The Thoracic Aorta Everything You Wanted to Know….but were afraid to ask
advertisement

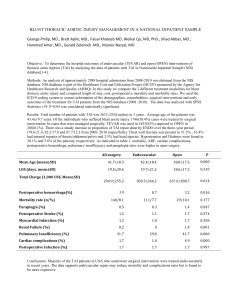
The Thoracic Aorta Everything You Wanted to Know….but were afraid to ask September 8, 2010 Bruce Margolis, DO, MBA ©2010 Genworth Financial, Inc. All rights reserved. Thoracic Aorta Company Confidential 1 Agenda Anatomy Definitions Epidemiology Etiology Pathophysiology Presentation Diagnosis Natural History Treatment Prognosis Underwriting Considerations Thoracic Aorta 2 Anatomy Thoracic Aorta 3 Definitions Normal Dimensions – Mid-descending 26-28 mm Dilation (Ballooning, Bulging, Ectasia) Aneurysm – Types • Saccular • Fusiform – Definition • When the diameter exceeds 4 cm or diameter exceeds 1.5 times normal Dissection – Tear in vessel wall results in false lumen – Types • Type A – involves ascending aorta • Type B – involves descending aorta Thoracic Aorta 4 Normal Aortic Dimensions Hager A. et al.; J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2002;123:1060-1066 Thoracic Aorta 5 Aortic Aneurysm Thoracic Aorta 6 Aortic Aneurysm (A) Tomodensitometric and (B) echocardiographic views of an aortic root aneurysm. Nataf P , Lansac E Heart 2006;92:1345-1352 Thoracic Aorta 7 Aortic Aneurysm Figure 23. Atherosclerotic vascular dis-ease in an aortic aneurysm. Axial postcontrast image (window = 440, level = 40) reveals a large contrast collection projecting from the undersurface of the aortic arch, consistent with aneurysm (arrow). the low attention material within the aneurysm represents thrombus http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/406630_15 Thoracic Aorta 8 Aortic Aneurysm Figure 24. Aortic aneurysm rupture. Axial postcontrast image (window = 440, level = 40) through the aortic arch reveals an aortic aneurysm with contrast penetrating the thrombus within the aneurysm (open arrow). http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/406630_15 Thoracic Aorta 9 Aortic Dissection Thoracic Aorta 10 Aortic Dissection Figure 12. Stanford type B (Debakey Type III) aortic dissection: descending thoracic aorta. (A) Axial postcontrast image (window = 440, level = 40) reveals intimal flap (arrow), t = true lumen, f = false lumen. (B) Oblique sagittal reconstruction reveals complex nature of the intimal flap (arrows). http://www.medscape.com/viewarticle/406630_15 Thoracic Aorta 11 Epidemiology Thoracic aneurysms – Prevalence greater than 3-4% of those over 65 – 6 cases per 100,000 person-years – Incidence increasing – In the top 15 causes of death – Thoracic aortic aneurysm – rupture 3.5/100,000 persons Thoracic aortic dissection – 2000 new cases/year – Acute - 3.5/100,000 persons – Male:Female ratio 2:1 Thoracic Aorta 12 Etiologies Underlying Etiologies – Atherosclerosis – Marfan’s – Type IV Ehlers-Danlos – Infection (syphillis) – Arteritis (giant cell, Takayasu, Behcet’s) – Trauma Risk Factors – Smoking – COPD – HTN – Male gender – Older age – High BMI – Abnormal aortic valve (e.g., bicuspid valve) – Family history Thoracic Aorta 13 Presentation Aneurysm – Most asymptomatic – Superior vena cava syndrome – Hoarseness – Bronchial obstruction – Dysphagia – Hemoptysis – Paralysis/paraplegia – Lower extremity embolism Dissection – Chest/back/neck pain – Neurologic signs – Horner syndrome – Hoarseness – Acute aortic regurgitation Thoracic Aorta 14 Diagnosis Chest x-ray – Widened mediastinum Echocardiogram – Transthoracic – aortic root – Transesophageal – ascending and descending Aortography – Delineates the lumen CT scan – Most widely used diagnostic tool MRI – Avoids contrast dye Thoracic Aorta 15 Echocardiography Nataf P , Lansac E Heart 2006;92:1345-1352 Thoracic Aorta 16 Natural History Annual Risk of Rupture 25 ASI = aortic dia (cm)/body surface area (m2) 20 15 10 5 0 <2.75 cm/m2 2.75-4.25 cm/m2 >4.25 cm/m2 Aortic Size Index (ASI) http://emedicine.medscape.com/article/242904=print Thoracic Aorta 17 Natural History Yearly Rupture or Dissection Rates for Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms: Simple Prediction Based on Size – 304 patients; 58.9% male; median age 65.8 – Aneurysm size – 43.7% were 4.0-4.9 cm – Location – 72% ascending – Follow up – average 43.1 months – End points Events No. Patients Dissection, rupture and death 2 Dissection, rupture (no death) 2 Dissection, death (no rupture) 5 Rupture and death (no dissection) 4 Rupture alone 5 Dissection alone 15 Death alone 44 Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 18 Natural History Cumulative incidence of acute dissection or rupture as a function of initial aneurysm size. Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 19 Natural History Kaplan-Meier cumulative hazard function of rupture or dissection. Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 20 Natural History Average yearly rates of negative outcomes during the first 5 years after presentation Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 21 Natural History Kaplan-Meier cumulative hazard function of rupture. Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 22 Natural History Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival before operative repair. Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 23 Natural History Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 24 Natural History Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 25 Natural History Kaplan-Meier cumulative survival Davies RR, et al. Ann Thorac Surg 2002;73:17 Thoracic Aorta 26 Treatment - Aneurysm Medical – BP control – Smoking cessation – No heavy lifting Surgical – Dacron tube graft – Ascending – may need to replace valve – Arch – graft – Descending – graft, stent grafts Thoracic Aorta 27 Treatment - Dissection Type A – Surgical Type B – Medical – Surgical • Acute with rupture, leak or distal ischemia. Thoracic Aorta 28 Treatment – Indications for Intervention Aortic size – Ascending diameter >5.5 cm – Descending diameter >6.5 cm – Growth rate >1 cm/yr (avg ascending 0.07 cm/yr; descending 0.19 cm/yr) Symptomatic aneurysm Traumatic rupture Pseudoaneurysm Large saccular aneurysm Mycotic aneurysm Aortic coarctation Bronchial compression Aortobronchial or aortoesophageal fistuala Thoracic Aorta 29 Treatment - Surgical Composite valve and graft replacement. Nataf P , Lansac E Heart 2006;92:1345-1352 Thoracic Aorta 30 Complications Bleeding CVA – 2-5% CHF Respiratory failure Graft leaks Fistula formation Spinal cord damage Renal failure Thoracic Aorta 31 Prognosis Aneurysm – Early post-op mortality 4-10%; lower for descending aneurysm repair; much higher for aortic arch repair – Stroke occurs 2-5% – Renal failure requiring dialysis – 7% – Spinal cord injury – 3% Dissection – Treated 10-yr survival rate 60% – Type A • 30% mortality surgical • 60% mortality medical – Type B • 10% mortality medical • 30% mortality surgical Thoracic Aorta 32 Underwriting Approach and Considerations Obtain cardiology and/or vascular medical records Review serial echos/scans as available Review blood pressure control Higher Risk – Aneurysm >5 cm – Poorly controlled blood pressure – Increase in size >0.5 cm/yr – Ongoing tobacco usage – Associated cardiovascular disease (CAD, PVD, carotid disease) – Non-atherosclerotic vascular disorders (Marfan’s, Ehlers-Danlos, etc) Lower Risk – Aneurysm <5 cm/stable/ well followed – Aneurysm repaired/stable Thoracic Aorta 33 Summary Thoracic aortic dilation/aneurysm fairly common with age Risk factors are traditional cardiovascular risk factors Most are asymptomatic Thoracic aortic rupture rare Thoracic dissection rare Ascending aorta most common site of aneurysm formation Low risk for aneurysms less than 4 cm REMEMBER In the end, it’s not what you call it………it’s size that matters! Thoracic Aorta 34