R genes: Structure, recognition, signaling, & evolution – part 1

R genes: Structure, recognition, signaling, & evolution – part 1
• Major classes of R genes
• R gene structure
• Early signaling events
• R gene evolution
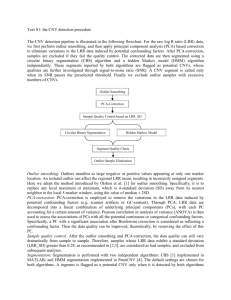
The zigzag model for plant pathogen interactions
Dangl and Jones. 2006. Nature 444:323-329
Plant immune system
Dangl. 2013. Science. 341:746
R protein structure
R proteins encompass multiple domains involved in different aspects of activation and signaling, and intramolecular interaction is involved.
Domains
TIR – Toll/Interleukin-1 receptor
CC – Coiled coil
NBS – Nucleotide binding site
LRR – Leucine-rich repeat
R protein classes
TIR-NBS-LRR, TNL
CC-NBS-LRR, CNL
NB-LRR, NBS-LRR, NLR – Nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat
Cloned disease resistance genes
NBS-LRR is largest class
Major subclasses of NBS-LRR are:
- CC-NBS-LRR
- TIR-NBS-LRR
R gene class and pathogen are not correlated
TIR-NBS-LRR are not found in cereals
Liu et al. 2007. J. Genet. Genom.
34:765-776
Major classes of R proteins
Liu et al. 2007. J. Genet. Genom.
34:765-776
P loop sequences
I-2
Mi-1
Nucleotide binding site (NBS) kinase 2 kinase 3a
GLPL
MHDV
4 hydrophobic amino acids followed by D (e.g. LIVLD )
Highly conserved tyrosine or arginine (e.g. FGNGSR)
Tammeling et al. (2002) Plant Cell 14, 2929–2939
Inferred structure of R protein nucleotide binding sites
McHale et al. 2006.
Genome Biology.
7:212
Inferred structure of LRR domain
McHale et al. 2006.
Genome Biology.
7:212
Variation in numbers of LRRs
Structural models of domains in NLR proteins
Takken. 2012. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15:375-384
Model of LRR motif of lettuce downy mildew resistance protein, Dm3
Michelmore. 2013. Annu. Rev. Phytopathol. 51:291-319
LRR is least conserved part of R genes
Michelmore and Meyers. 1998. Genome Res. 8: 1113-1130
NLR proteins are involved in plant & animal innate immunity
Bonardi et al. (2012) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 24:41-50
Evidence for intramolecular interaction between domains of a CNL protein
CPindependent HR when TEX’d
Co-expression of fulllength GPA2 with either LRR or ARC−LRR of Rx did not lead to a
CP-dependent HR. However, coexpression of GPA2 with Rx NBS−LRR resulted in a
CP-dependent HR (Figure 2B). This result demonstrates that a CC domain can be provided by fulllength CC−NBS−LRR protein. Our observation that Rx NBS−LRR produced a CP-dependent HR when expressed in rx genotype potato leaves can be explained in the same way (Figure 2C). Presumably, a CC domain was provided to
NBS−LRR by full-length homologues of Rx and GPA2 that are present in the rx potato genome (Bendahmane et al., 1999).
Moffett et al. (2002) EMBO J. 21:4511
Intramolecular interactions - continued
N protein oligomerizes in response to elicitor
Mestre. 2006. Plant Cell. 18:491-501
NLR proteins – Mechanisms for activation
Bonardi et al. (2012) Curr. Opin. Immunol. 24:41-50
NLR folding and signaling
Takken. 2012. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 15:375-384
Signaling by animal NLR proteins
Ting et al. 2008. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 8:372-379