Last updated: December 2, 2008 PHY 2054 Discussion – Fall ‘08
advertisement

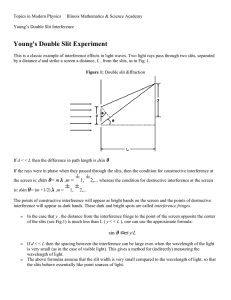
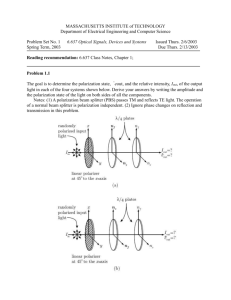
Last updated: December 2, 2008 PHY 2054 Discussion – Fall ‘08 Practice Exam Problems (Chapter 24) 1. Two beams of coherent light are shining on the same piece of white paper. With respect to the crests and troughs of such waves, darkness will occur on the paper where: (Conditions for Interference) the crest from one wave overlaps with the crest from the other.. with the trough from the other. a. b. the crest from one wave overlaps c. the troughs from both waves overlap. d. darkness cannot occur as the two waves are coherent. 2. Laser light sent through a double slit produces an interference pattern on a screen 3.00 m from the slits. If the second order maximum occurs at an angle of 12.0º, at what angle does the eighth order maximum occur? (Double-Slit Interference) a. No eighth order maximum occurs. b. 48.0º c. 56.3º d. Not enough information is given. 3. A Young’s double-slit apparatus is set up. A screen is positioned 1.60 m from the double slits, and the spacing between the two slits is 0.040 0 mm. The distance between alternating bright fringes is 1.42 cm. What is the light source wavelength? (Wavelength Measurement) a. 710 nm b. 490 nm c. 280 nm d. 355 nm 4. Waves from a radio station with a wavelength of 600 m arrive at a home receiver a distance 50 km away from the transmitter by two paths. One is a direct-line path and the second by reflection from a mountain directly behind the receiver. What is the minimum distance between the mountain and receiver such that destructive interference occurs at the location of the listener? Assume no phase change on reflection. (Radio Wave Interference) 5. a. 150 m b. 300 m c. 450 m d. 600 m Upon reflection, light undergoes a 180º phase change: (Phase Change due to Reflection) b. if the incident medium has the higher index of refraction. index of refraction. 6. a. always c. if the incident medium has the lower d. whenever the incident angle is less then the critical angle. What is the minimum thickness of a glycerin film (n = 1.47) on which light of wavelength 600 nm shines that results in constructive interference of the reflected light? Assume the film is surrounded front and back by air. (Interference in Thin Films) 7. a. 75 nm b. 102 nm c. 150 nm d. 204 nm Two flat glass plates are in contact along one end and are separated by a sheet of paper 4.0×10 -6 m thick at the other end. The top plate is illuminated by a monochromatic light source of wavelength 490 nm. How many dark parallel bands will be evident across the top plate? (Wedge-Shaped Films) a. 7 8. b. 9 c. 13 d. 17 When light shines on a lens placed on a flat piece of glass, interference occurs which causes circular fringes called Newton’s rings. The two beams that are interfering come: (Newton’s Rings) the top and bottom surface of lens. piece of glass. a. from b. from the top surface of the lens and the top surface of the c. from the bottom surface of the lens and the top surface of the piece of glass. d. from the top and bottom surface of the flat piece of glass. 9. A Fraunhofer diffraction pattern is created by monochromatic light shining through which of the following? (Fraunhofer Diffraction) a. single slit b. double slit c. triple slit d. more than 3 slits 10. Helium-neon laser light (λ = 632.8 nm) is sent through a single slit of width 0.30 mm. What is the width of the central maximum on a screen 1.0 m in back of the slit? (Single Slit Diffraction) mm b. 3.1 mm c. 4.2 mm d. 5.3 mm 11. The blue light from the sky has been polarized by: (Polarizing Processes) b. reflection. a. 2.0 c. double refraction. a. selective absorption. d. scattering. 12. Plane polarized light is sent through two consecutive polarizers, the first having its plane of polarization in the same direction as the incident light and the second having its plane at 90º to the original plane of polarization. A third polarizer, with plane of polarization at 30º to the original plane of polarization, is placed between the two other polarizers. What fraction of the original intensity now gets through? (Malus’s Law) a. 0 b. 0.56 c. 0.25 d. 0.19 13. The critical angle for sapphire surrounded by air is 34.4º. Calculate the polarizing angle for sapphire. (Brewster’s Angle) Answers: 1-b 2-c 3-d a. 60.5º b. 59.7º 4-a 6-b 5-c c. 58.6º 7-d 8-c c. 56.3 9-a 10-c 11-d 12-d 13-a