Where you lead, I will Follow: NYSAEYC 2005 Annual Conference Rochester, NY
advertisement

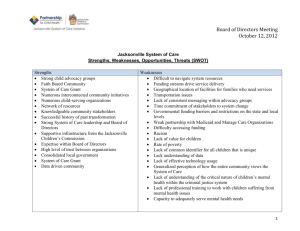
Where you lead, I will Follow: The Impact of Director Leadership on Overall Center Quality NYSAEYC 2005 Annual Conference Rochester, NY Saturday, April 13, 2005 For these slides, go to: http://www.udel.edu/cds/conferencematerials.html Agenda Leadership components 2003/2004 Quality Study Study of early care centers, teachers and directors Director characteristics linked to quality Implications for programs and directors of early care facilities and regulation Program Leadership Directors are either beacons or icebergs Directors mentor and nurture or restrict and confine Directors provide vision and consistency or contribute to chaos Directors make a difference So, what are the components of leadership? Communicate a vision Mentorship Knowledge base Teamwork Organization Passion Advocacy Decision-making Shared responsibility Communicate with all constituents The Research Study 587 early care and education settings in Delaware ALL types (Head Start, part-day, family child care, center-based, school-age) Purpose: To determine the baseline quality in the state prior to regulation changes Measured: characteristics, demographics, fees, job perception, quality, child-teacher interactions For the executive summary, go to: http://www.udel.edu/cds/conferencematerials.html Director Study 2004 104 programs composed of 451 groups (classrooms) in Delaware 23 Head Start programs 21 part-day programs (preschools) 60 full-day child care centers All programs had four or more groups (classrooms) Over 876 staff members (i.e., teachers and teacher assistants) A little bit about Delaware We’re rural, no, we’re urban, no we’re suburban In reality, the state is much like New York— all of the above Ethnicity: 20% African American 67% white 6% Hispanic 4% Asian American 2% Native American •11% of the families are living in poverty •18% of children are living in poverty Dela—where? What we know about Directors Wanted to discover: What was their background? What was their training and education? How did they see their programs? What was important to them? What type of programs did they operate? Directors’ Educational Backgrounds (n=101) Education Level Percentage Number Master’s Degree 12.9% 13 Bachelor’s Degree 49.4% 50 Associate’s Degree 19.8% 20 DE First Core Training 5.0% 5 Child Development Associate (CDA) 3.0% 3 High School Degree 9.9% 10 Focus of Post-secondary Degrees (n=73) Area of Study Early Childhood Education or Child Development Related Field (e.g., nursing, elementary education) Unrelated Field (e.g., English, Secondary Education) Percentage Number 57.5% 42 24.6% 18 17.9% 13 Directors’ Program Management Experience (n=102) Management Area of Training Percentage Number Staff Supervision 76.5% 78 Financial Management 45.1% 46 Working with Children with Disabilities/Risks 35.3% 36 Directors’ Experience with Training (n=99) Training Area Percentage Number Child Development 96.0% 95 Curriculum Planning 96.0% 95 Working with Families 83.1% 79 Promoting Language 80.0% 76 Promoting Literacy 71.6% 68 Working w/ Infants & Toddlers 45.3% 43 Working w/ school-agers 51.6% 49 Directors’ Experience with Training (n=99) (continued) Training Area Children’s Health and Nutrition Percentage Number 85.3%% 81 Safety and First Aid 95.8% 91 Behavior Management 90.5% 86 Teamwork 75.8% 72 Physical Plant Operations 56.8% 54 Directors’ Age (n=88) Program Type Average Range SD N Child Care 45 26-59 6.77 50 Head Start 48 32-66 5.83 19 Part-Day 47 40-66 5.44 19 Total 46 26-66 6.12 88 Directors’ Annual Salaries (n=83) Program Type Average Range SD N Child Care $30,699 $10,110 48 Head Start $28,518 Part-Day $29,878 Total $30,058 $11,000 to $60,000 $12,400 to $47,000 $3,600 to $86,000 $3,600 to $86,000 $10,226 18 $24,184 17 $13,979 83 Directors’ Salaries (n=83) 20 Frequency 15 10 5 Mean = $30,058.37 Std. Dev. = $13,969.644 N = 83 0 $0 $20,000 $40,000 $60,000 What is your current annual salary? $80,000 Directors’ Use of Technical Assistance Program Type Child Care Head Start Part-day Total Yes No 46 13 (78.0%) (22.0%) 19 2 (90.5%) (9.5%) 16 2 (88.9%) (11.1%) 81 17 (82.7%) (17.3%) Total 59 21 18 98 Program Funding Sources (n=97) Funding Sources Percentage Number Fee for service 100% 97 Child Care Subsidy Funds 57.7% 56 Grants 50.5% 48 Private donations 36.1% 35 Foundations 13.4% 13 Handbooks (n=101) Type Percentage Number Parent Handbook Staff Handbook 98.1% 99 93.1% 94 Program Policies 53.5% 54 Program Purpose (n=103) Percentage Provide a warm and loving environment 99.4% Provide for care so parents can work 67.3% Prepare children for school 82.0% Provide compensatory help for children at-risk Teach children appreciation of cultures 40.0% Promote children’s overall development 99.4% Provide religious instruction 23.3% 75.1% Overall quality When we look at overall program quality, what does it look like? Safety and health Furnishings and space arrangement Teacher-child Interactions Curriculum (literacy, social, aesthetics, physical) Program operations Family-program relations Staff relations Quality Profile of Center-Based Programs Serving Infants and Toddlers 100% 21.3% N=24 80% 60% 8.8% N=10 20.4% N=23 53.1% N=60 33.6% N=38 8.0% N=9 47.8% N=54 23.9% N=27 29.6% N=29 32.7% N=37 46.0% N=52 38.1% N=43 50.4% N=57 50.0% N=49 33.6% N=38 46.0% N=52 14.2% N=16 25.7% N=29 20.4% N=20 40% 20% 0% 25.7% N=29 Furnishings and Display for Children (N=113) 70.8% N=80 Personal Care Routines (N=113) Listening and Talking (N=113) Learning Activities (N=113) Interaction (N=113) Program Structure (N=113) Adult Needs (N=98) Figure Legend = rating of “poor” = rating of “mediocre” = rating of “good” Quality Profile of Center-Based Programs Serving 3 to 5-year-olds 100% 38.6% N=64 26.5% N=44 37.6% N=62 9.7% N=16 59.4% N=98 43.9% N=72 45.5% N=60 34.8% N=57 42.4% N=56 21.3% N=35 12.1% N=16 80% 60% 40% 48.2% N=80 42.8% N=71 47.9% N=79 42.4% N=70 20.0% N=33 20% 0% 13.3% N=22 Space and Furnishings (N=165) 30.7% N=51 Personal Care Routines (N=166) 20.0% N=33 Language and Reasoning (N=165) 42.4% N=70 Activities (N=165) 20.6% N=34 Interaction (N=165) Program Structure (N=164) Parents and Staff (N=132) Figure Legend = rating of “poor” = rating of “mediocre” = rating of “good” What is the impact of Directors? Separate the 104 programs (451 groups) into those with consistent quality and those with inconsistent quality Consistent Quality: Those programs whose groups were within one level of each other (e.g., three “good” and one “mediocre”) Inconsistent Quality: Those programs whose groups had a quality difference of more than one level (e.g., two “good,” one “mediocre,” and one “poor”) Types of Programs Consistent—good Consistent--mediocre Inconsistent—good Inconsistent--poor Definition Number Majority “good;” others “mediocre” Majority “mediocre;” Others either “good” or “poor” Majority “good;” at least one other “poor” 17 Majority “poor;” at least one other “good” 11 49 27 What makes programs consistent? What makes programs consistently “good” or “poor?” What are the factors that make program quality inconsistent? Three major components contribute to program quality consistency Resources (money) Teacher education Contributed to the quality of space, materials, curriculum and program operations Contributed to interactions, curriculum, and program operations Directors Directors’ Contribution to Program Consistency Materials Curriculum Program Operations Health and Safety Child-teacher interactions Family-program interactions Staff interactions As a group, strong directors could override the impact of… Staff with less education in child development and early childhood education Lower paid staff Moderate financial resources Since sources of funding And were able to keep quality consistent from classroom to classroom. As a group, weak directors… had inconsistent quality from group to group had centers that were financially in trouble had higher rates of turnover in staff had vacancies and opening in their programs Director Characteristics Linked with Leadership Education level Overall education level Specific education Early childhood curriculum Child development core knowledge Management and fiscal knowledge Experience Age Ability to secure funding from other sources Characteristics of Strong Directors They have a bachelors degree or higher in early childhood education or child development They have training in financial management They are able to secure outside sources of funding They are 40-60 years of age They have at least 10 years experience in the field of early care They are able to communicate to boards, parents, and staff well They seem themselves as mentors They take leadership responsibilities in the field So, what are the implications?