advertisement
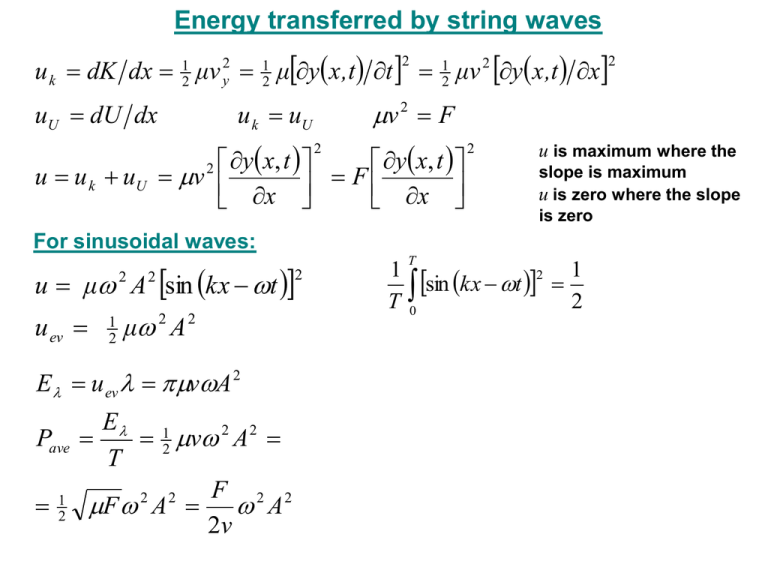
Energy transferred by string waves u k dK dx 12 μv y2 12 μy x,t t 12 μv 2 y x,t x 2 uU dU dx 2 v 2 F u k uU y x, t 2 y x, t u u k uU v F x x 2 2 u is maximum where the slope is maximum u is zero where the slope is zero For sinusoidal waves: u μ 2 A 2 sin kx t 2 u ev 1 2 μ 2 A 2 E u ev vA 2 Pave 1 2 E 1 2 v 2 A 2 T F 2 2 2 2 F A A 2v T 1 1 2 sin kx t T0 2 Question A stretched string has a linear mass density = 0.010 kg/m. A sinusoidal traveling wave moving on the string has the wave function The average power transmitted by the wave is __ W. y = (0.010 m)cos[(1.0 rad/m)x (100 rad/s)t] Recall: v = /k. 1. 2. 3. 4. 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0 Interference Interference – combination of waves (an interaction of two or more waves arriving at the same place) ( r , t ) ( r , t ) ( r , t) Important: principle of superposition 1 2 Valley Peak (b) (a) Waves source (b) (a) Valley No shift or shift by r2 r1 m Shift by r2 r1 m 12 m 0,1,2,... (a) If the interfering waves add up so that they reinforce each other, the total wave is larger; this is called “constructive interference”. (b) If the interfering waves add up so that they cancel each other, the total wave is smaller (or even zero); this is called “destructive interference”. Standing waves on a string Wave interference, boundaries, and superposition – Waves in motion from one boundary (the source) to another boundary (the endpoint) will travel and reflect. As wave pulses travel, reflect, travel back, and repeat the whole cycle again, waves in phase will add and waves out of phase will cancel. Standing waves on a string 1 L 1 1 2 L 22 2 2 L 32 3 L n2 n 2L 2 L 2 2L 3 3 n v 2L 2L 1 2L n v fn n nf1 n 2L Different boundary conditions: •Both ends fixed (see above) •Both ends free (the same as above) •One end fixed and on end free (next slide) n=1,2,3... f n nf1 Standing waves on a string One end fixed and on end free n=1 L 14 1 n=3 L 34 3 L n4 n v n Tn n f n v vn fn f1 n n 4 L 4L n n n 1,3,5... Principle of superposition and standing waves y1 ( x, t ) A cos( kx t ) y 2 ( x, t ) A cos( kx t ) y( x, t ) y1 ( x, t ) y2 ( x, t ) A cos(kx t ) A cos(kx t ) y( x, t ) 2 A sin( kx)sin( t ) Asw sin( kx)sin( t ) Asw 2 A Question A stretched string between 2 fixed ends has: Length L = 1.0 m Wave speed v = 100 m/s. The fourth harmonic frequency of vibration of the string is ___ Hz. 1. 50 2. 100 3. 150 4. 200 Question A stretched string has one free end and one fixed end, and is vibrating at its 5th harmonic frequency. The number of nodes in the wave function is ___. 1. 2. 3. 4. 1 2 3 4