Page 1 Section 3.3: Graphical Solution of Linear Programming Problems
advertisement

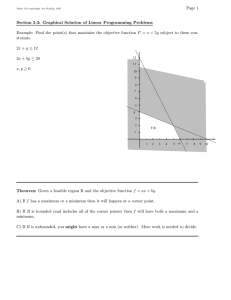
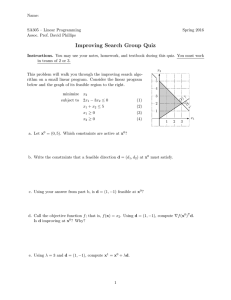
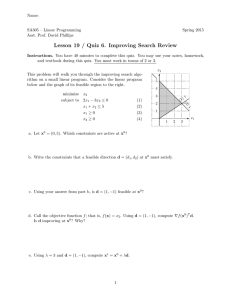
Page 1 Math 141-copyright Joe Kahlig, 10B Section 3.3: Graphical Solution of Linear Programming Problems Example: Find the point(s) that maximize the objective function P = x + 5y subject to these constraints. 2x + y ≤ 12 2x + 5y ≤ 20 12 11 x, y ≥ 0 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 F.R. 1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 Theorem: Given a feasible region R and the objective function f = ax + by. A) If f has a maximum or a minimum then it will happen at a corner point. B) If R is bounded (and includes all of the corner points) then f will have both a maximum and a minimum. C) If R is unbounded, you might have a max or a min (or neither). More work is needed to decide. 9 10 Page 2 Math 141-copyright Joe Kahlig, 10B Example: Maximize P = x + y subjected to x+y ≤8 3x + y ≥ 12 12 11 −2x + 3y ≥ 3 10 9 What is the maximum value of P ? 8 7 (2,6) 6 Where does P have a maximum? 5 F.R. 4 (4.2, 3.8) (3, 3) 3 2 1 1 Example: Maximize f = 3x − y for this feasible region. (2, 4) 4 Feasible Region (5, 0) 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 Page 3 Math 141-copyright Joe Kahlig, 10B Example: Minimize f = 3x − 2y for this feasible region. Points A (0,1) B (0,12) C (3,9) D (3,2) Feasible B E (3,0) Region C F (8.25, 3.75) H G (12,0) H (12,5) D F A E G