A B C D
advertisement

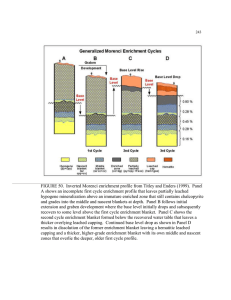
229 A Primary Mineralization B C D E Early Cycle Leaching and Enrichment Late Cycle Leaching and Enrichment Supergene Phyllosilicate Alteration Enrichment Blanket Zones Felsic Igneous Host Rocks Quartz-SericitePyrite Alteration Overprinting Base Level Quartz-Orthoclase Biotite Alteration Disseminated: Chalcopyrite & Pyrite 0.16% Cu Pyrite: Chalcopyrite 5-10 : 1 Total Sulfides 4-7 wt % Fracture Abundance n > 0.3 cm Goethite with minor jarosite Montmorillonite + Kaolinite Leached Cap 10 - 50 ft. % Kaolinite Partially Leached 10 - 200 ft. % Montmorillonite + Sericite Base Level Enriched Blanket 50 - 450 ft. % Kaolinite Sericite Hypogene Hematite with minor Jarosite Jarosite with minor Goethite Supergene Sulfide Enrichment Leached Zone 0.02 - 0.12 % Cu. Enrichment Zone 0.40 - 1.00 % Cu. Middle Blanket 0.20 - 0.40 % Cu. Nascent Blanket 0.05 - 0.30 % Cu. Protore 0.05 - 0.30 % Cu. Primary Mineralization FIGURE 40. Generalized Morenci enrichment profile. Panels A through D are modified from Titley and Marozas (1995). Panel A shows the characteristic features of hypogene mineralization that form the bulk geochemistry of the deposit prior to enrichment. Panel B shows the result of first-cycle enrichment that leaves a relatively thin leached capping beneath partially leached hypogene mineralization and an overlying leached capping. Panel C shows the result of second-cycle processes as a result of base level drop that leaves a hematitic leached capping behind at the site of the former first-cycle blanket and a thicker and higher grade enriched blanket at depth below. The thicker partially leached zone is caused by partial oxidation of residual hypogene mineralization or subsequent destruction of the upper portion of the enriched blanket below and can contain zones with copper oxides or copper sulfides in places. Typical thickness x %Cu for each zone are shown in units of ft-% on the left side of the panel. Panel D shows the typical alteration pattern formed when supergene argillic alteration overprints the quartz-sericite-pyrite hypogene alteration. Panel E is adapted from Lichtner and Biino (1992) and shows the downward supergene sulfide zoning in the leached enriched blanket. The enrichment zone contains chalcocite + djurleite >> covellite or chalcopyrite, the middle blanket contains covellite +/- chalcocite +/- chalcopyrite, and the nascent blanket contains chalcopyrite > chalcocite or covellite. This is a generalized vertical sequence, and not every zone is present or as well developed throughout the enriched blanket. Multiple cycles and structural displacement, particularly in the axial Chase Creek graben add significant complications to this generalized sequence.