Direct rapid and reliable detection of
advertisement

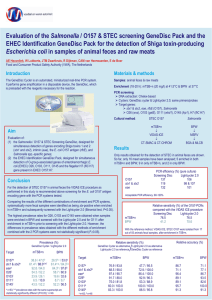
FEDERAL INSTITUTE FOR RISK ASSESSMENT Direct rapid and reliable detection of classical enterohaemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) from single colonies with the “GeneDisc” GeneDisc” RealReal-Time PCR System Lothar Beutin1*, Silke Jahn1 & Patrick Fach2 1. BfR 2. AFSSA Abstract Results & Discussion Enterohaemorrhagic E. coli (EHEC) producing Shiga toxins (Stx’s) cause bloody diarrhoea (HC) and Haemolytic Uraemic Syndrome (HUS) in humans. E. coli serogroups O26, O103, O111, O145 and O157 are most frequently associated with EHEC from HC and HUS. Besides Shigatoxins Stx1 and Stx2, EHEC encode intimin (eae-gene) involved in the intestinal A/E lesion. Many types of Stxproducing E. coli (STEC) are found in animals and food, but only some of these cause disease in humans. STEC are present in about 50% of cattle, sheep and goats. Meat, cheese and milk samples are frequently (2-25%) contaminated with STEC. Identification of STEC from food by screening only for Stx results in isolation of numerous STEC strains, but only 5% of these represent typical EHEC. All Subtypes of the Stx1 family are detected Here, we have evaluated a rapid automated quantitative Real-Time PCR system (GeneSystems®) for detection of typical EHEC strains and their virulence markers. Examination of bacterial colonies for stx- and eae-genes and for the five major EHEC O-groups with the “GeneDisc Cycler” is performed in about 60 minutes. The GeneDisc system detects reliably all genetic variants of stx and eae, except stx2f and eae-rho, the latter are not associated with EHEC. In the same way, genes associated with somatic O and H-antigens of EHEC were specifically detected. The sensitivity of the system allows detection of 2-3 EHEC colonies in a background of 50.000 apathogenic E. coli from plates. The results indicate that the system is very suitable for rapid and reliable detection of EHEC strains and possibly a tool for monitoring EHEC as requested by the EFSA. Detection of classical EHEC in food with the “GeneDisc Cycler” is under study. Introduction Traditional methods for identification of EHEC in clinical, food and environmental samples are laborious and time consuming. Commonly used rapid methods for detection of Shigatoxins (ELISA) or stx-genes (PCR) do not discriminate between highly virulent EHEC strains and STEC with undefined virulence potential. The adoption of multiplex PCR assays is a step forward to a reliable and rapid detection of EHEC according to their virulotypes and serotypes. Conventional multiplex PCR assays for detection of EHEC require preparation of target DNA from the bacteria and electrophoretic separation of amplicons. Difficulties may arise by interpreting the results on agarose-gels. Quantitative Real-time PCR assays bear the advantage that the PCR is combined with gene probe hybridization for a more rapid and specific detection assay. Stx1 (26) Stx1c (3) Stx1d (4) Stx1 family: 33 strains, including S. dysenteriae type 1 and S. sonnei were tested. All genetic variants of the Stx1 family were detected with the GeneDisc. Negative controls: A total of 151 stxnegative E. coli and 30 enterobacteriaceal strains reacted negative for stx in the GeneDisc system All Subtypes of the Stx2 family except stx2f are detected genetic distance Stx2b (6) Stx2 family: 35 strains representing the different genetic variants of the Stx2 family were tested. All genetic variants of the Stx2 family except stx2f were detected with the GeneDisc. Stx2e (3) Stx2f (3) not detected Stx2g (3) Stx2, 2c, 2dactivatable (20) Stx2f is not associated with severe disease in humans. HUS associated!! Detection of subtypes of the Intimin (eae)-family α (alpha = 5) ζ (zeta =1) Here, we have evaluated GeneDiscs for simultaneous detection of genes encoding Stx 1 and 2 (stx1 and stx2), intimins (eae), O-group associated genes of EHEC O26, O103, O111, O145 and O157 and the flagellar H7 (fliCH7) gene for EHEC O157:H7. τ (tau =3) β (beta = 16) κ (kappa =3) η (eta =2) ε (epsilon =9) O26 O103 Intimin family: 79 E. coli eae-positive strains and one eae-positive C. rodentium were tested. All intimin subtypes, except intimin-rho strains were clearly detected including the eae-genes associated with major EHEC types O26, O103, O111, O145 + O157. ρ (rho = 4/5) Material & Methods υ (ypsilon =1) γ (gamma =23) GeneDisc system: The GeneDiscCycler (GeneSystems, Bruz, France), is an apparatus to perform Real-Time PCR applications using the GeneDisc system. The GeneDisc is a disposable plastic reaction tray having the size of a compact disc. Its rim is engraved with 36 reaction microchambers preloaded with desiccated PCR primers and fluorescencelabelled gene probes for detection and quantification of gene targets. O145 + O157 Intimin-rho is not associated with EHEC and with severe disease in humans. θ (theta =10) O111 ι (iota =1) 14 10 4 2 0 Negative controls: 130 eae-negative E. coli and 32 other Enterobacteriaceae tested negative. Genetic distance (x100 nucleotides) Detection of EHEC O157 by screening for rfbEO157 and the fliCH7 genes: 32 E. coli O157 strains belonging to 12 different H-types, or non-motile (NM) were tested. All reacted positive for the rfbEO157 gene. Among all the E. coli O157 strains investigated, EHEC O157:H7 and O157:NM were specifically identified by a positive reaction for the fliCH7 gene. Negative controls: 221 non O157 E. coli strains and other Enterobacteriaceae reacted negative. Advantage of genotyping over serotyping: With the GeneDisc assay we could identified O-rough derivatives of O157 and non-motile fliC-H7 positive strains that are serologically untypable. Salmonella O30, Y. enterocolitica O9, Escherichia hermanii and O157-antigen positive Citrobacter freundii that crossreact serologically with E. coli O157 were negative for the rfbEO157 gene. Properties of Gene Discs: For duplex PCR assays the gene probes are labelled with reporter dyes 6-FAM (490-520 nm) and ROX (580-620 nm). 45 cycles are performed in about 55 min. Two types of GeneDiscs were evaluated: 1) “VTEC Screening” GeneDisc: wells 1+6) negative PCR control (6-FAM label) & PCR inhibition control (ROX-label); wells 2 + 3) rfbEO157 & stx1/stx2, wells 4 + 5) fliCH7 & eae. 2) “EHEC serotyping” GeneDisc: well 1) wzxO26 (FAM) & negative PCR control (ROX); 2) wzxO26 & wbd1O111 3) ihp1O145 & wbd1O111 4) ihp1O145 & wzxO103; 5) ihp1O157 & wzxO103; 6) ihp1O157 & PCR inhibition control. Detector systems: Primers and gene probes used for the discs were described (Nielsen et al., JCM 4, 2884-93 (2003); (Perelle et al: J Appl. Micro. 93: 250-60 (2002), Mol. Cell. Probes 18:18592 (2004), J. Appl Microbiol 94: 1162-68 (2005) Int. J. Food Micro. 113: 284-8 (2007). Bacteria: Reference strains for different types of stx (n=68), eae (n=79), O157 (n=32), H7 (n=23), O26 (n=29), O103 (n= 28), O111 (n=23) and O145 (n=30) were investigated. Reference strains for E. coli O-antigens O1-O186 and H1 to H56 served as negative controls, as well as 33 strains belonging to other types of Enterobacteriaceae. Detection of EHEC O26 (wzx-gene): 25 E. coli O26:[H11], of these 20 EHEC (stx1/stx2, eae-beta) 5 EPEC (eae-beta) and four O26:H32 (stx & eae-negative) were clearly identified with the GeneDisc. Negative controls: 332 non-O26 E. coli strains and other Enterobacteriaceae reacted negative. Advantage of genotyping over serotyping: One O-rough derivative of EHEC O26 was detected Detection of EHEC O103 (wzx-gene): 28 E. coli O103, of these 20 EHEC O103:H2 (stx1/stx2, eae-epsilon) and non-EHEC O103 (EPEC or other) were clearly identified with the GeneDisc. Negative controls: 325 non-O103 E. coli strains and other Enterobacteriaceae reacted negative. Advantage of genotyping over serotyping: One O-rough derivative of EHEC O103 was detected Detection of EHEC O111 (wbd1-gene): 23 E. coli O111, belonging to different H-types and pathotypes (EHEC, EPEC and apathogenic) were tested. Twelve were EHEC (stx1/stx2, eae-theta) and seven EPEC. All O111 strains were clearly identified with the GeneDisc. Negative controls: 333 non-O103 E. coli strains and other Enterobacteriaceae reacted negative. Advantage of genotyping over serotyping: Two O-rough derivative of EHEC O111 were detected. No cross-reaction with S. enterica O35 (serologically related to O111). Detection of EHEC O145 (ihp1-gene): 30 E. coli O145, of these 22 EHEC O145:[H28] (stx1/stx2, eae-gamma) were tested. Only EHEC O145 were clearly identified with the GeneDisc. Negative controls: 327 non-O145 E. coli strains and other Enterobacteriaceae reacted negative. Advantage of genotyping over serotyping: One O-rough derivative of EHEC O145 was detected Detection of EHEC strains in mixed cultures with apathogenic E. coli: 2 1 2-3 colonies of EHEC strains were clearly detected for their virulence genes and genotypes associated with somatic antigens when present in a background of approx. 50.000 non-pathogenic E. coli K-12 and grown overnight on agar-plates. Tests were performed with diluted bacteria washed from agar plates grown confluent overnight at 37°C. 3 1 1 hour 4 5 Conclusion: The GeneDisc assay is a specific and reliable assay for detection of EHEC according to their major virulence markers and to genes associated with classical EHEC types O26, O103, O111, O145 and O157. The assay can be performed with direct colonies from plates diluted in sterile water. The assay is suitable for detection of small numbers of EHEC in mixed cultures of bacteria and therefore promising for EHEC diagnostics from clinical, food and environmental samples but also for monitoring EHEC as requested by the EFSA. 6 *NRL-E.coli, Federal Institute for Risk Assessment • Diedersdorfer Weg 1 • D-12277 Berlin • Tel. + 49 30 - 84 12 2259• l.beutin@bfr.bund.de • www.bfr.bund.de