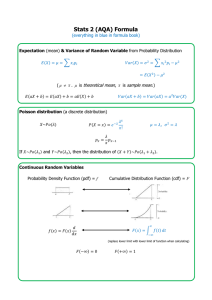
38 has come up 213 times to end March 2010 but
advertisement

38 has come up 213 times to end March 2010 but 20 has only come up 148 times See www.lottery.co.uk/st atistics/ for data This reference flowchart is one of a series of three, designed by Stella Dudzic. The series includes: Hypothesis tests for one sample, Hypothesis tests for two samples, and Experimental Design and Hypothesis tests for several samples: ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) The series is also available as a set of three full colour posters in A2 size for wall display. To view the colour posters and to place an order please visit the MEI website at www.mei.org.uk Yo u co uld us ea go odness of fit test to chec k if there is ev idence that the lo tter y is not fair Yes fig 1 Male Test on mean/ median female right handed 32 28 left handed 7 5 Do you have a large sample? Yes Do you know the variance? No Yes No Are the data from a Normal distribution? Contingency table No fig 2 Are the data single variable or bivariate? Single variable Test on variance With a large set of data, the scatter diagram for a bivariate Normal distribution is approximately elliptical cumulative probability What distribution are the data from? Yes Bivariate data observed D 0.5 0 x Test statistic for Kolmogorov-Smirnov test This reference flowchart is one of a series of three, designed by Stella Dudzic. The series includes: Hypothesis tests for one sample, Hypothesis tests for two samples, and Experimental Design and Hypothesis tests for several samples: ANOVA (Analysis of Variance) The series is also available as a set of three full colour posters in A2 size for wall display. To view the colour posters and to place an order please visit the MEI website at www.mei.org.uk Estimate variance as s² and use t test Poisson Poisson test Symmetrical Distribution Other For Normal population Wilcoxon single sample test Sign test test for variance Binomial test or Normal approximation Goo dness of fit test test or Kolmogorov-Smirnov (see fig 3) Are the variables categories or numbers? EXPECTED Normal test No Categories in a contingency table (see fig 1) 0.75 0.25 Do you know the variance? Estimate variance as s² and use Normal test Test of proportion fig 3 1 Normal test Number pairs Are the data fro m a bivariate Nor mal distribution? (see fig 2) test Yes No Pearson’s product moment correlation test Spearman’s rank correlation test or Kendall’s rank correlation test