Engineering Mechanics II Practice Exam #2
advertisement

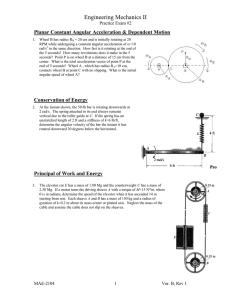
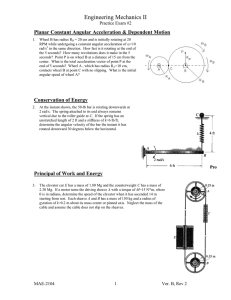
Engineering Mechanics II Practice Exam #2 Planar Constant Angular Acceleration & Dependent Motion 1. Wheel B has radius RB = 20 cm and is initially rotating at 20 RPM while undergoing a constant angular acceleration of =10 rad/s2 in the same direction. How fast is it rotating at the end of the 5 seconds? How many revolutions does it make in the 5 seconds? Point P is on wheel B at a distance of 15 cm from the center. What is the total acceleration vector of point P at the end of 5 seconds? Wheel A , which has radius R A=10 cm, contacts wheel B at point C with no slipping. What is the initial angular speed of wheel A? Conservation of Energy 2. At the instant shown, the 50-lb bar is rotating downwards at 2 rad/s. The spring attached to its end always remains vertical due to the roller guide at C. If the spring has an unstretched length of 2 ft and a stiffness of k=6 lb/ft, determine the angular velocity of the bar the instant it has rotated downward 30 degrees below the horizontal. Principal of Work and Energy 3. The elevator car E has a mass of 1.80 Mg and the counterweight C has a mass of 2.30 Mg. If a motor turns the driving wheel A with a torque of M=15 N*m, where is in radians, determine the speed of the elevator when it has ascended 14 m starting from rest. Each wheel A and B has a mass of 150 kg and a radius of gyration of k=0.2 m about its mass center at the axle. Neglect the mass of the cable and assume the cable does not slip on the wheels. MAE-2104 1 Ver. C, Rev 1 Engineering Mechanics II Practice Exam #2 Linked Planar Velocity and Acceleration 4. At a given instant, the slider block B is traveling to the right with the velocity and acceleration shown. Determine the angular speed and acceleration of the 5 inch radius wheel at this instant. Planar Rotating Reference Frames 5. Arm AB has length RAB =0.12 meter. It is rotating clockwise at a rate of A=2 rad/s that is increasing at A=3 rad/s2, and it is horizontal at the instant shown. Arm BC has length RBC = 0.09 meter. Collar C has a speed measured relative to arm BC of 4 m/s downward along arm BC, and is accelerating at 5 m/s2 downward, also measured relative to BC. Find the inertial velocity and acceleration of collar C at this instant. Planar Kinetics: Newton’s Law 6. Determine the acceleration of the center of mass of the cylinder at the instant shown. The tension in the rope is 12 N. The cylinder has a mass of 4 kg, and a radius of 0.02 m. Assume the cylinder does not slip as it rolls. MAE-2104 2 Ver. C, Rev 1