Vermont
advertisement

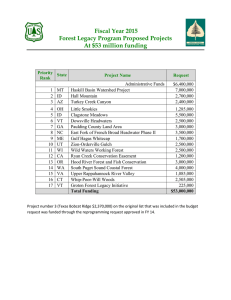
http://www.fs.fed.us/research/ Vermont Forest Service Research and Development (FS R&D) delivers research to Vermont through the Northern Research Station (NRS) and its field office in Burlington, which employs nine people. The research here focuses on natural resource use and physiological responses to environmental stress and development of applications for technology dissemination. Vermont Funding History Burlington-NRS-2 Sustaining Forests in a Changing Environment, NRS-7 Center for Research on Ecosystem Change, NRS-9 People and their Environments, and NRS-16 Restoration and Conservation of Urban and Rural Forests Northeastern States Research Cooperative (NSRC) VERMONT TOTAL FY 2013 Enacted ($) FY 2014 Enacted ($) FY 2015 Budget ($) $2,527,000 $2,551,000 $2,505,000 575,000 575,000 0 $3,102,000 $3,126,000 $2,505,000 share of the national amount of $6,914,000 for the Joint Fire Science Program. A recent NRS study showed that old-growth softwood trees like those shown here stored 25 percent more carbon than oldgrowth hardwoods. Photo by U.S. Forest Service. Northern Research Station Overview Headquartered at Newtown Square, PA, NRS develops and delivers leading-edge science and technology that helps people ensure the longterm health and productivity of rural and urban landscapes. NRS maintains 24 field locations and 24 experimental forests across 20 states in the Midwest and Northeast: Connecticut, Delaware, Illinois, Indiana, Iowa, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, Minnesota, Missouri, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Vermont, West Virginia, and Wisconsin. The FY 2015 President’s Budget is $50,495,000 of which $15,718,000 is for annualized Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA). In addition, $2,944,000 is provided for the National Fire Plan Research. NRS will also receive a competitive FY 2015 Program Changes The President’s Budget includes a station decrease of $4,126,000 from the FY 2014 Enacted level. At this level, the NRS will continue to provide cutting edge research in urban forestry and forest disturbance processes as well as develop practical tools to enhance forest productivity and increase production of clean air and water. The FIA program will continue to monitor and inventory the nation’s forests to better inform forest policy development and provide valuable data to enhance accelerated forest restoration. NRS will focus on the highest priority research by eliminating the Northeastern States Research Cooperative; research on mycology, long term soil productivity, and riparian research critical to water quality; and the invasive species program in MI and CT. FY 2013 Key Accomplishments Found that old-growth softwood forests measured in Vermont, New Hampshire, and Maine contained 25 percent more carbon than old-growth hardwoods, but old-growth hardwood forests have about the same amount of carbon as mature second-growth hardwood sites. This research is important for forest carbon management. NRS researchers worked to develop and improve methods to help children learn and remember important information about their environment. These techniques promote environmental literacy and ecological understanding. Contributed to designing a nationally consistent, objective, and transparent method and a database to monitor the effectiveness of best management practices for land disturbing activities on all national forests and grasslands. Priority Research in Vermont Forest Service R&D priority research areas build on existing local and regional research to solve issues important to the American people. Priority research activities in Vermont include: Forest Disturbance: As climate changes so will our forests. We need to understand how to manage our forests to adapt to climate change, including providing opportunities for new and changing species mixes, restoring forests and wetlands as temperatures and rainfall change, controlling invasive insects and diseases, and reducing wildfire risk. Vermont forest managers can access current tree and bird distribution maps and habitat projections under different climate change scenarios. Urban Natural Resources Stewardship: With most people living in urban areas, an emphasis on science and technology transfer is paramount to ensure the proper care of natural resources and the delivery of ecosystem services in urban and urbanizing landscapes. Vermont cities can access data online on urban natural resource composition and health. Watershed Management and Restoration: The availability of clean water is becoming limited in many parts of the U.S. It is important to understand where water shortages will occur, identify how future climate will affect rainfall and snowfall, and find ways to reduce water pollution and effectively manage and protect water sources. Forest Inventory and Analysis (FIA): The NRS FIA program conducts an updated annual inventory of Vermont’s forest resources in cooperation with the State Forester and other state organizations. FIA provides the science-based information needed by the nation’s leaders to make sound forest policy decisions and to better understand forest processes and associated threats to ecosystem health. Localized Needs Research in Vermont Focusing on critical regional and local research issues, NRS provides research results and tools and technologies including: American Chestnut Restoration: NRS researchers are helping restore American chestnut to Vermont’s forests. Recent work tested the cold hardiness of new hybrid/backcross stock in the northern portion of the chestnut’s original range. Climate Change Mitigation: NRS researchers in Vermont developed an online tool used to identify and reduce carbon dioxide emissions. The CarbonPlus Calculator, which has been adapted by several major cities, provides tips on how to reduce a carbon footprint and describes the many benefits trees provide in addition to absorbing carbon. Forest Management: NRS researchers have worked to develop and improve the Northeast Decision Model (NED), a collection of software products used by landowners, foresters, and other resource managers to produce sustainable management plans for forest properties. FOREST SERVICE RESEARCH & DEVELOPMENT (FS R&D) is a world leader in innovative science for sustaining global forest resources for future generations. Research findings and products benefit forest and rangeland managers, and everyone who uses goods or services from forests. We operate five research stations that encompass all 50 states, the Forest Products Laboratory located in Madison, Wisconsin, and the International Institute of Tropical Forestry located in Puerto Rico. Our researchers and support personnel are located at 67 field sites throughout the United States. We also maintain 80 experimental forests and ranges across the Nation. Our unique ability to integrate science and decision making and to work across boundaries between public, private, and tribal lands through strong partnerships advances the Agency’s three core themes of restoration, communities, and fire. The FS R&D program has two components: Priority Research Areas and Strategic Program Areas. The Priority Research Areas address urgent needs in seven areas: Forest Disturbance, Forest Inventory and Analysis, Watershed Management and Restoration, Bioenergy and Biobased Products, Urban Natural Resources Stewardship, Nanotechnology, and Localized Needs Research (region-specific needs). The Strategic Program Areas (SPAs) are the long-term programs from which Priority Research Areas are funded. The seven SPAs are: Wildland Fire and Fuels; Invasive Species; Recreation; Resource Management and Use; Water, Air, and Soil; Wildlife and Fish; and Inventory and Monitoring. The FY 2015 President’s Budget includes $275,315,000 for Forest and Rangeland Research, $19,795,000 for the FS R&D National Fire Plan, and $6,914,000 for the Joint Fire Science Program.