Section 1.Q Lecture Notes MATH 141-501 Quadratic Functions Many situations in business are
advertisement

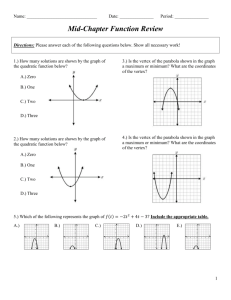
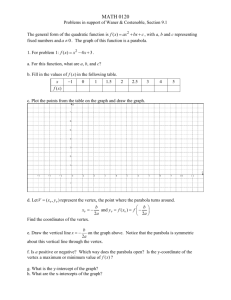
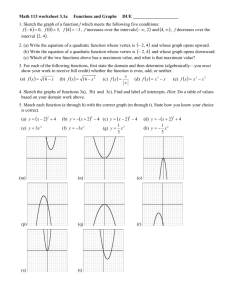
Section 1.Q Lecture Notes MATH 141-501 Quadratic Functions Many situations in business are and are better described by . There are two ways to write a . 1. Standard form • General formula: f (x) = • Example: f (x) = 2. Vertex form • General formula: f (x) = • Example: f (x) = 1 Graphs of Quadratic Functions A graph of a is called a . Note: If a > 0, the parabola If a < 0, the parabola 2 . . Vertex and Max/Min The is the point where . The y-value of the vertex is the • , if the parabola • , if the parabola 3 How to Find the Vertex In vertex form, it’s Easy. The vertex of y = (x − h)2 + k is simply (h, k). In standard form it’s . The x-coordinate of the vertex is The y-coordinate of the vertex is 4 . . Example: Find the vertex of the parabola given by y = 2x2 + 3x − 1. 5 The x-intercepts of a Quadratic Function The x-intercepts of a quadratic function are • • If f (x) = ax2 + bx + c, the x-coordinates of the xintercepts may be found by using x= . 6 The quadratic formula can give 7 Example Given the quadratic equation f (x) = 3x2 − 7x + 4, 1. Determine whether the graph of y = f (x) opens upward or downward. 2. Find the vertex of the parabola. 3. Where does the minimum value of f occur? 4. What is the minimum value of f ? 5. Is there a maximum value of f ? 6. What are the x-intercepts of f ? 8 Example (continued) 9 Applications to Business Previously, we discussed the revenue function We assumed that p was which made R(x) . 10 Nonlinear Revenue However, often the price is a function of the demand. If the price is a linear function of the demand (p = mx + b), then the revenue function R(x) = 11 Example ChalkboardCo, a manufacturer of chalkboards, has determined that its price-demand function is p(x) = −.5x+ 20, where x is the number of chalkboards (in thousands) and p is the price (in dollars). 1. Find the revenue function R(x) for ChalkboardCo 2. Find the vertex of R(x). 3. Interpret the vertex. What does this tell ChalkboardCo? 12