Name 1-8 /40 10
advertisement

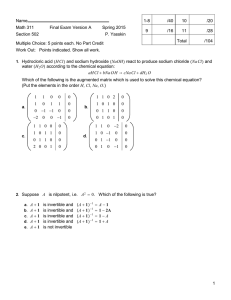
Name Math 311 Final Exam Version A Section 502 1-8 /40 10 /20 9 /16 11 /28 Total /104 Spring 2015 Solutions P. Yasskin Multiple Choice: 5 points each. No Part Credit Work Out: Points indicated. Show all work. 1. Hydrocloric acid H Cl and sodium hydroxide NaOH react to produce sodium chloride Na Cl and water H 2 O according to the chemical equation: aH Cl bNa O H cNa Cl dH 2 O Which of the following is the augmented matrix which is used to solve this chemical equation? (Put the elements in the order H, Cl, Na, O.) a. c. 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 2 0 0 1 0 d. H: Solution: b. a b 2d Cl : a c Na : b c O: b d 2. Suppose A is nilpotent, i.e. A 2 a. b. c. d. e. A A A A A 1 1 1 1 1 Solution: is invertible and is invertible and is invertible and is invertible and is not invertible A 1 1 A A A A A A 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 2 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 Correct Answer Each equation gets a row. 0. Which of the following is true? 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 0 2 1 1 1 1 A2 A 1 1 2A 1 A 1 A A 1 Correct Answer A2 1. 1 3. Consider the vector space M 2, 2 1 0 E1 of 2 E2 0 1 1 0 0 1 2 matrices with the basis 0 1 E3 1 0 9 5 Which of the following are the components of the matrix A a. A E 2 1 4 3 b. A E 5 4 3 2 c. A E 4 5 2 3 d. A E 1 2 3 4 e. A E 5 2E 1 1E 2 4E 3 3E 4 A 4E 1 5E 2 2E 3 3E 4 A 5E 1 4E 2 3E 3 2E 4 3 7 1 1 9 5 1 1 A 5E 1 4E 2 3E 3 2E 4 A 1E 1 2E 2 3E 3 4E 4 of real valued function on the interval 2 spanned by the basis v 1 subspace V Span x, x orthonormal basis for V? 5 x 2 x u2 c. u 1 d. u 1 e. u 1 3 x 2 2x x2, x w2, w2 x2, x2 7 1 1 1 x, v 2 whose second f x g x dx. Consider the f, g 2 0, 1 1 x . Which of the following is an 7 x2 2 3 2 x x 4 5 x2 u2 Correct Answer 2 u2 4 5 x2 3 5 x w1, w1 v2, w1 3 u2 1 x 1 1 x2 We apply Gram-Schmidt to v 1 w1 9 5 5 9 derivatives exist and are continuous with the inner product b. u 1 relative to the E basis? 1 1 1 1 4. Consider the vector space C 2 0, 1 u2 1 0 2 A x 1 Correct Answer 4 3 a. u 1 0 E4 x, x x 2 dx 2 3 w2 v2 1 1 x 3 dx 1 1 x 4 dx 1 x2 x, v 2 0 2 5 u2 u1 3 x 2 x2 5 x2 2 2 5. Consider the second derivative linear operator L : P 6 P6 : L p polynomials of degree less than 6. Find the image, Im L . HINT: Let p a bx cx 2 dx 3 ex 4 fx 5 . a. b. c. d. e. Im Im Im Im Im L L L L L Im L Span Span Span Span Span Lp 2c 6dx 12ex 2 20fx 3 L L L L L Span Span Span Span Span P6 : L p on the space of 1 1, x Correct Answer 1, x, x 2 x2, x3, x4, x5 x, x 2 , x 3 , x 4 , x 5 Ker L p Lp 0 2 Lp 2c 6dx 12ex 20fx 3 0 Ker L p a bx Span 1, x 7. d2p dx 2 Span 1, x, x 2 , x 3 polynomials of degree less than 6. Find the kernel, Ker L . HINT: Let p a bx cx 2 dx 3 ex 4 fx 5 . Ker Ker Ker Ker Ker on the space of 1 1, x 1, x, x 2 , x 3 Correct Answer 2 3 4 5 x ,x ,x ,x x, x 2 , x 3 , x 4 , x 5 6. Consider the second derivative linear operator L : P 6 a. b. c. d. e. d2p dx 2 Compute the line integral c d e F ds clockwise around the f 0 y 3 complete boundary of the plus sign, shown at the right, for the vector field a. 25 b. 5 F 2y, 4y 3 3x . 2 1 0 c. 0 0 d. 5 e. 25 4x 3 1 2 3 x Correct Answer We let P, Q F 4x 3 2y, 4y 3 3x and apply Green’s Theorem. There is an extra minus sign because we need F ds clockwise, but Green’s Theorem expects counterclockwise: Q P dx dy F ds P dx Q dy 3 2 dx dy 5 Area 5 5 25 x y 3 8. Consider the vector space M 2, 2 of 2 function, L : M 2, 2 M 2, 2 : L X AX corresponding eigenmatrix (eigenvector) of L? x y HINT: Let X 1 0 2 matrices. Let A . Consider the linear 0 2 XA. Which of the following is not an eigenvalue and . z w Solution: LX a. 2 X b. 1 X c. 0 X d. 0 X 1 e. 9. L x y 1 0 x y x y 1 0 0 y z w 0 2 z w z w 0 2 z 0 0 1 1 0 Correct Answer L 0 0 L 1 0 1 0 L 0 0 0 0 L 0 1 0 1 X L 0 0 16 points Which of the following is an inner product on Put ’s in the correct boxes. No part credit. Let x x1, x2 , y y1, y2 . 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 2 2 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 ? If not, why not? Why not? Inner Product? Yes x, y a. x 1 y 1 2x 2 y 2 b. x 1 y 1 2x 1 y 2 c. x 21 y 21 2x 22 y 22 d. x 1 y 1 x1y2 x2y1 2x 2 y 2 e. x 1 y 1 x1y2 x2y1 2x 2 y 2 f. x1y1 x1y2 x2y1 x2y2 g. x 1 y 1 x1y2 x2y1 x2y2 h. x 1 y 1 x2y2 No Not Not Not Positive but Not Symmetric Linear Positive Positive Definite 2x 2 y 2 4 Solutions: a. y, x y 1 x 1 2y 2 x 2 x, y x, ay bz a x, y b x, z 2 2 x, x x 1 2x 2 0 and 0 only if x 1 x 2 0 b. y, x y 1 x 1 2y 1 x 2 2y 2 x 2 x, y c. x, ay a 2 x 21 y 21 2a 2 x 22 y 22 a 2 x, y a x, y d. y, x y 1 x 1 y 1 x 2 y 2 x 1 2y 2 x 2 x, y x, ay bz a x, y b 2 2 2 2 x, x x 1 2x 1 x 2 2x 2 x1 x2 x 2 0 and 0 only if x 1 e. y, x y 1 x 1 y 1 x 2 y 2 x 1 2y 2 x 2 x, y x, ay bz a x, y b x, x x 21 2x 1 x 2 2x 22 x 1 x 2 2 x 22 0 and 0 only if x 1 f. x, x x 21 2x 1 x 2 x 22 x 1 x 2 2 0 but can 0 if x 1 x 2 0 g. x, x x 21 2x 1 x 2 x 22 x 1 x 2 2 0 but can 0 if x 1 x2 0 2 2 h. x, x x 1 x 2 0 if x 2 x 1 0 10. x, z x2 x, z x2 0 0 20 points Let M 2, 3 be the vector space of 2 3 matrices. Consider the subspace V Span A 1 , A 2 , A 3 , A 4 where A1 1 1 0 2 3 2 , A2 2 2 0 4 6 4 1 0 2 , A3 , A4 3 0 0 1 2 6 5 6 4 Find a basis for V. What is the dim V ? Solution: To see if A 1 , A 2 , A 3 , A 4 are linearly independent, we write: aA 1 bA 2 cA 3 dA 4 0 and solve for a, b, c, d. a 1 1 0 2 3 2 b 2 2 0 4 6 4 a 2b c d a 2b 2d 2a 4b 3c 5d 3a 6b 6d 1 2 1 1 0 1 2 0 2 0 0 0 2 6 0 2 4 3 5 0 R4 3 6 0 6 0 2 4 0 4 0 c 2c 2a 1 0 2 d 3 0 0 6d 4b 4d 1 2 6 0 0 0 5 6 4 0 0 0 0 0 0 6 equations 0 0 0 4 unknowns 1 2 1 1 0 0 0 1 3 0 0 0 2 6 0 R3 2R 1 0 0 1 3 0 R5 3R 1 0 0 3 9 R6 2R 1 0 0 2 6 R2 R1 R1 R2 1 2 0 2 0 0 0 1 3 0 2R 2 0 0 0 0 0 R4 R2 0 0 0 0 0 0 R5 3R 2 0 0 0 0 0 0 R6 2R 2 0 0 0 0 0 a 2b 2d 0, c 3d 0 a 2r 2s b r c 3s d s 2r 2s A 1 rA 2 3sA 3 sA 4 0 So they are not linearly independent. Further, with r 1 and s 0: A 2 2A 1 and with r 0 and s 1: A 4 2A 1 3A 3 So A 1 , A 2 also span and the above computation without columns 2 and 4 shows they are linearly independent. So A 1 , A 2 is a basis and dim V 2. 5 11. 28 points Compute F dS over the hemisphere z x2 25 y2 oriented upward, for the H vector field F x 3 4y 2 4z 2 , 4x 2 y 3 4z 2 , 4x 2 4y 2 HINT: Use Gauss’ Theorem by following these steps: z3 . a. Write out Gauss’ Theorem for the Volume, V, which is the solid hemisphere 0 z 25 x 2 y 2 . Split up the boundary, V, into two pieces, the hemisphere, H, and the disk, D, at the bottom. State orientations. Solve for the integral you want. b. Compute the volume integral using spherical coordinates. c. Compute the other surface integral over D by parametrizing the disk, computing the tangent vectors and normal vector, checking the orientation, evaluating the vector field on the disk and doing the integral. d. Solve for the original integral. Solution: a. Gauss’ Theorem: F dV F dS F dS V V F dS H D H is oriented upward. D is oriented downward. F dS F dV H F dS V D 2 b. In spherical coordinates: dV 2 /2 5 F dV 2 3 0 V 0 2 and sin sin d d d er e F r sin x3 4y 2 2 sin 0 r cos 0 F dS d. H er y3 5 5 0 0 F dV V F dS 2 . 6 1 54 5 3750 0 r cos , r sin , 0 . e 4z 2 , 4x 2 2 3 5 5 /2 cos î0 4y 2 4r 3 dr d z3 2 r4 r sin 2 k r cos 2 0 Reverse to point down: F N dr d 0 D N 4z 2 , 4x 2 F dS 3z 2 0 k cos 3 2 3y 2 0 c. The disk may be parametrized by R r, î 3x 2 F N 0, 0, r , , 4r 2 03 5 F N 0, 0, r 4r 3 1250 0 0 3750 1250 2500 D 6