PHY 4604 Fall 2008 – Practice Questions for Exam 2... 1. A particle of mass ( for
advertisement

PHY 4604 Fall 2008 – Practice Questions for Exam 2 (With Solutions)
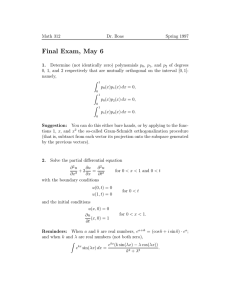
1. A particle of mass m moves in one dimension under the potential
(
∞
for x < 0,
V (x) =
V0 aδ(x − a)
for x > 0,
where V0 and a are positive quantities.
(a) Write down the general form of a stationary-state wave function of energy E > 0
in the regions x < 0, 0 < x < a, and x > a.
Solution: The general form of the stationary-state wave function is
for x < 0,
0
ψ(x) = A1 eikx + B1 e−ikx
for 0 < x < a,
ikx
−ikx
A2 e + B2 e
for x > a,
√
where k = + 2mE/~.
(b) By applying the appropriate boundary conditions, express the stationary-state
wave function from (a) in terms of just one unknown amplitude.
Solution: We must impose continuity of ψ at x = 0, where V (x) jumps to infinity:
A1 + B1 = 0
⇒
A1 = −B1
⇒
ψ(x) = S sin kx for 0 < x < a.
Given this, it simplifies matters slightly to rewrite
ψ(x) = C cos kx + D sin kx for x > a.
Then we must impose continuity of ψ at x = a:
C cos ka + D sin ka = S sin ka
D + C cot ka = S.
(1)
Finally, we must enforce ∆ψ 0 (a) = (2mV0 a/~2 )ψ(a):
2mV0 a
S sin ka
~2
D − C tan ka = S(1 + α tan ka),
−kC sin ka + kD cos ka = kS cos ka +
where α = 2mV0 a/(~2 k). The solution to Eqs. (1) and (2) is
C = −Sα sin2 ka,
D = S(1 + α sin ka cos ka).
Then, using sin θ cos φ − cos θ sin φ = sin(θ − φ),
for x < 0,
0
ψ(x) = S sin kx
for 0 < x < a,
S [sin kx + α sin ka sin k(x − a)] for x > a,
√
where k = + 2mE/~ and α = 2mV0 a/(~2 k).
(2)
(c) What is the reflection coefficient for a particle approaching from the far right?
Solution: The probability flux j is obviously zero in the region x < 0. Since j
must be spatially uniform in a stationary state, this means that in the region
x > a, the incident and reflected fluxes must cancel: jI + jR = 0. This in turn
means that the reflection coefficient
R = −jR /jI = 1.
2. A quantum mechanical system is described by a two-dimensional vector space spanned
by orthonormal basis vectors |1i and |2i. The Hamiltonian for this system is
Ĥ = (−4|1ih1| + 4|2ih2| + 3|1ih2| + 3|2ih1|) ,
where > 0. We will also consider the operator
Λ̂ = λ0 (|1ih2| + |2ih1|).
(a) Provide the matrix representations of Ĥ and Λ̂ in the basis {|1i, |2i}.
Solution: In the basis {|1i, |2i}, Ωmn = hm|Ω̂|ni for m, n = 1, 2.
−4 3
0 1
Ĥ ↔ ,
Λ̂ ↔ λ0
.
3 4
1 0
(b) Find the eigenvalues (E1 and E2 , with E1 < E2 ) and normalized eigenkets (|E1 i
and |E2 i) of Ĥ in the basis {|1i, |2i}.
The eigenvalues En satisfy
ˆ = (−4 − En )(4 − En ) − (3)2 = En2 − 252 .
0 = det(Ĥ − En I)
⇒ E1 = −5, E2 = 5.
E1 = −5:
0
a
1 3
=
0
b
3 9
⇒
1
a
3
=√
b
10 −1
√
or |E1 i = (3|1i − |2i) / 10.
Orthogonality implies that
√
|E2 i = (|1i + 3|2i) / 10.
ˆ )
(c) Find the matrix representation in the basis {|1i, |2i} of the propagator U (τ
defined by Û (τ )|Ψ(t)i = |Ψ(t + τ )i for any |Ψ(t)i.
Solution: As shown in Homework 4, Question 1, the propagator for a finitedimensional system is
X
Û (τ ) =
e−iEn t/~ |En ihEn |,
n
where |En i is the nth stationary state. Here,
e−i5τ /~
ei5τ /~
(3|1i − |2i)(3h1| − h2|) +
(|1i + 3|2i)(h1| + 3h2|)
10
10
1 i5τ /~
=
+ e−i5τ /~ )|1ih1| + (ei5τ /~ + 9e−i5τ /~ )|2ih2|
(9e
10
− 3(ei5τ /~ − e−i5τ /~ )(|1ih2| + |2ih1|)
1
= {[5 cos(5τ /~) + 4i sin(5τ /~)]|1ih1| + [5 cos(5τ /~) − 4i sin(5τ /~)]|2ih2|
5
− 3i sin(5τ /~)(|1ih2| + |2ih1|)} .
Û (τ ) =
Thus
1
Û (τ ) ↔
5
5 cos(5τ /~) + 4i sin(5τ /~)
−3i sin(5τ /~)
−3i sin(5τ /~)
5 cos(5τ /~) − 4i sin(5τ /~)
!
.
(d) Suppose that the state vector at time 0 is |Ψ(0)i = |2i. The value of the dynamical
variable λ corresponding to the operator Λ̂ is measured at time t > 0. What are
the possible measured values of λ and their respective probabilities P (λ, t)?
Solution: A measurement of Λ will yield one of the eigenvalues λn of Λ̂ with
probability P (λn , t) = |hλn |Ψ(t)i|2 , where |λn i is the eigenvector corresponding
to λn .
The eigenvalues λn of Λ̂ satisfy
ˆ = (−λn )2 − (λ0 )2 .
0 = det(Λ̂ − λn I)
⇒ λ1 = −λ0 , λ2 = λ0 .
λ1 = −λ0 :
1 1
a
0
=
1 1
b
0
⇒
Orthogonality implies that
1
a
1
=√
b
−1
2
√
or |λ1 i = (|1i − |2i) / 2.
√
|λ2 i = (|1i + |2i) / 2.
Using |Ψ(0)i = |2i and Û (τ ) from part(c),
3
4
|Ψ(t)i = Û (t)|Ψ(0)i = − i sin(5t/~)|1i + cos(5t/~) − i sin(5t/~) |2i.
5
5
Then
i
1
h±λ0 |Ψ(t)i = √ cos(5t/~) − (4 ± 3) sin(5t/~) ,
5
2
and
1 2
cos (5t/~) + (25 ± 24) sin2 (5t/~)
2
1 12 2
= ±
sin (5t/~).
2 25
P (±λ0 , t) =