ON THE HÖLDER CONTINUITY OF MATRIX FUNCTIONS FOR NORMAL MATRICES
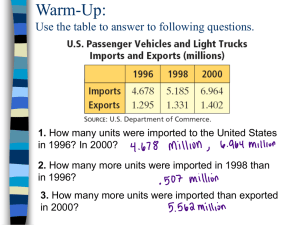
advertisement

Volume 10 (2009), Issue 4, Article 91, 5 pp.
ON THE HÖLDER CONTINUITY OF MATRIX FUNCTIONS FOR NORMAL
MATRICES
THOMAS P. WIHLER
M ATHEMATICS I NSTITUTE
U NIVERSITY OF B ERN
S IDLERSTRASSE 5, CH-3012 B ERN
S WITZERLAND .
wihler@math.unibe.ch
Received 28 October, 2009; accepted 08 December, 2009
Communicated by F. Zhang
A BSTRACT. In this note, we shall investigate the Hölder continuity of matrix functions applied
to normal matrices provided that the underlying scalar function is Hölder continuous. Furthermore, a few examples will be given.
Key words and phrases: Matrix functions, stability bounds, Hölder continuity.
2000 Mathematics Subject Classification. 15A45, 15A60.
1. I NTRODUCTION
We consider a scalar function f : D → C on a (possibly unbounded) subset D of the
complex plane C. In this note, we shall be particularly interested in the case where f is Hölder
continuous with exponent α on D, that is, there exists a constant α ∈ (0, 1] such that the quantity
(1.1)
[f ]α,D := sup
x,y∈D
x6=y
|f (x) − f (y)|
|x − y|α
is bounded. We note that Hölder continuous functions are indeed continuous. Moreover, they
are Lipschitz continuous if α = 1; cf., e.g., [4].
Let us extend this concept to functions of matrices. To this end, consider
n×n
H
H
Mn×n
(C)
=
A
∈
C
:
A
A
=
AA
,
normal
the set of all normal matrices with complex entries. Here, for a matrix A = [aij ]ni,j=1 , we use
the notation AH = [aji ]ni,j=1 to denote the conjugate transpose of A. By the spectral theorem
I would like to thank Lutz Dümbgen for bringing the topic of this note to my attention and for suggestions leading to a more straightforward
presentation of the material.
276-09
2
T HOMAS P. W IHLER
n×n
normal matrices are unitarily diagonalizable, i.e., for each X ∈ Mnormal
(C) there exists a
H
H
unitary n × n-matrix U , U U = U U = 1 = diag (1, 1, . . . , 1), such that
U H XU = diag (λ1 , λ2 , . . . , λn ) ,
where the set σ(X) = {λi }ni=1 is the spectrum of X. For any function f : D → C,
with σ(X) ⊆ D, we can then define a corresponding matrix function “value” by
f (X) = U diag (f (λ1 ), f (λ2 ), . . . , f (λn )) U H ;
see, e.g., [5, 6]. Here, we use the bold face letter f to denote the matrix function corresponding
to the associated scalar function f .
We can now easily widen the definition (1.1) of Hölder continuity for a scalar function f :
D → C to its associated matrix function f applied to normal matrices: Given a subset D ⊆
n×n
is Hölder continuous with
Mn×n
normal (C), then we say that the matrix function f : D → C
exponent α ∈ (0, 1] on D if
[f ]α,D := sup
(1.2)
X,Y ∈D
X6=Y
kf (X) − f (Y )kF
kX − Y kαF
is bounded. Here, for a matrix X = [xij ]ni,j=1 ∈ Cn×n we define kXkF to be the Frobenius
norm of X given by
n
X
kXk2F = trace X H X =
|xij |2 ,
X = (xij )ni,j=1 ∈ Mn×n (C).
i,j=1
Evidently, for the definition (1.2) to make sense, it is necessary to assume that the scalar
function f associated with the matrix function f is well-defined on the spectra of all matrices X ∈ D, i.e.,
[
(1.3)
σ(X) ⊆ D.
X∈D
The goal of this note is to address the following question: Provided that a scalar function f
is Hölder continuous, what can be said about the Hölder continuity of the corresponding matrix
function f ? The following theorem provides the answer:
Theorem 1.1. Let the scalar function f : D → C be Hölder continuous with exponent α ∈
n×n
(0, 1], and D ⊆ Mn×n
normal (C) satisfy (1.3). Then, the associated matrix function f : D → C
is Hölder continuous with exponent α and
[f ]α,D ≤ n
(1.4)
1−α
2
[f ]α,D
holds true. In particular, the bound
(1.5)
kf (X) − f (Y )kF ≤ [f ]α,D n
1−α
2
kX − Y kαF ,
holds for any X, Y ∈ D.
2. P ROOF OF T HEOREM 1.1
We shall check the inequality (1.5). From this (1.4) follows immediately. Consider two
matrices X, Y ∈ D. Since they are normal we can find two unitary matrices V , W ∈ Mn×n (C)
which diagonalize X and Y , respectively, i.e.,
V H XV = DX = diag (λ1 , λ2 , . . . , λn ) ,
W H Y W = DY = diag (µ1 , µ2 , . . . , µn ) ,
J. Inequal. Pure and Appl. Math., 10(4) (2009), Art. 91, 5 pp.
http://jipam.vu.edu.au/
H ÖLDER C ONTINUITY OF M ATRIX F UNCTIONS
3
where {λi }ni=1 and {µi }ni=1 are the eigenvalues of X and Y , respectively. Now we need to use
the fact that the Frobenius norm is unitarily invariant. This means that for any matrix X ∈ Cn×n
and any two unitary matrices R, U ∈ Cn×n there holds
kRXU k2F = kXk2F .
Therefore, it follows that
(2.1)
2
kX − Y k2F = V DX V H − W DY W H F
2
= W H V DX V H V − W H W DY W H V F
2
= W H V DX − DY W H V F
n X
2
=
W H V DX − DY W H V i,j i,j=1
2
n X
n
X
=
W H V i,k (DX )k,j − (DY )i,k W H V k,j =
i,j=1 k=1
n X
2
2
H
W
V
|λj − µi | .
i,j
i,j=1
In the same way, noting that
f (X) = V f (DX )V H ,
f (Y ) = W f (DY )W H ,
we obtain
kf (X) − f (Y
n X
2
2
=
W H V i,j |f (λj ) − f (µi )| .
)k2F
i,j=1
Employing the Hölder continuity of f , i.e.,
|f (x) − f (y)| ≤ [f ]α,D |x − y|α ,
x, y ∈ D,
it follows that
(2.2)
kf (X) − f (Y
)k2F
≤
[f ]2α,D
n X
2
2α
H
W V i,j |λj − µi | .
i,j=1
For α = 1 the bound (1.5) results directly from (2.1) and (2.2). If 0 < α < 1, we apply Hölder’s
inequality. That is, for arbitrary numbers si , ti ∈ C, i = 1, 2, . . ., there holds
!α
!1−α
X
X
X
1
1
|ti | 1−α
.
|si ti | ≤
|si | α
i≥1
i≥1
i≥1
In the present situation this yields
2
kf (X) − f (Y )k ≤
[f ]2α,D
n X
2α 2−2α
H
H
|λj − µi | W V i,j W V i,j i,j=1
≤ [f ]2α,D
n X
2
2
H
W V i,j |λj − µi |
i,j=1
J. Inequal. Pure and Appl. Math., 10(4) (2009), Art. 91, 5 pp.
!α
n X
2
H
W V i,j !1−α
.
i,j=1
http://jipam.vu.edu.au/
4
T HOMAS P. W IHLER
Therefore, using the identity (2.1), there holds
kf (X) − f (Y )kF ≤ [f ]α,D kX − Y
kαF
n X
2
H
W V i,j ! 1−α
2
.
i,j=1
Then, recalling again that k·kF is unitarily invariant, yields
! 1−α
n 2 2
X
1−α
1−α
= W H V F = k1k1−α
=n 2 ,
W H V i,j F
i,j=1
This implies the estimate (1.5).
3. A PPLICATIONS
We shall look at a few examples which fit in the framework of the previous analysis. Here,
we consider the special case that all matrices are real and symmetric. In particular, they are
normal and have only real eigenvalues.
Let us first study some functions f : D → R, where D ⊆ R is an interval, which are
continuously differentiable with bounded derivative on D. Then, by the mean value theorem,
we have
f (x) − f (y) = sup |f 0 (ξ)| < ∞,
[f ]1,D = sup x − y ξ∈D
x,y∈D
x6=y
i.e., such functions are Lipschitz continuous.
Trigonometric Functions: Let m ∈ N. Then, the functions t 7→ sinm (t) and t 7→ cosm (t) are
Lipschitz continuous on R, with constant
√
m−1
d
d
√
m
−
1
m
m
m
m
√
Lm := [sin ]1,R = [cos ]1,R = sup sin (t) = sup cos (t) = m
.
m
t∈R dt
t∈R dt
Thence, we immediately obtain the bounds
m
m
√
m
m
√
ksin (X) − sin (Y )kF ≤
kcos (X) − cos (Y )kF ≤
√
m
√
m
m−1
√
m
m−1
m−1
√
m
m−1
kX − Y kF
kX − Y kF
for any real symmetric n × n-matrices X, Y . We note that
√
m−1
1
m−1
√
lim
= e− 2 ,
m→∞
m
√
and hence Lm ∼ m with m → ∞.
2
Gaussian Function: For fixed m > 0, the
√ Gaussian 1function f : t 7→ exp(−mt ) is Lipschitz
continuous on R with constant [f ]1,R = 2m exp(− 2 ). Consequently, we have for the matrix
exponential that
√
exp(−mX 2 ) − exp(−mY 2 ) ≤ 2me− 12 kX − Y k ,
F
F
for any real symmetric n × n-matrices X, Y .
We shall now consider some functions which are less smooth than in the previous examples.
In particular, they are not differentiable at 0.
J. Inequal. Pure and Appl. Math., 10(4) (2009), Art. 91, 5 pp.
http://jipam.vu.edu.au/
H ÖLDER C ONTINUITY OF M ATRIX F UNCTIONS
5
Absolute Value Function: Due to the triangle inequality
| |x| − |y| | ≤ |x − y|,
x, y ∈ R,
the absolute value function f : t 7→ |t| is Lipschitz continuous with constant [f ]1,R = 1, and
hence
k|X| − |Y |kF ≤ kX − Y kF ,
(3.1)
for any real symmetric
√ n × n-matrices X, Y . We note that, for general matrices, there is an
additional factor of 2 on the right hand side of (3.1), whereas for symmetric matrices the
factor 1 is optimal; see [1] and the references therein.
p-th Root of Positive Semi-Definite Matrices: Finally, let us consider the p-th root (p > 1) of a
real symmetric positive semi-definite matrix. The spectrum of such matrices belongs to the non1
negative real axes D = R+ = {x ∈ R : x ≥ 0}. Here, we notice that the function f : t 7→ t p
is Hölder continuous on D with exponent α = p1 and [f ] 1 ,D = 1. Hence, Theorem 1.1 applies.
p
In particular, the inequality
1
1 p
p−1
p
p
(3.2)
X − Y ≤ n 2 kX − Y kF
F
holds for any real symmetric positive-semidefinite n × n-matrices X, Y . We note that the
estimate (3.2) is sharp. Indeed, there holds equality if X is chosen to be the identity matrix,
and Y is the zero matrix.
We remark that an alternative proof of (3.2) has already been given in [2, Chapter X] in the
context of operator monotone functions. Furthermore, closely related results on the Lipschitz
continuity of matrix functions and the Hölder continuity of the p-th matrix root can be found in,
e.g., [2, Chapter VII] and [3], respectively.
R EFERENCES
[1] H. ARAKI AND S. YAMAGAMI, An inequality for Hilbert-Schmidt norm, Comm. Math. Phys.,
81(1) (1981), 89–96.
[2] R. BHATIA, Matrix Analysis, Volume 169 of Graduate Texts in Mathematics, Springer-Verlag New
York, 2007.
[3] Z. CHEN AND Z. HUAN, On the continuity of the mth root of a continuous nonnegative definite
matrix-valued function, J. Math. Anal. Appl., 209 (1997), 60–66.
[4] D. GILBARG AND N.S. TRUDINGER, Elliptic partial differential equations of second order, Classics in Mathematics, Springer-Verlag Berlin, 2001 (Reprint of the 1998 edition).
[5] G.H. GOLUB
edition, 1996.
AND
C.F. VAN LOAN, Matrix Computations, Johns Hopkins University Press, 3rd
[6] N.J. HIGHAM, Functions of Matrices, Society for Industrial Mathematics, 2008.
J. Inequal. Pure and Appl. Math., 10(4) (2009), Art. 91, 5 pp.
http://jipam.vu.edu.au/