Chapter 23 Quiz not Which of the following is a principal ray?
advertisement
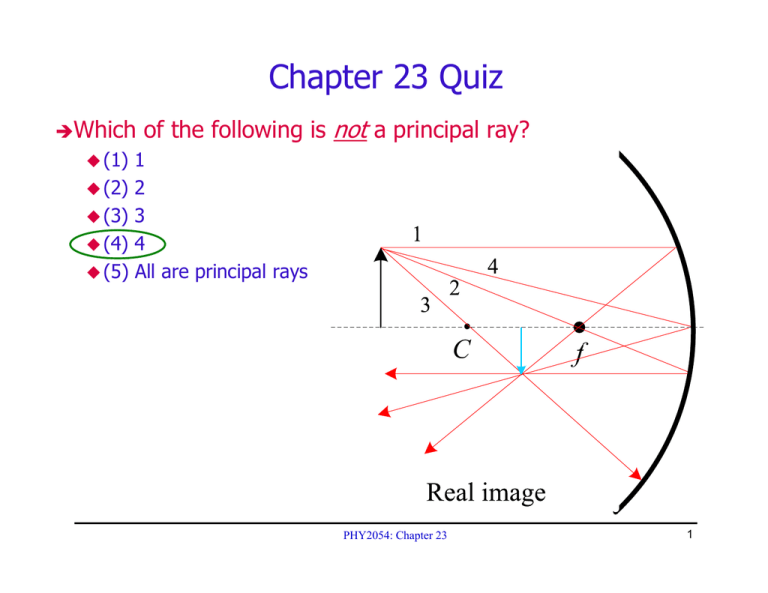
Chapter 23 Quiz ÎWhich (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) of the following is not a principal ray? 1 2 3 4 All are principal rays PHY2054: Chapter 23 1 Concave and Convex Mirrors R f = 2 PHY2054: Chapter 23 2 Images from Mirrors Location C f Size 1 1 1 + = p q f h′ q M ≡ =− h p q > 0 along reflected ray PHY2054: Chapter 23 3 Mirror Example ¾ 2 cm tall object (h = 2), 80 cm from mirror (p = 80) ¾ Mirror: 100 cm radius of curvature concave towards object (R = +100) 1 1 1 + = ⇒ q = 133.3 80 q 50 M =− 133.3 q =− = −1.67 80 p 3 1 h′ = ( −1.67 ) h = −3.33 C f 2 Roughly agrees with ray diagram (good to check it) PHY2054: Chapter 23 4 Images Formed by Refraction n1 n2 n2 − n1 + = p q R n1q h′ M = =− h n2 p PHY2054: Chapter 23 5 Image from Flat Refractive Surface R=∞ n1 n2 n2 + =0⇒q =− p p q n1 n1q M =− = +1 n2 p Same size virtual image! PHY2054: Chapter 23 6 Example: Image in Pool n1 = 1.333 n2 = 1.0 n2 q=− p n1 1 q=− p ≅ −0.75 p 1.333 So depth of image is about 3/4 depth of object PHY2054: Chapter 23 7 Atmospheric Refraction ¾ ¾ Refraction in atmosphere makes sun always appear higher in sky Can see the sun even when it is below the horizon! PHY2054: Chapter 23 8 Atmospheric Refraction Causes Various Mirages PHY2054: Chapter 23 9 Approaching Car on Hot Road PHY2054: Chapter 23 10 Floating Iceberg! Cold Air, Warm Water PHY2054: Chapter 23 11 “Squashed” Sun Setting Over Ocean PHY2054: Chapter 23 12 Thin Lenses PHY2054: Chapter 23 13 Thin Lenses f f Converging Lens Rays parallel to axis refract and pass through focal point f>0 f f Diverging Lens Rays parallel to axis refract and appear to emerge from focal point f<0 PHY2054: Chapter 23 14 Location and Size of Image (Recall Mirror) h′ q M ≡ =− h p 1 1 1 + = p q f PHY2054: Chapter 23 15 Finding Image from Lens: Example ¾ f = 10 cm ¾ p = 30 cm ¾ h = 4 cm 1 1 1 + = ⇒ q = +15cm 30 q 10 q 15 M = − = − = −0.5 30 p h′ = −2cm PHY2054: Chapter 23 16 Principal Ray Diagrams for Lenses q>0 PHY2054: Chapter 23 17 Principal Ray Diagrams for Lenses (cont) q<0 PHY2054: Chapter 23 18 Principal Ray Diagrams for Lenses (cont) q<0 PHY2054: Chapter 23 19 Calculating Focal Length for Thin Lenses ⎛ 1 1 1 ⎞ = ( n − 1) ⎜ − ⎟ f R R ⎝ 1 2⎠ Lensmaker’s equation Sign convention R>0 R<0 PHY2054: Chapter 23 20 Calculating Focal Length Example Let n = 1.5, R = 10 1 1 ⎞ ⎛1 = 0.5 ⎜ − ⎟ = 0.05 f ⎝ 10 ∞ ⎠ 1 1 ⎞ ⎛1 = 0.5 ⎜ − ⎟ = 0.1 f ⎝ 10 −10 ⎠ 1 1 ⎞ ⎛1 = 0.5 ⎜ − ⎟ = 0.1 f ⎝ 10 −10 ⎠ So f1 = f2/2 1 has twice the “power” of 2 PHY2054: Chapter 23 21 Quiz on Lenses Î All the lenses below have either flat sides or radius of curvature R. Rank in descending order the value of 1/f (lens power), i.e. from most positive to most negative ⎛ 1 1 1 ⎞ = ( n − 1) ⎜ − ⎟ f R R 2⎠ ⎝ 1 (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) A, C, B, E, D C, A, D, B, E B, A, C, E, D D, E, B, C, A C, A, E, D, B Each term adds to lens power Flat A B C D PHY2054: Chapter 23 E 22 Quiz on Mirrors ÎAn upright object is located in front of a convex mirror a distance greater than the focal length. The image formed by the mirror is: (1) (2) (3) (4) (5) real, inverted, and smaller than the object virtual, inverted, and larger than the object real, inverted, and larger than the object real, erect, and larger than the object virtual, erect, and smaller than the object 1 1 1 = − q f p f < 0, so q < 0 M = −q/p < +1 PHY2054: Chapter 23 23