Polynomial Operations: Practice & Examples
advertisement

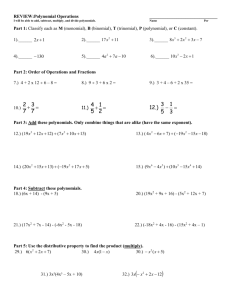
POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS ADDITION AND SUBTRACTION: Adding and subtracting polynomials is the same as the procedure used in combining like terms. When adding polynomials, simply drop the parenthesis and combine like terms. When subtracting polynomials, distribute the negative first, then combine like terms. Examples: Addition: 2 3 7 3 4 10 2 3 3 4 7 10 5 17 Subtraction: 5 12 1 2 3 7 5 12 1 2 3 7 3 15 8 MULTIPLICATION: 1. Monomial times Monomial: To multiply a monomial times a monomial, just multiply the numbers then multiply the variables using the rules for exponents. Example: 2 5 2 · 5 · · · 10 2. Monomial times Polynomial: Simply use the distributive property to multiply a monomial times a polynomial. Examples: a. 2 3 8 2 23 28 2 6 16 b. 5 2 3 6 5 2 5 3 5 6 10 15 30 3. Binomial times a Binomial: To multiply two binomials, use the FOIL method (First times first, Outside times outside, Inside times inside, and Last times last). Example: 2 3 3 2 23 3 2 6 6 Special Products: The following formulas may be used in these special cases as a short cut to the FOIL method. Difference of Squares: Perfect Squares: 2 Example: 3 43 4 9 16 Example: 4 24 4 8 16 Example: 2 3 23 3 6 9 4. Polynomial times polynomial: To multiply two polynomials where at least one has more than two terms, distribute each term in the first polynomial to each term in the second. Examples: a. 3 4 6 5 6 5 3 36 35 4 46 45 6 5 3 18 15 4 24 20 3 17 39 20 b. 2 34 5 1 24 25 21 34 35 31 8 10 2 12 15 3 8 22 17 3 DIVISION: 1. Division by Monomial: Each term of the polynomial is divided by the monomial and it is simplified as individual fractions. Examples: a. b. !" #"! #" 3 !" #" #" #" ! #" 2 5 " 2. Division by Binomial or Larger Polynomial: Use the long division format as follows: • • • Both the divisor and the dividend must be written in descending order. Any missing powers should be replaced by zero. All remainders are in fraction form (remainder⁄divisor) and are added to the quotient. Examples: a. 2 2 15 / 3 5 x−5 x + 3 x − 2 x − 15 2 3 5 15 5 15 0 b. 0 # 3 2 1 3x 2 + 2 x + 1 3x − 2 9 x 3 + 0 x 2 − x + 3 9 6 6 6 4 3 3 3 2 5 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS PRACTICE Add the following polynomials (Write answers in descending order): 1. 71 2 51 1 3 2. 8# 4 3# 2 3. 62# 1 22# 92 1 4. 32# 1 92# 32 2 5. 5 4 3 5 2 6. 4 4 7 3 9 3 7. 3 2 1 3 1 Subtract the following polynomials (Write answers in descending order): 8. 4 3 8 2 9. 8 3 5 5 8 10. 5 3 7 8 8 11. 2 7 3 7 12. 3 3 9 5 7 6 9 13. 5 5 5 6 6 8 5 14. 5 3 5 7 9 8 5 Multiply the following polynomials: 15. 8 3 16. 9 8 17. 1 3 # 1 18. 19. 2 9 5 20. 5 2 4 21. 52 32 52 42 6 22. 4 7 6 23. 6 2 24. 6 9 25. 4 33 5 26. 8 7 27. 6 15 2 28. 5 42 5 29. 2 4 9 30. 64 564 1 31. 65 765 7 32. 3 5 33. 2 3 34. 2 55 4 7 Divide the following polynomials: 35. 45. 36. 37. 38. # 46. # # 47. # 67 # 8 ! 9 48. 39. 40. # 7 9 / 41. 2 6 / 42. 3 15 5 / 3 43. 2 5 10 / 2 44. 2 5 # 9 2 / 49. : 0 : ;; ; << <# = 0 = #;; ; 50. 4> 3> 1 / > 4 51. 20 13 2 / 5 2 52. 12 6 3 9 / 3 3 53. 8 2 3 / 2 1 54. 3 6 4 / 2 1 POLYNOMIAL OPERATIONS PRACTICE ANSWERS 1. 121 1 5 2. 11# 6 3. 82# 92 4. 122# 32 1 5. 8 6 6 6. 7 7 2 7. 2 2 8. 4 9 2 9. 16 8 5 10. 6 3 5 11. 5 6 3 12. 2 10 6 18 13. 11 8 10 14. 2 12 8 10 15. 24 # # 16. 72 # 17. 1 # 3 # 18. ! 19. 18 # 10 20. 10 20 21. 152# 252 202 302 22. 4 28 24 23. 8 12 24. 3 54 25. 12 29 15 26. 15 56 27. 30 17 2 28. 10 33 20 29. 8 14 9 30. 364 244 5 31. 365 49 32. 9 30 25 33. 3 5 6 34. 10 17 6 35 35. 3 2 36. 2 37. 3 # 38. 5 39. # ? # 5 40. 9 41. 2 # 42. 5 43. # 9 5 44. 2 5 9 45. @ 4@ 16 # 46. 3> 7 ; 47. 22 7 <# 48. 1 41 16 ! 49. 4> 3 ; 50. 3> 8 ; 51. 4 1 52. 2 2 1 53. 4 3 # 54. 3 3 1