1418-1, Capacitors
and Capacitive
Circuits
Experiment 6: Using Capacitors in
Voltage-Divider Networks
• To verify that capacitors can be used
in AC voltage-divider circuits without
the use of resistors.
Objective
• Capacitors can be used in an a-c voltage
divider application in a circuit in a
manner similar to a resistive voltagedivider network.
Note: Care must be taken when
capacitors are used in this way, since their
capacitive reactance is frequencysensitive and the design will be good only
within a narrow range of frequencies.
Introduction
Basic two component ckt
• Where frequency enters into a voltagedivider design, resistors and not
capacitors should be used.
• Remember, when capacitors are used in
voltage-divider circuits, they usually
require a constant frequency signal
source.
• Capacitors consume little power, so the
power drain will be small in a capacitive
voltage-divider network.
• A voltage-divider circuit is a typical
series circuit containing two or more
components. To simplify the experiment,
we will be using only two capacitors.
• The following slide will review the
general rules for a series circuit and we
will review some of the formulas needed
to analyze the circuit.
Basic theory review
1. The current is the same through all
parts/components of the circuit.
a) The current “I” equals the applied
voltage “E” divided by the total circuit
impedance “Z”.
2. The applied voltage must be equal to the
sum of all the voltage drops.
IT for Reactive Circuit
Formulas for E1 & E2 for
reactive circuits
Formula for E1 for Capacitive
Circuit
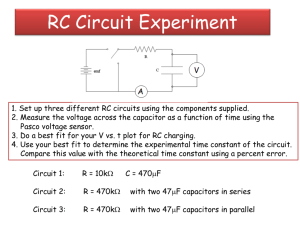
1. Calculate the voltages for the circuits
a) Record values in table in lesson
2. Build the following three circuits.
3. Measure the voltages you calculated
4. Calculate %error using formula given
for each circuit and record %error
Procedure
Circuit 1
Ckt 1 wiring example:
%error formula
Circuit 2
Ckt 2 wiring example:
%error formula
Circuit 3
Ckt 3 wiring example:
%error formula
• The data from the three voltage-divider
circuits verified the voltage-divider
principle when capacitors are used as the
only components in the circuit.
• In each case, the division of voltage was
predictable (with the values of the
capacitors known).
Final Discussion
• Remember to use the discussed formulas
when predicting the values of EC1 & EC2
and any other values in a multicomponent
divider circuit.
Questions?
Resources
• Rubenstein. (2001). Lesson 1418:
Capacitors and capacitive circuits.
Cleveland: Cleveland Institute of
Electronics.
The End
Developed and Produced by the
Instructors in the CIE Instruction
Department.
© Copyright 04/2012
All Rights Reserved / April 2012