJ: Information Today, Inc./American Society for Information Science and Technology, Volume 37, Chapter 5, pp. 179255. http://ivl.slis.indiana.edu/km/pub/2003-borner-arist.pdf Shiffrin, Richard M. and Börner, Katy (Eds.) (2004). Mapping Knowledge Domains. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, America 101(Suppl_1). 101(Suppl 1) http://www.pnas.org/content/vol101/suppl_1/ Börner, Katy, Sanyal, Soma and Vespignani, Alessandro (2007). Network Science. In Blaise Cronin (Ed.), Annual Review of Information Science & Technology, Information Today, Inc./American Society for Information Science and Technology, Medford, NJ, Volume 41, Chapter 12, pp. 537-607. http://ivl.slis.indiana.edu/km/pub/2007-borner-arist.pdf Börner, Katy, Ma, Nianli, Duhon, Russell Jackson & Zoss, Angela. (2009). Science & Technology Assessment Using Open Data and Open Code. IEEE Intelligent Systems. Vol. 24(4), 78-81, IEEE Computer Systems.. Places & Spaces: Mapping Science exhibit, see also http://scimaps.org. 4 Computational Scientometrics Opportunities Advantages for Funding Agencies Supports monitoring of (long-term) money flow and research developments, evaluation of fundingg strategies g for different p programs, g , decisions on p project j durations,, fundingg patterns. p Staff resources can be used for scientific program development, to identify areas for future development, and the stimulation of new research areas. Advantages for Researchers Easy access to research results, results relevant funding programs and their success rates, rates potential collaborators, competitors, related projects/publications (research push). More time for research and teaching. Advantages for Industry Fast and easy access to major results, experts, etc. Can influence the direction of research by entering information on needed technologies (industry-pull). Advantages Ad antages for Publishers P blishers Unique interface to their data. Publicly funded development of databases and their interlinkage. For Society Dramatically improved access to scientific knowledge and expertise. Process of Computational Scientometrics , Topics Börner, Katy, Chen, Chaomei, and Boyack, Kevin. (2003) Visualizing Knowledge Domains. In Blaise Cronin (Ed.), Annual Review of Information Science & Technology, Volume 37, Medford, NJ: Information Today, Inc./American Society for Information Science and Technology Technology, chapter 55, pp pp. 179 179-255. 255 Latest ‘Base Map’ of Science Kevin W. Boyack, Katy Börner, & Richard Klavans (2007). Mapping the Structure and Evolution of Ch i Research. Chemistry R h 11th 11 h International I i l Conference C f on Scientometrics Si i andd Informetrics. I f i pp. 112-123. 112 123 Uses combined SCI/SSCI from 2002 • 1.07M papers, 24.5M references, 7,300 journals • Bibliographic coupling of p p r aggregated papers, r t d tto journals Initial ordination and clustering of journals gave 671 clusters Coupling counts were reaggregated at the journal cluster level to calculate the • (x,y) positions for each journal cluster • by association, (x,y) positions ii for f each h jjournall Math Law Computer Tech Policy Statistics Economics CompSci Vision Education Phys-Chem Chemistry Physics Psychology Brain Environment Psychiatry MRI Biology BioMaterials BioChem Microbiology Pl t Plant Cancer Animal Disease & Treatments Virology Infectious Diseases Science map applications: Identifying core competency Kevin W. Boyack, Katy Börner, & Richard Klavans (2007). Funding patterns of the US Department of Energy (DOE) Math Law Computer Tech Policy Statistics Economics CompSci Vision Education Phys-Chem Chemistry Physics Psychology Brain Environment Psychiatry GeoScience MRI Biology GI GeoScience BioBi Materials BioChem Microbiology Plant Cancer Animal Virology Infectious Diseases Science map applications: Identifying core competency Kevin W. Boyack, Katy Börner, & Richard Klavans (2007). Funding Patterns of the National Science Foundation (NSF) Math Law Computer Tech Policy Statistics Economics CompSci Vision Education Phys-Chem Chemistry Physics Psychology Brain Environment GeoScience Psychiatry MRI Biology GI BioBi Materials BioChem Microbiology Plant Cancer Animal Virology Infectious Diseases Science map applications: Identifying core competency Kevin W. Boyack, Katy Börner, & Richard Klavans (2007). Funding Patterns of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Math Law Computer Tech Policy Statistics Economics CompSci Vision Education Phys-Chem Chemistry Physics Psychology Brain Environment Psychiatry GeoScience MRI Biology GI BioBi Materials BioChem Microbiology Plant Cancer Animal Virology Infectious Diseases Science map applications: Identifying core competency Kevin W. Boyack, Katy Börner, & Richard Klavans (2007). Funding Patterns of the National Institutes of Health (NIH) Math Law Computer Tech Policy Statistics Data: SCI/SSCI 2002: proprietary DOE: FOIR NIH: http://projectreporter.nih.gov NSF: http://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch SciMap to DOE/NIH/NSF linkage data not available. Economics Education Psychology CompSci Vision Phys-Chem Chemistry Physics Brain Environment Psychiatry GeoScience MRI Biology GI BioBi Materials BioChem Algorithms/Tools: DrL available Microbiology Plant Cancer Virology Animal Infectious Diseases Mapping Indiana’s Intellect Intellectual al Space Data: Proprietary Identify Id if Pockets of innovation Pathways from ideas to products Interplay I l off industry i d andd academia d i Algorithms/Tools: Custom DB queries and code, not available. Mapping the Evolution of Co-Authorship Networks Ke, Visvanath & Börner, (2004) Won 1st price at the IEEE InfoVis Contest. 13 Data: Available as mdb from http://iv.slis.indiana.edu/ref/iv04contest p // / / Algorithms/Tools: Complete workflow with pointers to code are at http://iv.slis.indiana.edu/ref/iv04contest 14 Studying the Emerging Global Brain: Analyzing and Visualizing the Impact of Co-Authorship Teams Börner Dall’Asta Börner, Dall Asta, Ke & Vespignani (2005) Complexity, Complexity 10(4):58 10(4):58-67. 67 Research question: • Iss science sc e ce driven d ve by prolific p o c single s g e experts e pe ts or by high-impact co-authorship teams? Contributions: • New approach to allocate citational Data: credit. Available as mdb from • Novel weighted graph representation. http://iv.slis.indiana.edu/ref/iv04contest p // / / • Visualization of the growth of weighted co-author network. Algorithms/Tools: • Centrality measures to identify Customauthor DB queries and code, not available. i impact. • Global statistical analysis of paper production and citations in correlation with co co-authorship authorship team size over time time. • Local, author-centered entropy measure. 15 113 Years of Physical Review http://scimaps.org/dev/map_detail.php?map_id=171 Bruce W. Herr II and Russell Duhon (Data Mining & Visualization), Elisha F. Hardy (Graphic Design), Shashikant Penumarthy (Data Preparation) and Katy Börner (Concept) Data: Available via Scholarly Database if APS permits access http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu/ p // / (Bob Kelly, Director Journal Information Systems The American Physical Society, 631-591-4064) Algorithms/Tools: Custom DB queries and code, not available. Spatio-Temporal Information Production and Consumption of Major U.S. Research Institutions Börner, Katy, Penumarthy, Shashikant, Meiss, Mark and Ke, Weimao. (2006) M i the Mapping h Diffusion Diff i off Scholarly S h l l Knowledge K l d Among A Major M j U.S. U S Research R h Institutions. Scientometrics. 68(3), pp. 415-426. Research questions: 1 Does space still matter 1. in the Internet age? 2. Does one still have to studyy and work at major j research institutions in order toData: have access to high quality data and expertise and to produce high Available via Scholarly Database if you attended Sackler quality research? Colloquium q l bon “Mapping pp g Knowledge w g Domains” in 3 Does 3. D the h IInternet llead d to more global l citation i i May 2003 patterns, i.e., more citation links between papers http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu/ produced at geographically distant research instructions? Contributions: Algorithms/Tools: Answer to Qs 1 + 2 isCustom YES. DB queries and code, not available. Answer to Qs 3 is NO. Novel N l approach h to analyzing l i the h dduall role l off institutions as information producers and consumers and to study and visualize the diffusion of information among them. Mapping Topic Bursts Co-word space of the top 50 highly frequent and bursty words used in the top 10% most highly cited PNAS publications in 1982-2001. Mane & Börner. (2004) PNAS, 101(Suppl. 1): 5287-5290. Data: Available via Scholarly Database if you attended Sackler Colloquium q on “Mapping pp g Knowledge w g Domains” in May 2003 http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu/ Algorithms/Tools: Custom DB queries and code, not available. 18 Mapping Transdisciplinary Tobacco Use Research Centers Publications C Compare R01 investigator i i based b d funding f di with i h TTURC Center awards in terms of number of publications and evolving co-author networks. Z & Börner, Zoss Bö forthcoming. f th i Data: NIH awards linked to resulting publications We hope it will become available to more researchers. Algorithms/Tools: Al i h /T l Custom DB queries and NWB Tool Reference Mapper Duhon & Börner, Börner forthcoming. forthcoming Data: References from NSF proposals that have been funded. Proprietary. Algorithms/Tools: Al i h /T l RefMapper is part of Sci2 Tool, shared if NSF permits. Overview Science of Science Studies Science of Science Cyberinfrastructure (http://sci.slis.indiana.edu): (http //sci slis indiana ed ) Scholarly Database (SDB) (http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu) that provides free access to 23 million scholarly records Sci S i2 Tool T l which hi h reads d SDB data d andd supports the h id identification ifi i off activity i i bursts, the extraction and display of co-author/inventor/investigator networks, and topical analysis, among others. Mapping Science Exhibit http://sci.slis.indiana.edu Scholarly Database http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu // Nianli Ma “From From Data Silos to Wind Chimes” Chimes C Create public bli ddatabases b that h any scholar h l can use. Sh Share the h b burden d off ddata cleaning l i and d federation. Interlink creators, data, software/tools, publications, patents, funding, etc. La Rowe, Gavin, Ambre, Sumeet, Burgoon, John, Ke, Weimao and Börner, Katy. (2007) The Scholarly Database and Its Utility for Scientometrics Research. In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Scientometrics and Informetrics, Madrid, Spain, June 2527, 2007, pp. 457-462. http://ella.slis.indiana.edu/~katy/paper/07-issi-sdb.pdf Scholarly Database: Web Interface Anybody can register for free to search the about 23 million records and download results as data dumps. Currently the system has over 130 registered users from academia, academia industry, and government from over 60 institutions and four continents. Since March 2009: Users can download networks: - Co-author - Co-investigator - Co-inventor Co ve o - Patent citation and tables for burst analysis in NWB. SDB D Demo http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu Scholarly Database: # Records, Years Covered Datasets available via the Scholarly Database (* internally) Dataset # Records Years Covered Updated Restricted Access Medline 17 764 826 17,764,826 1898 2008 1898-2008 PhysRev 398,005 1893-2006 Yes PNAS 16,167 1997-2002 Yes JCR 59,078 1974, 1979, 1984, 1989 1994-2004 Yes 3, 875,694 1976-2008 Yes* NSF 174,835 1985-2002 Yes* NIH 1,043,804 1961-2002 Yes* Total 23,167,642 , , 1893-2006 4 USPTO Yes Aim for comprehensive time, geospatial, and topic coverage. Temporal and Geospatial Coverage 3 Comparison with Major Publication Data commonly l used d in i scientometric i i studies di NIH Grants Medline Publications NSF Grants US Patents Sci2 Tool http://sci.slis.indiana.edu p “Open Code for S&T Assessment” Branded OSGi/CIShell based tool with NWB plugins p g and many new plugins. Geo Maps Sci Maps GUESS Network Vis Hierarchical Circular Visualization Horizontal Time Graphs Börner, Katy, Huang, Weixia (Bonnie), Linnemeier, Micah, Duhon, Russell Jackson, Phillips, Patrick, Ma, Ni li Zoss, Nianli, Z Angela, A l Guo, G Hanning H i & Price, P i Mark. M k (2009). (2009) R Rete-Netzwerk-Red: N kRd A Analyzing l i andd Visualizing Scholarly Networks Using the Scholarly Database and the Network Workbench Tool. Proceedings of ISSI 2009: 12th International Conference on Scientometrics and Informetrics, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, July 14-17 . Vol. 2, pp. 619-630. Sci2 Tool Geo Maps Circular Hierarchy Serving Non-CS Algorithm Developers & Users Users Developers CIShell Wizards CIShell IVC Interface NWB Interface 36 Sci2 Tool: Supported Data Formats Personal Bibliographies Bibtex (.bib) Endnote Export Format (.enw) Data Providers Web of Science by Thomson Scientific/Reuters (.isi) Scopus by Elsevier ((.scopus) scopus) Google Scholar (access via Publish or Perish save as CSV, Bibtex, EndNote) Awards Search by National Science Foundation (.nsf) Scholarly Database (all text files are saved as .csv) Medline publications by National Library of Medicine NIH funding awards by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) NSF funding f di awards d b by the h N National i l SScience i F Foundation d i (NSF) U.S. patents by the United States Patent and Trademark Office (USPTO) Medline papers – NIH Funding Network Formats NWB (.nwb) Pajek (.net) GraphML (.xml or .graphml) XGMML (.xml) Burst Analysis Format Burst (.burst) Other O h Formats F CSV (.csv) Edgelist (.edge) Pajek (.mat) TreeML T ML (.xml) ( l) 37 NWB=Sci2 Tool: Algorithms (July 1st, 2008) p y and handout See https://nwb.slis.indiana.edu/community 38 NWB=Sci2 Tool: Output Formats NWB tool can be used for data conversion. Supported output formats comprise: CSV (.csv) ( ) NWB (.nwb) Pajek (.net) Pajek (.mat) ( mat) GraphML (.xml or .graphml) XGMML (.xml) GUESS Supports pp export p of images g into common image file formats. Horizontal Bar Graphs saves out raster and ps files. 39 Exemplary p y Analyses y and Visualizations Individual Level A. Loading ISI files of major network science researchers, extracting, analyzing and visualizing paper-citation networks and co-author networks. B. Loadingg NSF datasets with currently active NSF fundingg for 3 researchers at Indiana U Will be presented in hands-on Workshop on Thursday Sept 3, 2009, 1-5pm Institution Level C. Indiana U, Cornell U, and Michigan U, extracting, comparing Co-PI Together with guidance on howand to design networks. workflows using 100+ algorithms and how to dissect and design effective Scientific Field Level visualizations. D. Extracting co-author networks, patent-citation networks, and detecting bursts in SDB data. Bonus: Create your custom tool. Scii2 Tool S T l Demo D http://sci.slis.indiana.edu http://www.nsf.gov/awardsearch Outlook CIShell/OSGi is at the core of different CIs and a total of 169 unique plugins are used in the - Information Visualization (http://iv.slis.indiana.edu), ( p ), - Network Science (NWB Tool) (http://nwb.slis.indiana.edu), - Scientometrics and Science Policy (Sci2 Tool) (http://sci.slis.indiana.edu), and - Epidemics (http://epic.slis.indiana.edu) research communities. Most interestingly, a number of other projects recently adopted OSGi and one adopted CIShell: Cytoscape (http://www.cytoscape.org) lead by Trey Ideker, UCSD is an open source bioinformatics software platform for visualizing molecular interaction networks and integrating these interactions with gene expression profiles and other state data (Shannon et al., 2002). T Taverna Workbench W kb h (http://taverna.sourceforge.net) (h // f ) lead l d by b Carol C lG Goble, bl U University i i off M Manchester, h UK is a free software tool for designing and executing workflows (Hull et al., 2006). Taverna allows users to integrate many different software tools, including over 30,000 web services. MAEviz (https://wiki.ncsa.uiuc.edu/display/MAE/Home) managed by Shawn Hampton, NCSA is an open-source, p extensible software p platform which supports pp seismic risk assessment based on the MidAmerica Earthquake (MAE) Center research. TEXTrend (http://www.textrend.org) lead by George Kampis, Eötvös University, Hungary develops a framework for the easy and flexible integration, configuration, and extension of plugin-based components in support of natural language processing (NLP), classification/mining, and graph algorithms for the analysis of business and governmental text corpuses with an inherently temporal component. As the functionality of OSGi-based software frameworks improves and the number and diversity of dataset and algorithm plugins increases, the capabilities of custom tools or macroscopes will expand. Overview Science of Science Studies Science of Science Cyberinfrastructure (http://sci.slis.indiana.edu): (http //sci slis indiana ed ) Scholarly Database (SDB) (http://sdb.slis.indiana.edu) that provides free access to 23 million scholarly records Sci S i2 Tool T l which hi h reads d SDB data d andd supports the h id identification ifi i off activity i i bursts, the extraction and display of co-author/inventor/investigator networks, and topical analysis, among others. Mapping Science Exhibit Mapping Science Exhibit – 10 Iterations in 10 years http://scimaps.org The Power of Maps (2005) Science Maps for Economic Decision Makers (2008) The Power of Reference Systems (2006) Science Maps for Science Policy Makers (2009) Science Maps for Scholars (2010) Science Maps as Visual Interfaces to Digital Libraries (2011) Science Maps for Kids (2012) Science Forecasts (2013) The Power of Forecasts (2007) How to Lie with Science Maps (2014) Exhibit has been shown in 72 venues on four continents. Currently at - NSF, 10th Floor, 4201 Wilson Boulevard, Arlington, VA - Wallenberg Hall, Stanford University, CA - Center of Advanced European Studies and Research, Bonn, Germany - Science Train, Germany. 46 Debut D b off 5th Iteration I i off Mapping M i SScience i E Exhibit hibi at MEDIA X was on M May 18 18, 2009 at W Wallenberg ll b H Hall, ll Stanford University, http://mediax.stanford.edu, http://scaleindependentthought.typepad.com/photos/scimaps 47 Th Power The P r off Maps M p Four Early Maps of Our World VERSUS Si E Six Early l M Maps off S Science i (1st Iteration of Places & Spaces Exhibit - 2005) Th Power The P r off Reference R f r n Systems S t m Four Existing Reference Systems VERSUS Si P Six Potential i lR Reference f S Systems off S Science i (2nd Iteration of Places & Spaces Exhibit - 2006) The Power of Forecasts F Four Existing E i ti F Forecasts t VERSUS Six Potential Science ‘Weather’ Weather Forecasts (3rd Iteration of Places & Spaces Exhibit - 2007) 114 Years of Physical Review - Bruce W. Herr II, Russell Duhon, Katy Borner, Elisha Hardy, Shashikant Penumarthy - 2007 58 Maps of Science: Forecasting Large Trends in Science - Richard Klavans, Kevin Boyack - 2007 Science Maps for Economic Decision Making Four Existing Maps VERSUS Six Science Maps (4th Iteration of Places & Spaces Exhibit - 2008) 59 Science Maps for Science Policy Making Four Existing Maps VERSUS Six Science Maps (5th Iteration of Places & Spaces Exhibit - 2009) A Clickstream Map of Science – Bollen, Johan, Herbert Van de Sompel, Aric Hagberg, Luis M.A. Bettencourt, Ryan Chute, Marko A. Rodriquez, Lyudmila Balakireva - 2008 64 Council for Chemical Research - Chemical R&D Powers the U.S. Innovation Engine. Washington, DC. Courtesy of the Council for Chemical Research - 2009 65 Additional Elements of the Exhibit Illuminated Diagram Display Hands--on Science Maps for Kids Hands Worldprocessor Globes Illuminated Diagram Display W. Bradford Paley, Kevin W. Boyack, Richard Kalvans, and Katy Börner (2007) Mapping, Illuminating, and Interacting with Science. SIGGRAPH 2007. Questions: p Who is doingg research on what topic and where? What is the ‘footprint’ of interdisciplinary research fields? p have scientists? What impact Large-scale, high resolution prints illuminated via projector or screen. Interactive touch panel. Contributions: Interactive, high resolution interface to access and make sense of data about scholarly activity. 68 Science Maps in “Expedition Zukunft” science train visiting 62 cities in 7 months, 12 coaches, 300 m long. Opening was on April 23rd, 2009 by German Chancellor Merkel, http://www.expedition-zukunft.de 79 Thi is This i the th only l mockup k in i this thi slide lid show. h E Everything hi else l iis available il bl today. d All papers, maps, cyberinfrastructures, talks, press are linked from http://cns.slis.indiana.edu