HOMEWORK for JUNE 30, 2005
advertisement

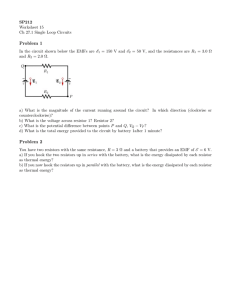
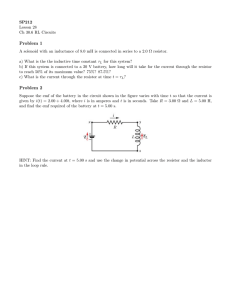
HOMEWORK for JUNE 30, 2005 For the following circuits, draw the circuit and fill out the V M ?Z T table (including the battery or batteries). Also mark a point between each pair of circuit elements (resistors or batteries) and determine the electric potential at that point; let the negative terminal of the largest battery be set at zero potential. Also indicate the direction of the electric current in each circuit. 1. A series circuit consisting, in order, of a 5-H resistor, a 22-volt battery going to , and a 6-H resistor. V 5H 6H 11 H M 2A 2A 2A ?Z 10 V 12 V 22 V T 20 W 24 W 44 W 2. A series circuit consisting, in order, of a 40-V battery going to , a 1-H resistor, a 3-H resistor, a 16-V battery going to , and a 4-H resistor. V 1H 3H 4H M 3A 3A 3A 3A 3A ?Z 3V 9V 12 V 40 V 16 V T 9W 27 W 36 W 120 W 48 W 3. A 14-V battery going to , a 1-H resistor, a 20-V battery going to , a 2-H resistor, a 16-V battery going to , and a 3-H resistor. V 1H 2H 3H M 5/3 A 5/3 A 5/3 A 5/3 A 5/3 A 5/3 A ?Z 5/3 V 10/3 V 5V 14 V 20 V 16 V T 25/9 W 50/9 W 25/3 W 70/3 W 100/3 W 80/3 W Total power dissipated in resistors œ 50/3 W, same as the net power supplied by the three batteries.