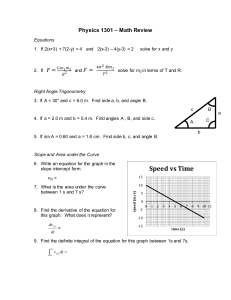
WIR 2
advertisement
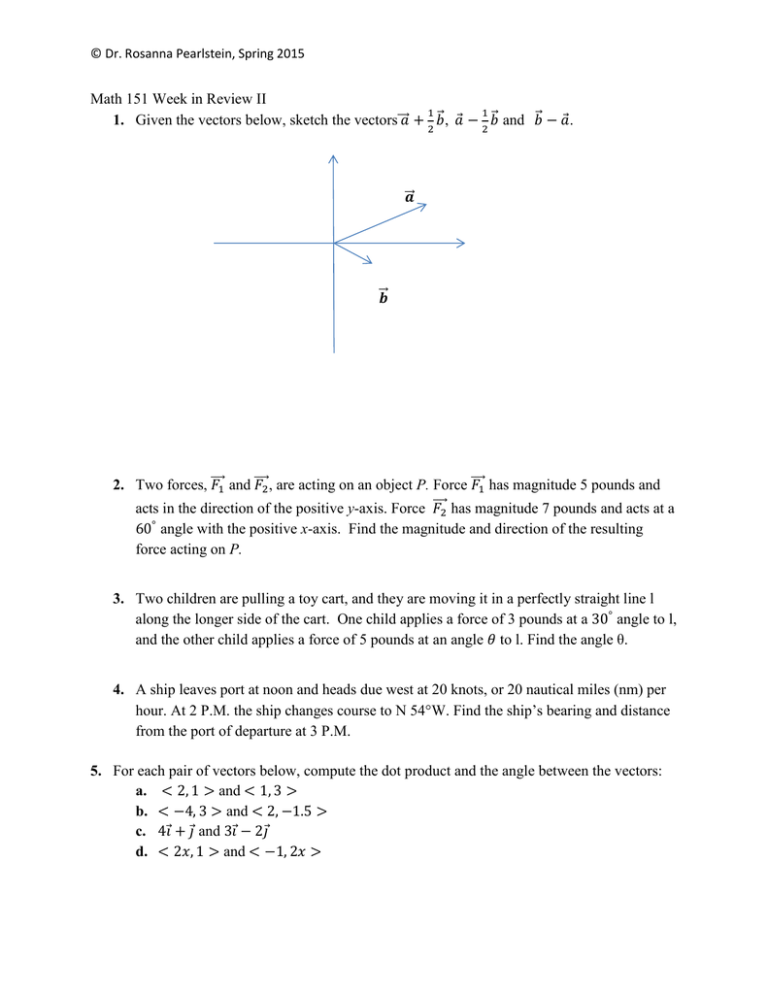
© Dr. Rosanna Pearlstein, Spring 2015 Math 151 Week in Review II 1 1 1. Given the vectors below, sketch the vectors⃗⃗⃗𝑎 + 2 𝑏⃗, 𝑎 − 2 𝑏⃗ and 𝑏⃗ − 𝑎. ⃗ 𝒂 ⃗𝒃 2. Two forces, ⃗⃗⃗ 𝐹1 and ⃗⃗⃗ 𝐹2 , are acting on an object P. Force ⃗⃗⃗ 𝐹1 has magnitude 5 pounds and ⃗⃗⃗2 has magnitude 7 pounds and acts at a acts in the direction of the positive y-axis. Force 𝐹 60° angle with the positive x-axis. Find the magnitude and direction of the resulting force acting on P. 3. Two children are pulling a toy cart, and they are moving it in a perfectly straight line l along the longer side of the cart. One child applies a force of 3 pounds at a 30° angle to l, and the other child applies a force of 5 pounds at an angle 𝜃 to l. Find the angle θ. 4. A ship leaves port at noon and heads due west at 20 knots, or 20 nautical miles (nm) per hour. At 2 P.M. the ship changes course to N 54W. Find the ship’s bearing and distance from the port of departure at 3 P.M. 5. For each pair of vectors below, compute the dot product and the angle between the vectors: a. < 2, 1 > and < 1, 3 > b. < −4, 3 > and < 2, −1.5 > c. 4𝑖 + 𝑗 and 3𝑖 − 2𝑗 d. < 2𝑥, 1 > and < −1, 2𝑥 > © Dr. Rosanna Pearlstein, Spring 2015 6. Given the vectors 𝑣 =< 5, 1 > and 𝑤 ⃗⃗ =< 1, 5 >, a. Find the scalar projection of 𝑣 onto 𝑤 ⃗⃗ . b. Find the vector projection of 𝑣 onto 𝑤 ⃗⃗ . c. Can you tell what the scalar projection of 𝑤 ⃗⃗ onto 𝑣 is? 7. Find the distance from point (7, -8) to the line 𝑦 = −2𝑥 + 1. 8. A constant force 𝐹 = 11𝑖 + 14𝑗 moves an object along a straight line from point (3, 5) to point (7, 6). Find the work done if the force’s magnitude is measured in newtons and the distance in meters. 9. An object is pushed to the top of a 20-meter ramp by a force of 15 newtons which is applied at an angle of 38° to the horizontal direction. How much work is done if the ramp makes a 11° angle with the horizontal direction? 10. For each of the parametric equations below, find a Cartesian equation. Sketch the curve and indicate the direction of motion as the parameter increases. a. 𝑥 = 𝑡 − 1, 𝑦 = 2 + √𝑡 b. 𝒓(𝜃) =< 3 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃, −5𝑐𝑜𝑠𝜃 >, 0 ≤ 𝜃 ≤ 2𝜋 c. 𝑥 = 𝑠𝑖𝑛𝜃, 𝑦 = −2𝑐𝑠𝑐𝜃, 0 < 𝜃 < 𝜋 11. The position at time t of an object moving in the xy-plane is 𝒓(𝑡) =< 𝑡 + 3, 𝑡 2 − 5 >, where t is measured in seconds. a. Does the object pass through point (4, 4)? Why yes or why not? b. Does the object pass through point (4, -4)? Why yes or why not? c. Find a Cartesian equation for the path of the object and sketch its graph. 12. Find the vector equation and parametric equations for a. The line through points (6, -1), (5, 3). b. The line through point (1, 2) orthogonal to the line 𝑥 = 3𝑡 + 1, 𝑦 = −2 − 4𝑡. 13. Consider the two lines: 𝐿1 : < −𝑡 + 3, 2𝑡 − 5 > and 𝐿2 : < 1 − 2𝑡, −3 + 𝑡 >. a. Are the two lines parallel, perpendicular or neither? b. If the two lines are not parallel, find the point of intersection of the two lines.