Chapter 22 Quiz Snell’s Law describes: (a) Huygens’ construction (b) Magnification
advertisement

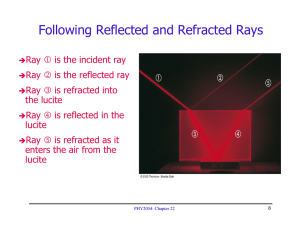
Chapter 22 Quiz ÎSnell’s Law describes: (a) Huygens’ construction (b) Magnification (c) Reflection (d) Refraction PHY2054: Chapter 22 9 Chapter 22 Quiz ÎFor refracted light rays, the angle of refraction: (a) is always equal to the incident angle (b) is always greater than the incident angle (c) is always less than the incident angle (d) is always equal to the critical angle (e) can be less than, greater than, or equal to angle of incidence PHY2054: Chapter 22 10 Dispersion ÎWhen light travels from one medium to another: Speed decreases Wavelength decreases Frequency constant ÎRefractive cn = c / n λn = cn / f = ( c / n ) / f = λ / n index is variable on λ n decreases as λ increases Depends n PHY2054: Chapter 22 11 Dispersion În decreases as λ increases red light (λ = 700 nm) ⇒ n is smaller (less bending) For blue light (λ = 400 nm) ⇒ n is bigger (more bending) Angular spreading (“dispersion”) of colors due to refraction For PHY2054: Chapter 22 12 Rainbows Formed by Dispersion ÎLight is refracted by spherical water droplets must be behind you (rainbow is circular, with sun on axis) Red light bent at a lesser angle (top of rainbow) Violet light bent at a greater angle (bottom of rainbow) Sun PHY2054: Chapter 22 13 Understanding Refraction in Wave Picture ÎConsider a row of soldiers slowing down in the mud Wave fronts “turn” due to change of speed in the medium Analysis based on Huygens principle Closer analysis yields Snell’s law with cn = c / n PHY2054: Chapter 22 14 Critical Angle Îθ < θc beam partly reflected & partly refracted at boundary Rays Îθ 1, 2, 3 > θc beam is entirely reflected at the boundary (ray 5) Total internal reflection occurs only when n1 > n2 sin θ c = n2 / n1 90° PHY2054: Chapter 22 15 Critical Angles (to vacuum) Substance sin θc = 1/ n N Critical angle 1 90.0° Air 1.00029 88.6° Ice 1.31 49.8° Water 1.333 48.6° Ethyl Alcohol 1.36 47.3° Glycerine 1.473 42.8° Crown glass 1.52 41.1° Sodium chloride 1.54 40.5° Quartz 1.544 40.4° Heavy flint glass 1.65 37.3° Tooth enamel 1.655 37.2° Sapphire 1.77 34.4° Heaviest flint glass 1.89 31.9° Diamond 2.42 24.4° Vacuum PHY2054: Chapter 22 16 Intensity During Transition to Critical Angle ÎTransition is actually very smooth ray is reflected and refracted As incident angle approaches critical angle, intensity of refracted ray goes to zero and reflected ray takes all the intensity Incident PHY2054: Chapter 22 17 Fiber Optics ÎBased on total internal reflection Fiber has inner “core” of optically dense glass Outer “cladding” of less optically dense glass ÎLight rays passed through core to make shallow reflections with surface ⇒ 100% reflection at each bounce PHY2054: Chapter 22 18 Fiber Optic Construction ÎTrick is to make core absorb no light So light can be transmitted over long distances Requires ultra-pure glass (no impurities, variations) ÎMany fibers can be carried in a bundle PHY2054: Chapter 22 19 Construction of Fiber Optic Cable Single mode fiber PHY2054: Chapter 22 20 Medical applications ÎVisual ÎUses scoping of internal organs, arteries, joints, etc. bundles of fibers to form an image PHY2054: Chapter 22 21 Fiber Optic Cables PHY2054: Chapter 22 22 Communications Applications ÎOptical fibers can carry digital information Telephone, ÎHigh networks, Internet frequency of light ⇒ high rate of information transfer “High ÎSignals Not bandwidth”, several Tb/s over single fiber can travel ∼ 100 km before needing boost susceptible to electrical noise ÎReplacing copper wires for long distance communication PHY2054: Chapter 22 23 Chapter 22 Quiz ÎTotal internal reflection (a) refers to light being reflected from a plane mirror (b) may occur when a fisherman looks at a fish in a lake (c) may occur when a fish looks at a fisherman on a lake PHY2054: Chapter 22 24 Chapter 22 Quiz ÎTotal internal reflection (a) refers to light being reflected from a plane mirror (b) may occur when a fisherman looks at a fish in a lake (c) may occur when a fish looks at a fisherman on a lake PHY2054: Chapter 22 25 National Lambda Rail Fiber Infrastructure www.nlr.net/ Only NLR Backbone links shown PHY2054: Chapter 22 26 Florida Lambda Rail (10 Florida Universities) www.flrnet.org/ PHY2054: Chapter 22 27