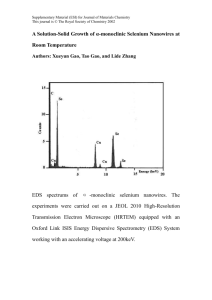
Convex Optimization with Greedy Methods Zheming Gao May 12, 2015 Texas A&M University
advertisement

Convex Optimization with Greedy Methods
Zheming Gao
Texas A&M University
Beihang University
gorgeous1992@tamu.edu
May 12, 2015
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
1 / 21
Overview
1
Introduction to Greedy Algorithms
2
Aims & Plans: Apply Greedy Algorithms for Convex Optimization
3
Expected Results
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
2 / 21
Introduction: Set up & Notations
Definition (Hilbert Space)
H is a Hilbert space if it is a complete inner product space with its norm
induced by the inner product:
1
k · k = (· , ·) 2
Definition (Dictionary)
A set of functions D = {ϕ} is called a dictionary if
kϕk = 1
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
and
span{D} = H
May 12, 2015
3 / 21
Introduction: Greedy Techniques I
Used For:
finding a good approximant of a given function f ∈ H via
finite linear combinations of elements from the dictionary D and at step m
the algorithm generates the approximant (m-sparse approximation)
fm =
m
X
cj ϕij
(cj ∈ R, ϕij ∈ D)
i=1
We want:
lim kfm − f k = 0
m→∞
Investigate:
kfm − f k ∼ m−α
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
4 / 21
Introduction: Greedy Techniques II
Definition (Approximation Error)
We define the m-term Approximation Error as
σm (f , D) :=
P
m (D)
inf kf
P
s∈ m (D)
− sk
is a collection of the linear combinations of m elements from D:
X
m
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
(D) := {
m
X
cj ϕij |cj ∈ R, ϕij ∈ D}
j=1
May 12, 2015
5 / 21
Introduction: Greedy Techniques III
Definition
For a general dictionary D, define the calss of functions:
1
A01 (D, M) := {f ∈ H|f =
X
ck ϕk , |Λ| < ∞ and
ϕk ∈D,k∈Λ
X
|ck | 6 M}
k∈Λ
and define A1 (D, M) as the closure (in H) of A01 (D, M).
2
[
A1 (D) =
A1 (D, M)
M>0
The semi-norm of f in A1 (D):
|f |A1 (D) :=
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
inf
{M}
f ∈A1 (D,M)
May 12, 2015
6 / 21
Introduction: Greedy Techniques IV
Theorem (DeVore-Temlyakov, 1996)
If f ∈ A1 (D) ⊂ H, then
1
σm (f , D) 6 C |f |A1 (D) m− 2
Goal: If fm is the approximant generated by greedy algorithm, we
want to get the rate of error ||fm − f || ∼ m−1/2 .
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
7 / 21
Types of Algorithms I
There are 3 main types of greedy algorithms:
Pure Greedy Algorithm (PGA)
Relaxed Greedy Algorithm (RGA)
Orthogonal Greedy Algorithm (OGA)
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
8 / 21
Types of Algorithms II
1
Pure Greedy Algorithm (PGA):
Step m = 0: Define f0 := 0
Step m: choose ϕm ∈ D, such that
|(ϕm , f − fm−1 )| = sup |(ϕ , f − fm−1 )|
ϕ∈D
Define the next approximant:
fm = fm−1 + (f − fm−1 , ϕm )ϕm
Theorem (DeVore-Temlyakov, 1996)
Figure: RGA
If f ∈ A1 (D), fm is generated by PGA, then
1
||fm − f || 6 |f |A1 (D) m− 6
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
9 / 21
Types of Algorithms III
2
Relaxed Greedy Algorithm (RGA):
Step m = 0: Define f0 := 0
Step m: choose ϕm ∈ D, such that
|(ϕm , f − fm−1 )| = sup |(ϕ , f − fm−1 )|
ϕ∈D
Define the next approximant:
fm = (1 −
1
1
)fm−1 + ϕm
m
m
Theorem (DeVore-Temlyakov, 1996)
Figure: RGA
If f ∈ A1 (D), fm is generated by RGA, then
1
||fm − f || 6 |f |A1 (D) m− 2
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
10 / 21
Types of Algorithms IV
3
Orthogonal Greedy Algorithm (OGA):
Step m = 0: Define f0 = 0
Step m: Define
|(ϕm , f − fm−1 )| = sup |(ϕ , f − fm−1 )|
ϕ∈D
and Hm := span{ϕ1 , . . . , ϕm }
Define the next approximant:
fm = PHm (f )
which is the orthogonal projection on Hm .
Theorem (DeVore-Temlyakov, 1996)
If f ∈ A1 (D), fm is generated by OGA, then
1
||fm − f || 6 |f |A1 (D) m− 2
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
11 / 21
Types of Algorithms V
Figure: OGA
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
12 / 21
Plans
Interested in applying greedy techniques
for solving the problem:
Given a convex function E : H → R, try
to find the globle minimum of E :
Example
To find the minimum of
f (x) = ax 2 + bx + c (a ≥ 0)
E (x ∗ ) = inf E (x)
x∈H
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
x∗ = −
b
2a
May 12, 2015
13 / 21
Preparation I
Definition (Convex Function)
E : H → R is a convex function if
∀u, v ∈ H, t ∈ [0, 1]
E (tu + (1 − t)v ) 6 tE (u) + (1 − t)E (v )
Figure: Convex Function
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
14 / 21
Preparation II
Definition (Frechet Derivative)
We call that E is Frechet differentiable at x ∈ H if there exists a bounded
linear functional, denote by E 0 (x), such that
|E (x + h) − E (x) − hE 0 (x), hi|
=0
h→0
||h||
lim
Definition (Solution Space)
Given a Hilbert Space H and a convex function E , define
Ω := {x ∈ H|E (x) 6 E (0)}
i.e.
inf E (x) = inf E (x)
x∈H
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
x∈Ω
May 12, 2015
15 / 21
Example
Given a dictionary D from H, use greedy algorithms to get a sequecne
{xm } ∈ Ω, such that
X
xm ∈
(D) and x ∗ = lim xm
m
m→∞
Chebyshev Greedy Algorithm (CGA(co)):
Step m = 0: Set x0 := 0.
Step m: choose ϕm from D, such that
|hE 0 (xm−1 ) , ϕm i| = sup {|hE 0 (xm−1 ) , g i|}
g ∈D
Φm = span{ϕj }m
j=1
E (xm ) = inf E (x)
x∈Φm
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
16 / 21
Conditions on E
Condition 0: E has a Frechet derivative E 0 (x) ∈ H at each point x
in Ω, which is bounded, and
||E 0 (x)|| 6 M0 , x ∈ Ω
Uniform Smootheness (US): There are 0 < α, 1 < q 6 2 and
0 < M, such that for all x, x 0 with ||x − x 0 || 6 M, x ∈ Ω,
E (x 0 ) − E (x) − E 0 (x 0 − x) 6 α||x 0 − x||q
(1)
Uniform Convexity (UC): There are 0 < β, 2 6 p < ∞ and 0 < M,
such that for all x, x 0 with ||x − x 0 || 6 M, x ∈ Ω,
E (x 0 ) − E (x) − E 0 (x 0 − x) > β||x 0 − x||p
(2)
Particularly, we say E is strongly convex when p = 2.
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
17 / 21
Previous work I
Theorem (Temlyakov)
Let E be a uniformly smooth convex function with modulus of smoothness
ρ(E , u) 6 γu q , where 1 < q 6 2. Then we have for CGA(co):
E (xm ) − inf E (x) 6 Cm1−q
x∈Ω
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
18 / 21
Previous work II
Theorem (H.Nguyen & G.Petrova)
Let E be a convex function that satisfiesPCondition 0, the US, and the
UC conditions. Let the minimizer x ∗ = i ci (x ∗ )ϕi ∈ Ω with support
|S| := |{i : ci (x ∗ ) 6= 0}| < ∞, where {ϕi } is an orthonormal basis for H
Then, at step m,
1
If p 6= q,
E (xm ) − E (x ∗ ) 6 Cm
−
p(q−1)
p−q
where C = C (|S|, p, q, α, β, E ).
2
If p=q=2,
E (xm ) − E (x ∗ ) 6 C̃ γ m−1
where C̃ = E (0) − E (x ∗ ), γ = γ(α, β, E ).
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
19 / 21
Expected Results
Error Estimate
1
Greedy methods
2
Different Conditions
3
Better convergence under
various conditions on E
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
Improve the results of the algorithms
given in Dr.Temlyakov’s paper.
May 12, 2015
20 / 21
The End
Thank you
Zheming Gao (Texas A&M)
May 12, 2015
21 / 21