Fall 2005 Math 152 Section 10.1
advertisement
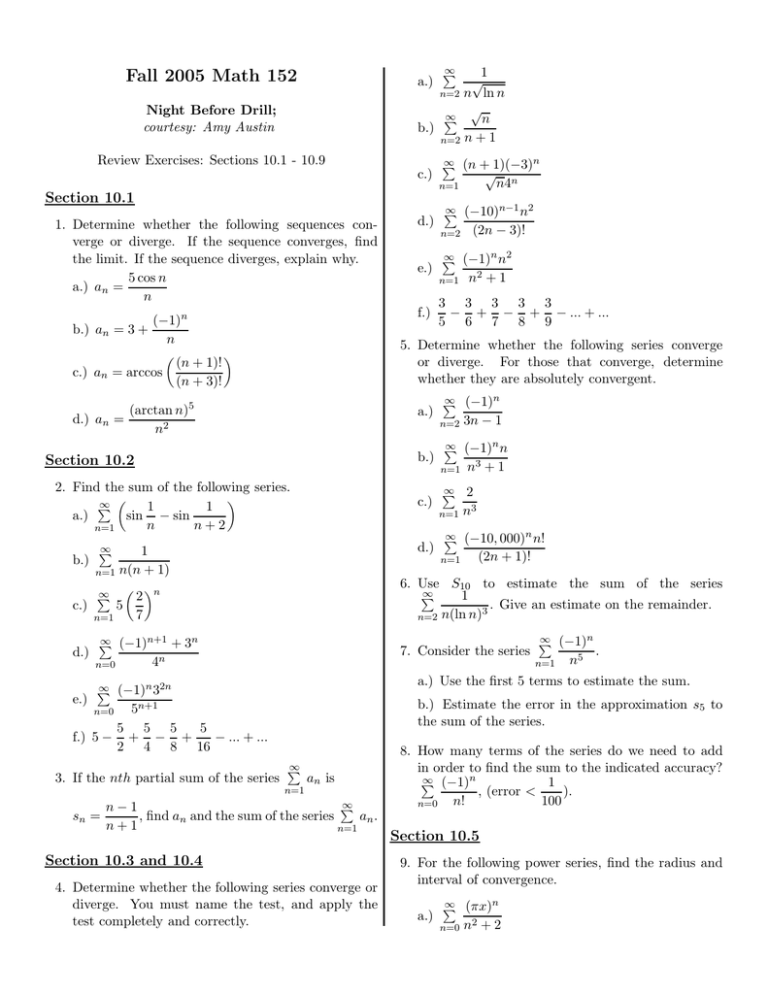
a.) Night Before Drill; courtesy: Amy Austin Review Exercises: Sections 10.1 - 10.9 c.) Section 10.1 1. Determine whether the following sequences converge or diverge. If the sequence converges, find the limit. If the sequence diverges, explain why. 5 cos n a.) an = n (−1)n b.) an = 3 + n c.) an = arccos (n + 1)! (n + 3)! a.) b.) 2. Find the sum of the following series. ∞ P 1 1 a.) sin − sin n n+2 n=1 c.) d.) ∞ P 1 b.) n=1 n(n + 1) e.) ∞ (−1)n+1 + 3n P ∞ (−10)n−1 n2 P n=2 (2n − 3)! ∞ (−1)n n2 P n=1 n2 + 1 3 3 3 3 3 − + − + − ... + ... 5 6 7 8 9 ∞ (−1)n P n=2 3n − 1 ∞ (−1)n n P n=1 n3 + 1 ∞ 2 P n=1 n3 ∞ (−10, 000)n n! P n=1 (2n + 1)! ∞ (−1)n P n=1 n5 . a.) Use the first 5 terms to estimate the sum. ∞ (−1)n 32n P b.) Estimate the error in the approximation s5 to the sum of the series. 5n+1 5 5 5 5 f.) 5 − + − + − ... + ... 2 4 8 16 n=0 sn = n4n 7. Consider the series 4n 3. If the nth partial sum of the series √ n=1 6. Use S10 to estimate the sum of the series ∞ P 1 . Give an estimate on the remainder. 3 n=2 n(ln n) n 2 c.) 5 7 n=1 n=0 e.) ∞ (n + 1)(−3)n P 5. Determine whether the following series converge or diverge. For those that converge, determine whether they are absolutely convergent. Section 10.2 d.) d.) f.) (arctan n)5 d.) an = n2 ∞ P ∞ P 1 √ n=2 n ln n √ ∞ P n b.) n=2 n + 1 Fall 2005 Math 152 ∞ P n=1 an is ∞ P n−1 an . , find an and the sum of the series n+1 n=1 Section 10.3 and 10.4 4. Determine whether the following series converge or diverge. You must name the test, and apply the test completely and correctly. 8. How many terms of the series do we need to add in order to find the sum to the indicated accuracy? ∞ (−1)n P 1 , (error < ). n! 100 n=0 Section 10.5 9. For the following power series, find the radius and interval of convergence. a.) ∞ (πx)n P n=0 n2 + 2 b.) c.) d.) ∞ (2x − 1)n P 17. Find the coefficient of (x − 4)3 in the Taylor Series √ for the function f (x) = x at a = 4. n!4n n=0 ∞ (2n − 1)!(x + 2)n−1 P 1 sin x − x + x3 6 . This function 18. Consider f (x) = x5 can be expressed as a series, by using the known Maclaurin series for sin x. Find the first four nonzero terms of this series. 5n−1 n=1 ∞ (−1)n (x − 1)n P √ n=1 n 10. Suppose it is known that ∞ P cn xn is convergent n=0 when x = 4 and divergent when x = 6. What can Section 10.9 be said about the convergence or divergence of the For the problems 16-17, answer the following questions: following series: a.) Find Tn (x) at the given value of a. Also, find the ∞ P remainder term. a.) cn 8n b.) Use Taylor’s Inequality to estimate the accuracy n=0 ∞ P of the approximation Tn (x) for x in the given interval. b.) cn (−3)n n=0 2 ∞ 19. f (x) = 2 , n = 4, a = 2, 1 ≤ x ≤ 2.5 P n x c.) cn (−4) n=0 √ 20. f (x) = 1 + x, n = 2, a = 1, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1.1 ∞ P d.) cn (5)n n=0 Section 10.6 11. Find a power series for the following functions and find the corresponding radius of convergence. 1 a.) f (x) = 1−x 1 b.) f (x) = 4 + x2 c.) f (x) = ln(2 − x) arctan x d.) f (x) = x x e.) f (x) = 2 (x + 1)2 Z 12. Write 0.5 0 1 dx as an infinite series. 1 + x4 Section 10.7 13. Find the Taylor Series for f (x) = e4x at x = −1. 14. Find the first three nonzero terms of the Taylor Se1 ries for f (x) = 2 centered at x = 3. x Z 15. Find a Maclaurin series for Z 16. Express 0 1 cos(x2 ) dx x 2 e−x dx as an infinite series. Use the first 2 terms of this series to approximate the sum and estimate the error.