Definitions PES 100 –Physics in Everyday Life – Exam #1 Study... Chapters 1 and 2: Linear Motion, Rotational Motion
advertisement

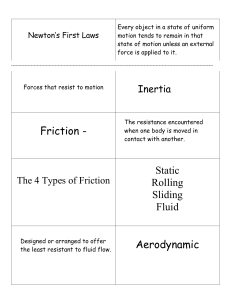
PES 100 –Physics in Everyday Life – Exam #1 Study Guide Chapters 1 and 2: Linear Motion, Rotational Motion Definitions 1. Some quantities in physics we describe as vector quantities. What two elements to all vector quantities have in common? A. Name and number B. Position and speed C. Magnitude (or value) and direction D. Size and shape Mass, weight, force, position, velocity, acceleration, vector quantity, angular velocity, angular acceleration, moment of inertia, sliding friction, static friction, work, impulse, angular impulse, conservation, radian, right-hand rule, center of mass, Newton’s Laws: 1st, 2nd, 3rd (linear), 1st, 2nd, 3rd (angular), Potential Energy, Kinetic Energy Units 2. The International Standard (SI), or metric system, units for mass are: A. Kilograms (kg) B. Newtons (N) C. Pounds (lb) 3. The acceleration due to gravity in the metric system is: A. 4.5 m/s every second B. 32 m/s every second C. 9.8 m/s every second SI units: length, time, mass, energy, force, power, grav. acc. , work, momentum, impulse English units: length, time, power Relationships 4. You travel at a constant velocity for one hour, so you have moved a certain distance. If your velocity had been greater, your distance would have been: A. Greater B. Less 5. Angular momentum depends on all but which of the following quantities? A. Gravity B. Mass C. Distance the mass is from the spin axis Force and linear acceleration, weight, torque & angular acceleration, velocity, position, KE, PE, momentum, angular momentum, frictional force, linear impulse, angular impulse, torque & force & lever arm, moment of inertia, static friction vs. sliding friction Applications 6. A truck applies his brakes in order to come to a stop at a red light. Which of Newton’s laws is best used to describe this situation? A. Newton’s 1st Law of linear motion B. Newton’s 1st Law of rotational motion C. Newton’s 2nd Law of linear motion Parabolic trajectories Elevators Mechanical devices: ramps, pulleys, levers Bumper cars Merry-go-rounds and swings Moving a rock with a lever. Moving a cabinet. Rollers, wheels, bearings Bumpers, bungee cords, springs R. Gist 1 Fall 2004