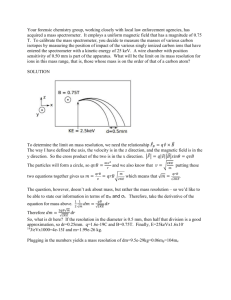
Particle tracks What is the direction of the uniform magnetic field? electron e

Particle tracks
Î
What is the direction of the uniform magnetic field?
electron e – positron e + electron e –
PHY2049: Chapter 28 1
Cosmic Ray Example
Î
Protons with energy 1 MeV move ⊥ earth B field of 0.5 gauss or 5 × 10 -5 T. Find radius & frequency of orbit.
K = 1
2 mv
2 ⇒ v =
2 K m
K m
=
( )(
×
= 1.67 10
− 27 kg
− 19
)
× − 13
J
R = mv
= eB
2 mK eB
R = 2900 m f =
1
=
T 2 π v
R
=
2 π ( v
)
= eB
2 π m f = 760Hz
Frequency is independent of v!
PHY2049: Chapter 28 2
Helical Motion in B Field
Î
If velocity of particle has 2 components
v v
||
Only v
⊥ v r
⊥
(parallel to B and perp. to B)
= v sin φ contributes to circular motion
v
||
= v cos φ is unchanged
Î
So the particle moves in a helical path v
⊥
v
||
v
⊥ is the constant velocity along the B field is the velocity around the circle v
||
φ v
R = mv
⊥ qB
B
3 PHY2049: Chapter 28
Helical Motion in Earth’s B Field
Particles moving along field lines cause Aurora Borealis and
Australis: http://science.nasa.gov/spaceweather/aurora/gallery_01oct03.html
PHY2049: Chapter 28 4
Magnetic Force on Current-Carrying Wire
Î
Magnitude of force sin
φ
Easy to derive from charge, number density & drift velocity of individual charge carriers
Î
Direction of force: RHR
PHY2049: Chapter 28 5
Example
Î
A 4 m long wire carries current of 500 A in NE direction
Magnitude of force (B = 0.5 gauss = 5 × 10 -5 T, pointing N) sin φ = ( )
(
×
− 5
)
( )( ) = 0.071N
Direction of force?
Upwards, from RHR
Î
Can adjust current in wire to balance against gravity
iBL sin φ = mg
Calculate mass from density, length and cross-sectional area m = ρ LA
Good exam problem!
PHY2049: Chapter 28 6
Magnetic Force
Î
A vertical wire carries a current in a vertical magnetic field. What is the direction of the force on the wire?
(a) left
(b) right
(c) no force
(d) into the page
(e) out of the page
B
I is parallel to B, so no magnetic force I
PHY2049: Chapter 28 7
Torque on Current Loop
Î
Rectangular current loop in uniform magnetic field (lengths a & b)
Forces in left & right branches are 0
Force in top branch is into plane
Force in bottom branch is out of plane
Î
Equal forces give net torque!
Bottom side up, top side down (RHR)
τ
Rotates around horizontal axis
= Fd = ( ) =
Î
µ = NiA ⇒ “magnetic dipole moment”
Assuming N turns
τ = µ B, true for any shape!!
Î
If plane tilted angle θ to B field
τ = µ Bsin θ
θ is angle between normal and B b
PHY2049: Chapter 28 a
B a
Plane normal is ⊥ B
( θ = 90 ° )
8 b
Magnetic Force
Î
A rectangular current loop is in a uniform magnetic field.
What direction is the net force on the loop?
(a) + x
(b) + y
(c) no force
(d) – x
(e) – y
B
Forces cancel on opposite sides of loop z x
PHY2049: Chapter 28 y
9
Magnetic Dipole Moment
PHY2049: Chapter 28 10
Torque Example
Î
A 3-turn circular loop of radius 3 cm carries 5A current in a B field of 2.5 T. Loop is tilted 30 ° to B field.
30 °
Î
µ = 3 π 2 = × × × (
0.03
) 2
= ⋅ 2
Î
B
Î
Rotation is always in direction to align µ with B field
PHY2049: Chapter 28 11
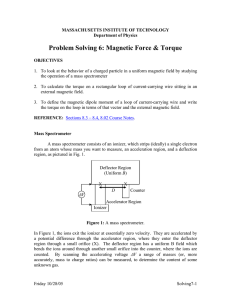
Mass Spectrometer
Î
Originally developed by physicists. Now an important tool in chemistry, biology, environmental studies, forensics, pharmaceutics, etc.
Î
Sample is vaporized, broken into fragments of molecules, which are positively ionized. Positive ions are first accelerated by a potential difference V, and then their trajectories are bent by B. Varying B
(sometimes V) allows ions of different masses to reach the detector.
PHY2049: Chapter 28 12
Mass Spectrometer (simplified)
Î
Sample is vaporized, broken into fragments of molecules, which are positively ionized. Positive ions are first accelerated by a potential difference V, and then their trajectories are bent by B. Varying B (sometimes V) allows ions of different masses to reach the detector.
Spectrometer determines mass from B
(sometimes from V) m = q ( Br ) 2
2 V
D
13 PHY2049: Chapter 28
Hall Effect: Do + or – Charges Carry Current?
Î
Î
+ charges moving counter-clockwise experience upward force
Upper plate at higher potential
Î
Î
– charges moving clockwise experience upward force
Upper plate at lower potential
Very quickly, equilibrium between electrostatic & magnetic forces is established and potential difference stops growing:
F up
= qv B F down
= qE induced
= q
V
H w
V
H
= v Bw = "Hall Voltage"
¾ This type of experiment led to the discovery (E. Hall, 1879) that current in conductors is carried by negative charges
¾ Hall effect is used to measure moderate to moderately high B (10 -4 T – 3 T)
¾ It is also used to measure the speed of computer hard drive
PHY2049: Chapter 28 14