Nebraska
advertisement

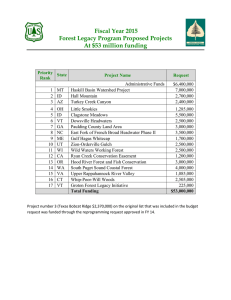
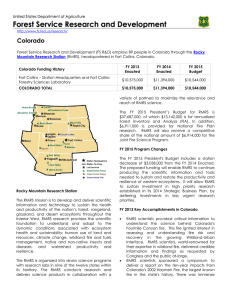
http://www.fs.fed.us/research/ Nebraska Forest Service Research and Development (FS R&D) conducts research relevant to state of Nebraska through the Rocky Mountain Research Station (RMRS), headquartered in Fort Collins, Colorado and through the National Agroforestry Center, headquartered in Lincoln, Nebraska. FY 2015 Program Changes The FY 2015 President's Budget includes a station decrease of $3,038,000 from the FY 2014 Enacted. The proposed funding will enable RMRS to continue producing the scientific information and tools needed to sustain and restore the productivity and resilience of western ecosystems. It will allow RMRS to sustain investment in high priority research established in its 2014 Strategic Business Plan, by deferring investments in less urgent research priorities. FY 2013 Key Accomplishments in Nebraska Rocky Mountain Research Station The RMRS mission is to develop and deliver scientific information and technology to sustain the health and productivity of the nation’s forest, rangeland, grassland, and desert ecosystems throughout the Interior West. RMRS research provides the scientific foundation to understand and adapt to the dynamic conditions associated with ecosystem health and sustainability: human use of land and resources, climate change, wildland fire and fuels management, native and non-native insects and diseases, and watershed productivity and resilience. The RMRS is organized into seven science programs with research labs in nine of the twelve states within its territory. The RMRS conducts research and delivers science products in collaboration with a variety of partners to maximize the relevance and reach of RMRS science. The FY 2015 President’s Budget for RMRS is $37,687,000, of which $13,142,000 is for annualized Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA). In addition, $6,911,000 is provided for National Fire Plan research. RMRS will also receive a competitive share of the national amount of $6,914,000 for the Joint Fire Science Program. Researchers from the Forest Service, ARS and collaborating universities found that the ability of plant communities to use water efficiently is compromised as precipitation patterns become more extreme. Because of this effect, scientists expect that grasslands will act as early indicators of drought-induced losses. RMRS scientists, in collaboration with the Forest Service’s Remote Sensing Application Center, developed modeling methods to produce the National Land Cover Dataset Tree Canopy Cover layer for the conterminous US, which is the baseline tree canopy cover information for the nation. In an effort to better estimate forest disturbance through time, RMRS scientists developed methods to integrate forest inventory data with observations and models of historic forest disturbance trends on Landsat time series. This research provides essential information for the design of more resilient landscapes to disturbances. Forest Service RMRS researchers are developing techniques to evaluate wildlife habitat connectivity for a substantial number of native species across large regions. Researchers identified species at risk of habitat fragmentation, as well as the sufficiency of protected habitat. Results will inform and guide conservation, restoration, and mitigation strategies. The RMRS Inventory & Monitoring program analyzed the genetic characteristics of aspen across the North American range, finding that aspen diploids are capable of reproducing by seed, whereas triploids are generally infertile. This research will help guide land management decisions in the restoration of declining aspen ecosystems. Priority Research Forest Service R&D Priority Research Areas build on local and regional research to solve issues important to the American people. Examples of priority research conducted by the RMRS include: Forest Disturbance: Managing forests to sustain ecosystem health requires knowledge of how forests change over time in response to natural disturbances and management actions. RMRS scientists developed geospatial tools to help land managers anticipate future conditions, spot ecological trends, and design effective adaptive strategies. Watershed Management and Restoration: Sustaining healthy watersheds is fundamental to ensure a safe and reliable water supply. RMRS scientists developed the GRAIP tool, a data driven road inventory method and model which assesses the risks to aquatic resources from road related sediment discharge. This tool enables land managers to prioritize mitigation on open roads and de-commission roads most at risk of delivering sediment to the stream. This research was cited in the Environmental Protection Agency’s (EPA) rule to regulate runoff from forest roads, and figured prominently in the U.S. Supreme Court's decision to uphold the EPA's policy on forest road runoff as a nonpoint source. Bioenergy and Bio-Based Products: RMRS researchers are exploring biomass utilization by mobile fast-pyrolysis to convert residual forest biomass into biochar (black carbon) and biofuel near harvest sites. These carbon-rich biochar amendments return nutrients to the soil, supplement long-resident soil carbon pools, and improve water retention, microbial biomass, and nutrient cycling. Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA): The FIA program provides data on conditions and trends for public and private forest lands in the United States. The RMRS Inventory & Monitoring program completed the first-ever high-resolution analysis of climatic patterns using tree-ring data from the FIA plot grid. This technique will enable fine-scale reconstruction of El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) influence on forest growth across large areas. Localized Needs Research in Nebraska The RMRS invests in research and science delivery specific to issues of local and regional importance. Examples include: Invasive Plant Prevention: RMRS researchers, in collaboration with the Nebraska National Forest and Grasslands, and South Dakota State University are developing management models that will help land managers prevent the introduction and spread of a newly introduced non-native plant species (Falcaria vulgaris) in the Northern Great Plains Grasslands. USDA National Agroforestry Center (NAC): RMRS scientists, in collaboration with the National Agroforestry Center and South Dakota State University are evaluating the potential of applying silvopasture concepts and techniques. The NAC, located in Lincoln, Nebraska, is a Forest Service and Natural Resources Conservation Service partnership. The NAC works with a national network of cooperating agencies and universities to develop and deliver agroforestry science and technology. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT (FS R&D) is a world leader in innovative science for sustaining global forest resources for future generations. Research findings and products benefit forest and rangeland managers, and everyone who uses goods or services from forests. We operate five research stations that encompass all 50 states, the Forest Products Laboratory located in Madison, Wisconsin, and the International Institute of Tropical Forestry located in Puerto Rico. Our researchers and support personnel are located at 67 field sites throughout the United States. We also maintain 80 experimental forests and ranges across the Nation. Our unique ability to integrate science and decision making and to work across boundaries between public, private, and tribal lands through strong partnerships advances the Agency’s three core themes of restoration, communities, and fire. The FS R&D program has two components: Priority Research Areas and Strategic Program Areas. The Priority Research Areas address urgent needs in seven areas: Forest Disturbance, Forest Inventory and Analysis, Watershed Management and Restoration, Bioenergy and Biobased Products, Urban Natural Resources Stewardship, Nanotechnology, and Localized Needs Research (region-specific needs). The Strategic Program Areas (SPAs) are the long-term programs from which Priority Research Areas are funded. The seven SPAs are: Wildland Fire and Fuels; Invasive Species; Recreation; Resource Management and Use; Water, Air, and Soil; Wildlife and Fish; and Inventory and Monitoring. The FY 2015 President’s Budget includes $275,315,000 for Forest and Rangeland Research, $19,795,000 for the FS R&D National Fire Plan, and $6,914,000 for the Joint Fire Science Program.