Quiz 1 Quiz 2 12/2/2010
advertisement

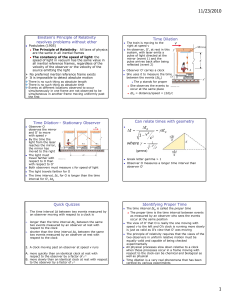
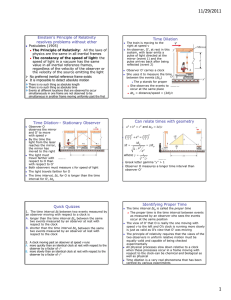
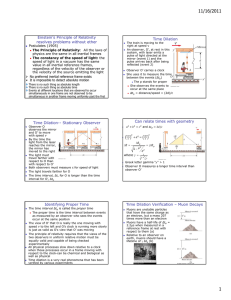
12/2/2010 • • • • • • Quiz 1 Absolute zero is the temperature at which: A. All motion ceases B. Water freezes C. Theoretically a gas has zero volume D. All of the above E. None of the above Quiz 2 We vused which law to determine he value of absolute zero: A. Lambert’s Law B. Boyle’s Law C. Faraday’s Law D. Charles Law E. Kepler’s law Jacques Alexandre César Charles The gas increases by 1/273 of its volume at 0°C for each °C rise of temperature. This means that the coefficient of expansion of all gases is the same. The law is only approximately true. Quick Quiz What is the most likely cause of error in the determination of Absolute Zero done in lab? • A. Human error • B. Thermometer readings • C. Syringe readings • D. Some uncontrolled factor, like water vapor in the air in syringe • E. Gravity Quiz 4: Who invented the artificial machine? Quiz 3: After who is he absolute temeprature scale named? A. Celsius B. Fahrenheit C. Rankine D. Kelvin E. Charles KELVIN, Lord (William Thomson) (1824 - 1907) • Proposed an absolute scale of temperature in 1848. Refrigeration Apalachicola Museum A. John Gorrie First Ice Machine Gorrie-1850 B. Lord Kelvin C. John Carrier D. Ferdinand Carre E. Bernard Machen Ferdinand Carre -developed successful Ice Business 1 12/2/2010 Quiz 5: What is the name of the relativity you experience riding in a car or an airplane? A. Galilean relativity B. Special relativity C. General relativity According to Galilean Relativity, the laws of mechanics are the same in all inertial frames of reference • An inertial frame of reference is one in which Newton’s Laws are valid • Objects subjected to no forces will move in straight lines Galilean Relativity – Example 1852 There is a stationary observer on the ground Einstein’s Principle of Relativity resolves problems without ether • Postulates (1905) – The Principle of Relativity: All the laws of physics are the same in all inertial frames – The constancy of the speed of light: the speed of light in a vacuum has the same value in all inertial reference frames, regardless of the velocity of the observer or the velocity of the source emitting the light No preferred inertial reference frame exists It is impossible to detect absolute motion There is no such thing as absolute length There is no such thing as absolute time Events at different locations that are observed to occur simultaneously in one frame are not observed to be simultaneous in another frame moving uniformly past the first Quick Quiz 7 The time interval Δt between two events measured by an observer moving with respect to a clock is A. longer than the time interval Δtp between the same two events measured by an observer at rest with respect to the clock B. shorter than the time interval Δtp between the same two events measured by an observer at rest with respect to the clock Quiz 8 A clock moving past an observer at speed v runs A. more quickly than an identical clock at rest with respect to the observer by a factor of -1 B. more slowly than an identical clock at rest with respect to the observer by a factor of -1 Quick Quiz 6 An inertial reference frame is one which: A. Is rotating B. Is always stationary C. Is at rest or moving at a constant velocity D. Is accelerating E. Is a fiction of the human mind Identifying Proper Time • The time interval Δtp is called the proper time – The proper time is the time interval between events as measured by an observer who sees the events occur at the same position The view of O’ that O is really the one moving with speed v to the left and O’s clock is running more slowly is just as valid as O’s view that O’ was moving The principle of relativity requires that the views of the two observers in uniform relative motion must be equally valid and capable of being checked experimentally All physical processes slow down relative to a clock when those processes occur in a frame moving with respect to the clock-can be chemical and biological as well as physical Time dilation is a very real phenomena that has been verified by various experiments 2 12/2/2010 The Twin Paradox • A thought experiment involving a set of twins, Speedo and Goslo • Speedo travels to Planet X, 20 light years from earth-his ship travels at 0.95c – After reaching planet X, he immediately returns to earth at the same speed, keeping his eyes shut for the whole trip • When Speedo returns, he has aged 13 years, but Goslo has aged 42 years Goslo’s perspective is that he was at rest while Speedo went on the journey Speedo thinks he was at rest and Goslo and the earth raced away from him on a 6.5 year journey and then headed back toward him for another 6.5 years The paradox – which twin is the traveler and which is really older? Quiz 10: In time dilation and length contraction the factor γ is A. Less than 1 B. Greater than 1 C. Always equal to 1 L LP LP 1 v2 c2 The Twin Paradox – The Resolution Quick Quiz 9 How can one twin or the other know detect a difference? A. There is not—this is a flaw in the theory of relativity B. One twin needs to have a pendulum C. One twin needs psychological help after the trip • Relativity applies to reference frames moving at uniform speeds • The trip in this thought experiment is not symmetrical since Speedo must experience a series of accelerations during the journey • Therefore, Goslo can apply the time dilation formula with a proper time of 42 years – This gives a time for Speedo of 13 years and this agrees with the earlier result • There is no true paradox since Speedo is not in an inertial frame Pair Production • An electron and a positron are produced and the photon disappears – A positron is the antiparticle of the electron, same mass but opposite charge • Energy, momentum, and charge must be conserved during the process • The minimum photon energy required is 2me = 1.02 MeV Quick Quiz 11 What is the frequency of the photon that produces a pair with zero speed? A. 1.02x1.6x10-19/6.2x10-34 = 2.6x1014 Hz B. 1.02x106/6.2x10-34=1.6x1027 Hz C. 1.02/6.2x10-34=2.6x1033 Hz D. 1.02x106x1.6x10-19/6.2x10-34 = 2.6x1020 Hz Pair Annihilation-Inverse of Pair Production • In pair annihilation, an electronpositron pair produces two photons • It is impossible to create a single photon • Conserved – Momentum – Energy – Charge Quick Quiz: Which conservation law dictates that 2 photons must be produced? A. Energy B. Momentum C. Charge 3