5/9/2011 Phy 2049: Physics II Phy 2049: Homework
advertisement

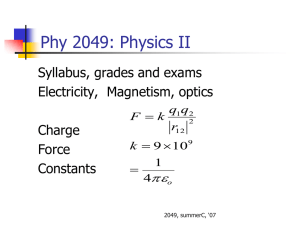
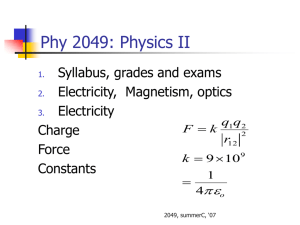
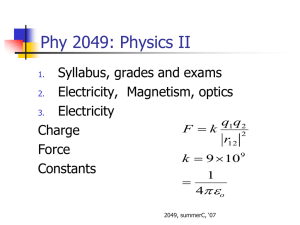
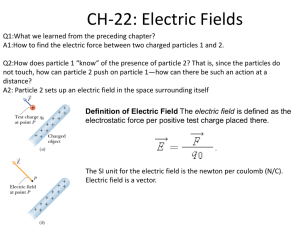
5/9/2011 Phy 2049: Physics II Phy 2049: Homework Syllabus, grades and exams Electricity, Magnetism, optics F = k Charge Force Constants q1q 2 r12 k = 9 × 10 = 1 4 πε 2 9 o Phy 2049: Homework Phy 2049: Homework Visit wileyplus Physics is a little like riding bicycle. No one has learned how to ride a bicycle by reading an owner’s manual. It is hard in the beginning, but then it becomes instinctive. That is when you start to enjoy the scenery Try doing homework in a group. Charges and Polarization Two kinds of charges, positive and negative, unit is 1.6x10-19 Coulombs. Like Charges repel. It takes force to hold them in place. Induction: Because the summer semester is quite short, the homework assignments are rather large. I would suggest that you do as many as you can at the earliest chance possible. I would certainly urge you not to try them all the night before they are due. Polarization is attractive. Like charges move back and unlike charges move up. Contact leads to repulsion. Only like charges are left to be redistributed. Coulomb’s law Superposition (Addition) of forces as vectors Induction and contact Electric fields and field lines Natural particles Electrons are very light (m = 9.11 x10-31 kg). Their charge is 1.6x10-19 Coulomb. Protons and neutrons are same weight (nearly so, m = 1.67x10-27 kg = 1/NA ). Protons are positively charged but the neutrons are neutral. Electrons move in a metal, hence induction. 1 5/9/2011 Touching charges Induction and Contact Three identical balls, 2q, q and –q A touches B and separated back. B touches C and separated back Ratio of Force FAB now to force FAB at the start. What is the force between the balls in each case? • How much charge is transferred when they touch? • Calculate the force between the balls after they have touched? • Phy 2049: Physics II F =k q1q2 r12 2 k = 9 × 109 1 = 4πε o • Coulomb’s Law rˆ • F in Newtons, r in meter, q in Coulomb and k is the fix. • F is a vector, directed along a line joining the charges. • The force can be added like a vector Phy 2049: Physics II Two equally charged particles are held 2.5X 10-3 m apart and then released from rest. The initial acceleration of the first particle is observed to be 5.0 m/s2 and that of the second to be 11.0 m/s2. The mass of the first particle is 6.3X10-7 kg. What is the mass of the second particle? Phy 2049: Physics II Two equally charged particles are held 2.5X 10-3 m apart and then released from rest. The initial acceleration of the first particle is observed to be 5.0 m/s2 and that of the second to be 11.0 m/s2. The mass of the first particle is 6.3X10-7 kg. What is the mass of the second particle? What is the magnitude of the charge of each particle? Directions of Forces M1a1= M2a2 = F = kq2/r2 M2= M1a1/a2 = 2.86x10-7 kg q2 = r2 M1a1/k q = 4.68x10-11 C Between two charged particles forces are directed along a line joining them. Can be added as vectors What is the magnitude of the charge of each particle? 2 5/9/2011 Phy 2049: Physics II In Fig. at right, the particles have charges q1 = -q2 = 298 nC and q3 = -q4 = 280 nC, and distance a = 4.0 cm. What are the a) Fx and b) Fy components of the net electrostatic force on particle 3? Force and Electric Fields • • • • F = qE Electric field is the force felt by a unit positive charge Electric field lines come out of a positive charge and go into a negative charge. They do not cross Summary 1. 2. 3. Coulombs law Properties of charges Electric fields 3