PHY 2053, Section 3794, Fall 2009, Quiz 10 w
advertisement

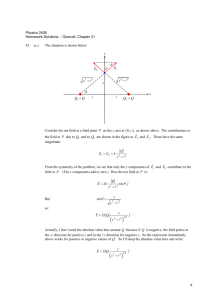
PHY 2053, Section 3794, Fall 2009, Quiz 10 1. One end of a uniform 7.0 m long rod of weight w is supported by a cable. The other end rests against the wall, where it is held by friction. The coefficient of static friction between the wall and the rod is µs = 0.50. Determine the minimum distance, x, from point A at which an additional weight w (the same as the weight of the rod) can be hung without causing the rod to slip at point A. Let T be the tension in the cable and N the normal force at the wall, with friction given by FR ≤ µs N . Then: Fx : N − T cos(θ) = 0 T sin(θ) + FR − 2 × w = 0, and L τ : T × L sin(θ) − w × − w × x = 0, 2 where torque has been calculated around point A. From the first two equations we have: Fy : 2 × w = T sin(θ) + FR ≤ T sin(θ) + µs × T cos(θ) =⇒ T sin(θ) ≥ 2×w , 1 + µs × cot(θ) while from the third equation we find ( T sin(θ) = w × ) 1 x + . 2 L Putting these together we have ( ) ( ) 2 2 1 1 x≥L − = 7.0 × − = 4.9 m. 1 + µs × cot(θ) 2 1 + 0.50 × 1.327 2 2. A planet of radius 8.00 × 103 km spins with an angular velocity of 20.0 × 10−5 rad/s about an axis through the North Pole. What is the ratio of the normal force experienced by a person at the equator to that experienced by a person at the North Pole? Assume a constant gravitational acceleration of 1.60 m/s2 and that both people are stationary relative to the planet and are at sea level. At the North Pole we have NN P − mg = 0 =⇒ NN P = mg, while at the equator we have Neq − mg = −mω 2 R =⇒ Neq = mg − mω 2 R. Thus the ratio Neq /NN P is given by: Neq ω2R (2.00 × 10−4 )2 × 8.00 × 106 =1− =1− = 1.000 − 0.200 = 0.800. NN P g 1.60