SCH4U Carbohydrates Assignment: Page 128 # 1-6 2.5 Starch and Cellulose
advertisement
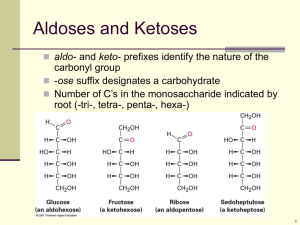
SCH4U Carbohydrates 2.5 Starch and Cellulose Assignment: Page 128 # 1-6 Simple and Complex Carbohydrates Carbo (Cn) Hydrates (H2O)n P Simple carbohydrates (monosaccharides) are often called simple sugars P Simple sugars are aldoses or ketoses P Complex carbohydrates (polysaccharides) are made of simple carbohydrates linked together Sugars • Monosaccharides have molecular formulas that are usually multiples of CH 2O • Glucose is the most common monosaccharide • Monosaccharides are classified by location of the carbonyl group and by number of carbons in the carbon skeleton Triose sugars (C 3H 6O 3) Pentose sugars (C 5H 10O 5) Hexose sugars (C 5H 12O 6) Glyceraldehyde Ribose Galactose Glucose Dihydroxyacetone Ribulose Fructose Some basic vocabulary OH monosaccharide O HO HO OH OH glucose – metabolic sugar HO OH disaccharide OH O HO OH O O HO OH Lactose – milk sugar oligosaccharide or polysaccharide OH O OH OH O HO OH O HO O OH O OH HO Cellulose – plant cells walls OH O OH O HO O OH Features of oligosaccharides P They can be branched P Combine simple sugars as different isomers (alpha and beta) b OH Gal HO GlcNAc OH O OH O 4 O 3 O H 3C OH OH O O OH 1 Fuc OH NHAc a b Starch á 1,4 - polyglucose O HO OH O HO O HO OH O HO O HO OH O HO Glycogen (starch): a storage form of glucose O HO OH O HO O n Starch 25% Amylose, 75% Amylopectin P Amylose - á 1,4-linear (branches every 200 units) P Amylopectin - á 1,4-linear with á -1,6 (branch OH every 20 units) HO HO O OH HO O O HO HO OR Amylose Structure Amylopectin Structure Digesting Starch Amylase in saliva “fits” amylose (starch) P Digestion of starch begins in our mouths P Amylase is an enzyme that helps to break starch into simple sugars for absorption Substrate (sucrose) Glucose Enzyme (sucrose) Fructose Chemistry of Digestion: Carbohydrates Figure 21-6: Carbohydrate digestion Amaranth starch (Bar: 1 µm) Arrowroot starch (Bar: 20 µm) Buckwheat starch (Bar: 5 µm) Cassava starch (Bar: 10 µm) Corn starch (Bar: 10 µm) Oat starch (Bar: 5 µm) Potato starch (Bar: 50 µm) Rice starch (Bar: 2 µm) Kidney bean starch (Bar: 20 µm) Cellulose Structure b-1,4 polyglucose • Very large molecule • Crystalline (hydrogen-bonded) and noncrystalline regions Cellulose structure â 1,4-polyglucose P Polymers with alpha glucose are helical P Polymers with beta glucose are straight P Hydrogen bonds between cellulose make parallel fibres very strong for plant structures Gluacose Glu bcose ag anblducosriensgtructures Star1 cli4 – h: nkg aa g louefcos meonomers. Cellul1 oli4 –se: nka gb g luefcos o meonomers. Cellulose microfibrils in a plant cell wall Cell walls Microfibril 0.5 µm Plant cells Cellulose molecules b Glucose monomer Digesting Cellulose We do not have an enzyme that “fits” P Digestion of cellulose does not occur in human digestion P We do not have an enzyme that “fits” the 3D shape of cellulose • Enzymes that digest starch by hydrolyzing alpha linkages can't hydrolyze beta linkages in cellulose • Cellulose in human food passes through the digestive tract as insoluble fiber • Some microbes use enzymes to digest cellulose • Many herbivores, from cows to termites, have symbiotic relationships with these microbes Examples of carbohydrate-based drugs OSO 3– O HO HO –O 3SHN –O 2C O HO O –O 3SO O –O 3SHN OH O O HO O HO –O 3SHN OCH 3 O CO 2– OSO 3– O OSO 3– Heparin pentasaccharide – anti-coagulant OH HO HO H 2N H 3C OH HN HO NH 2+ O OH OH O HO H 2N O Acarbose – diabetes NH HO NH OH OH O OHC O OH OH O HO O OH OH H 3C HO O NHCH 3 O OH OH CO 2– O HO AcHN HN H 2N OH OH CH 3 Streptomycin – antibiotic Relenza – anti-flu drug NH 2+ NH 2+ Examples of glycosylated natural products O O OH O OH HO H3C OH CH3 O O CH3 H3 C O OH O O HO O H3 C O OH OH CH3 OH O O Doxorubicin – anti-cancer drug HO HO H3 C O O HO H3C O O HO CH3 OH CH3 Erythromycin A – antibiotic HO CH 3 H3 C N(CH3 )2 OH CH3 NH3 + CH 3 O H3 C O OH O Digoxin – cardiovascular O O Monosaccharide building blocks used in mammalian glycoconjugates OH HO O HO HO OH OH OH HO Galactose (Gal) HO HO O OH NHAc N-Acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) OH CO 2– OH HO AcHN O HO OH Glucose (Glc) HO HO OH O Sialic acid (Sia) OH OH Glucuronic acid (GlcUA) OH HO O HO HO O OH OH HO OH Fucose (Fuc) OH Mannose (Man) OH O H 3C HO HO OH O HO OH O OH NHAc N-Acetylgalactosamine (GalNAc) HO HO O OH OH Xylose (Xyl) Pectin Used as thickeners (jelly) Polysaccharides are synthesized inside cells Extracellular milieu Carbohydratespecific receptor Monosaccharides Cell surface glycoconjugates Metabolic interconversions ER/Golgi Monosaccharide "building blocks" Cytosol Glycoconjugate assembly in the secretory compartments Oligosaccharides are major components of the cell surface Glycoprotein Glycolipid Oligosaccharides