UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENTS III & IV B.E. INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING
advertisement
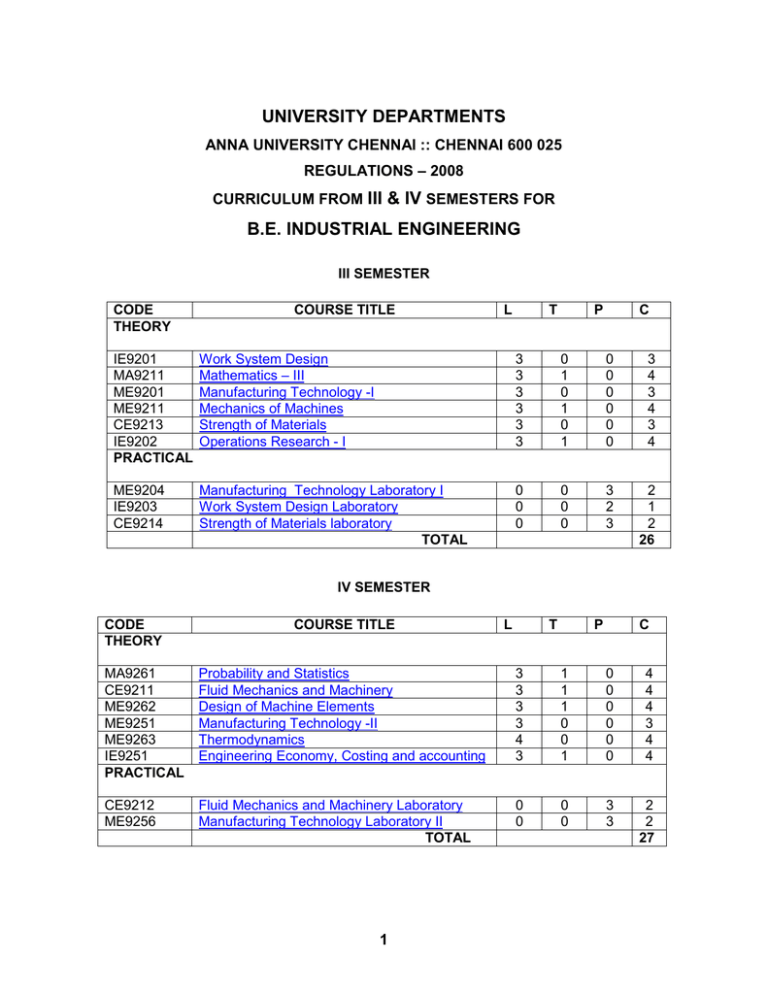
UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENTS ANNA UNIVERSITY CHENNAI :: CHENNAI 600 025 REGULATIONS – 2008 CURRICULUM FROM III & IV SEMESTERS FOR B.E. INDUSTRIAL ENGINEERING III SEMESTER CODE THEORY COURSE TITLE L T P C IE9201 MA9211 ME9201 ME9211 CE9213 IE9202 PRACTICAL Work System Design Mathematics – III Manufacturing Technology -I Mechanics of Machines Strength of Materials Operations Research - I 3 3 3 3 3 3 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 4 3 4 3 4 ME9204 IE9203 CE9214 Manufacturing Technology Laboratory I Work System Design Laboratory Strength of Materials laboratory TOTAL 0 0 0 0 0 0 3 2 3 2 1 2 26 IV SEMESTER CODE THEORY COURSE TITLE L T P C MA9261 CE9211 ME9262 ME9251 ME9263 IE9251 PRACTICAL Probability and Statistics Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Design of Machine Elements Manufacturing Technology -II Thermodynamics Engineering Economy, Costing and accounting 3 3 3 3 4 3 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 4 4 4 3 4 4 CE9212 ME9256 Fluid Mechanics and Machinery Laboratory Manufacturing Technology Laboratory II TOTAL 0 0 0 0 3 3 2 2 27 1 IE9201 WORK SYSTEM DESIGN LTPC 3 0 0 3 Objective To impart knowledge in the area of Method study and Time study so that students can implement these principles and techniques to improve productivity in manufacturing and Service sectors. 1. PRODUCTIVITY 9 Total time for a job or operation, total work content and ineffective time, – Production and Productivity - Productivity and standard of living, Factors affecting Productivity, Productivity measurement Models. 2. METHODS ENGINEERING 9 Methods Engineering-Steps -Tools and techniques, Motion study. 3. WORK MEASUREMENT 9 Stop watch time study, performance rating, allowances, Development of Standard data, learning effect. Work measurement in Automated Processes. Computerised Labour standards. 4. APPLIED WORK MEASUREMENT 9 Work sampling, Group Timing Technique (GTT), predetermined time systems, types, Methods Time Measurement (MTM), Wage incentive plans. 5. WORK DESIGN FOR OFFICE WORK 9 Organization and methods (O & M), Work measurement of office work, Work Analysis techniques applied to support staff, Form design and control. TOTAL: 45 TEXT BOOK Barnes, R.M. Motion and Time Study, Design and measurement of work, John Wiley sons(Asia), Seventh edition,2002. REFERENCE BOOKS 1. 2. 3. Benjamin W.Niebel, Andris Freivalds, Methods, standards & Work Design, McGraw hill, Eleventh edition, 2002. ILO, Introduction to Work Study, Oxford and IBH publishing , 2001 Maynard H.B, Industrial Engineering Hand book,McGraw-Hill,2001 2 MA9211 MATHEMATICS III LTPC 3 1 0 4 1. FOURIER SERIES 9+3 Dirichlet’s conditions – General Fourier series – Odd and even functions – Half-range Sine and Cosine series – Complex form of Fourier Series – Parseval’s identity – Harmonic Analysis. 2. PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 9+3 Formation – Solutions of first order equations – Sandard types and Equations reducible to standard types – Singular solutions - Lagrange’s Linear equation – Integral surface passing through a given curve – Solution of linear equations of higher order with constant coefficients. 3. APPLICATIONS OF PARTIAL DIFFERENTIAL EQUATIONS 9+3 Method of separation of Variables – Solutions of one dimensional wave equation, -Onedimensional heat equation – Steady state solution of two-dimensional heat equation – Fourier series solutions in Cartesian coordinates. 4. FOURIER TRANSFORM 9+3 Fourier integral theorem – Fourier transform pair-Sine and Consine transforms – Properties – Transform of simple function – Convolution theorem - Parseval’s identity. 5. Z – TRANSFORM AND DIFFERENCE EQUATION 9+3 Z-transform-Elementary properties-Inverse z transform – Convolution theoremFormation of difference equation-Solution of difference equation using z transform. Total: 45+15=60 TEXT BOOK 1) B.S.Grewal, “Higher Engineering Mathematics”, Khanna Publications (2007) REFERENCES 1) Glyn James, “Advanced Modern Engineering Mathematics, Pearson Education (2007) 2) B.V.Ramana, “Higher Engineering Mathematics” Tata McGraw Hill 2007. 3) N.P.Bali, and Manish Goyal, “A Text Book of Engineering 7th Edition (2007) Lakshmi Publications (P) Limited, New Delhi. 3 LTPC ME9201 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY – I 3 0 0 3 OBJECTIVE This course aims to impart the knowledge about various manufacturing processes. It deals with metal casting, metal forming and metal joining processes. After this course, a student will have a good exposure about the manufacturing processes and various operations and machinery. This also gives the recent trends in these processes also. 1. FOUNDRY TECHNOLOGY 11 Pattern and core making – moulding sand and testing - green sand moulding – melting furnaces: cupola and induction furnaces – special casting processes – shell, investment, die casting, centrifugal castings principles of gating system design - fettling and finishing of castings – defects in casting. 2. HOT AND COLD WORKING 7 Hot and cold working process, rolling – introduction – rolling mills – rolling operations – production of seamless tube. 3. FORGING 9 Introduction – forging operations – drop forging – warm forging – extrusion and drawing: extrusion practice – hot, cold, impact and hydrostatic extrusion. drawing process: defects and residual stresses, drawing equipment, stretch forming, deep forming, spinning processes and sheet metal forming. 4. ADVANCES IN FORMING PROCESS 9 High energy rate forming process; explosive forming, electro- hydraulic, electro magnetic forming, dynapack machine, advances in super forging. plastic materials and processes: types of plastics – types of moulding – compression moulding - transfer moulding – injection moulding. 5. PRINCIPLES AND APPLICATIONS OF JOININGPROCESSES 9 Gas welding, basic arc welding processes: thermit welding, electron beam welding, laser beam welding, and solid state welding: cold welding, ultrasonic welding, friction welding, resistance welding and explosive welding and welding defects. principles and applications of brazing and soldering – recent development in joining processes. Total : 45 TEXT BOOK 1. Kalpakjian, S., “Manufacturing Engineering and Technology”, Pearson Education India Edition, 2006 REFERENCES 1. Roy. A. Lindberg, Processes and Materials of Manufacture, PHI / Pearson Education, 2006 2. Hajra Choudhury S.K and Hajra Choudhury. A.K., Elements of Workshop Technology, Volume I and II, Media Promoters and Publishers Private Limited, Mumbai, 1997. 3. Paul Degarma E, Black J.T. and Ronald A. Kosher, Elighth Edition, Materials and Processes, in Manufacturing Prentice – Hall of India, 1997. 4. Sharma, P.C., A Text book of Production Technology, S. Chand and Co. Ltd.,2004. 5. P.N. Rao, Manufacturing Technology Foundry, Forming and Welding, TMH2003; 2nd Edition 4 6. S. Gowri, P. Hariharan, A. Suresh Babu, Manufacturing Technology I, Pearson Education, 2008 5 ME9211 MECHANICS OF MACHINES LTPC 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVES: 1. To understand the principles in the formation of mechanisms and their kinematics. 2. To understand the effect of friction in different machine elements. 3. To analyse the forces and toques acting on simple mechanical systems 4. To understand the importance of balancing and vibration. 1. KINEMATIC OF MECHANICS 10 Mechanisms – Terminology and definitions – kinematics inversions of 4 bar and slide crank chain – kinematics analysis in simple mechanisms – velocity and acceleration polygons – Analytical methods – computer approach – cams – classifications – displacement diagrams - layout of plate cam profiles – derivatives of followers motion – circular arc and tangent cams. 2. GEARS and GEAR TRAINS 9 Spur gear – law of toothed gearing – involute gearing – Interchangeable gears – Gear tooth action interference and undercutting – nonstandard teeth – gear trains – parallel axis gears trains – epicyclic gear trains – automotive transmission gear trains. 3. FRICTION 8 Sliding and Rolling Friction angle – friction in threads – Friction Drives – Friction clutches – Belt and rope drives – brakes – Tractive resistance. 4. FORCE ANALYSIS 9 Applied and Constrained Forces – Free body diagrams – static Equilibrium conditions – Two, Three and four members – Static Force analysis in simple machine members – Dynamic Force Analysis – Inertia Forces and Inertia Torque – D’Alembert’s principle – superposition principle – dynamic Force Analysis in simple machine members. 5. BALANCING AND VIBRATION 9 Static and Dynamic balancing – Balancing of revolving and reciprocating masses – Balancing machines – free vibrations – Equations of motion – natural Frequency – Damped Vibration – bending critical speed of simple shaft – Torsional vibration – Forced vibration – harmonic Forcing – Vibration solation. TEXT BOOK 1. Ambekar A.G., “Mechanism and Machine Theory” Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2007 2. Shigley J.E., Pennock G.R and Uicker J.J., “Theory of Machines and Mechanisms”, Oxford University Press, 2003 6 REFERENCES 1. Thomas Bevan, “Theory of Machines”, CBS Publishers and Distributors, 1984. 2. Ghosh.A, and A.K.Mallick, “Theory and Machine”, Affiliated East-West Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi, 1988. 3. Rao.J.S. and Dukkipatti R.V. “Mechanisms and Machines”, Wiley-Eastern Ltd., New Delhi, 1992. 4. John Hannah and Stephens R.C., “Mechanics of Machines”, Viva Low Prices Student Edition, 1999. 5. V.Ramamurthi, Mechanisms of Machine, Narosa Publishing House, 2002. 6. Robert L.Norton, Design of Machinery, McGraw-Hill, 2004. STANDARDS IS 2458:2001, Vocabulary of Gear Terms – Definitions related to Geometry. IS 3756 : 2002, Method of Gear Correction – Addendum modification for External cylindrical gears with parallel axes. IS 5267 : 2002 Vocabulary of Gear Terms – Definitions Related to Worm Gear Geometry. IS 12328 : Part 1 : 1988 Bevel Gear Systems Part -1 Straight Bevel Gears. IS12328 : 1988 Bevel Systems Part – 2 Spiral Bevel Gears. 7 CE9213 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS (Mechanical, Manufacturing, Industrial, Mining, Printing, Material Science & Engineering) LTPC 3 0 03 Objective : To study the behaviour of deformable bodies due to external loads, bending of beams and effect of torsion on circular bars. 1. STRESS, STRAIN AND DEFORMATION OF SOLIDS 10 Rigid and deformable bodies –- Axial and Shear Stresses – Deformation of simple and compound bars – Thermal stresses – Elastic Constants - Volumetric strains- Stresses and deformation of thin cylinders and thin shells – Stresses on inclined planes – Principal stresses and principal planes – Mohr’s circle of stress. 2. BENDING OF BEAMS 12 Beams – types and transverse loading on beams – shear force and bending moment in beams – Cantilever beams – Simply supported beams and over-hanging beams Theory of simple bending – bending stress distribution – Load carrying capacity – Proportioning of sections – Leaf springs – Flitched beams – Shear stress distribution. 3. DEFLECTION OF BEAMS 7 Double Integration method – Macaulay’s method – Area moment method – Conjugate beam method for computation of slopes and deflections in determinate beams. 4. ENERGY PRINCIPLES 9 Strain energy and strain energy density – Strain energy in axial force , shear, flexure and torsion – Castigliano’s and Engessor’s theorems – Principle of virtual work – Application of energy theorems for computing deflections in beams – Maxwell’s reciprocal theorem. 5. TORSION 7 Theory of simple torsion - Stresses and deformation in circular and hollow shafts – Stepped shafts – Shafts fixed at both ends – Stresses and deflection in helical springs. Total L = 45 TEXT BOOKS: 1. Egor. P.Popov “ Engineering Mechanics of Solids” Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi 2001 2. Bedi, D.S., “Strength of Materials”, Khanna Book Publishing Co. (P) Ltd. Delhi 2000 3. Rajput.R K - Strength Of Materials - S.Chand & Co, New Delhi, 1996 REFERENCE : 1. Irwing H.Shames, James M.Pitarresi, “Introduction to Solid Mechanics, Prentice Hall of India, New Delhi, 2002 2. Roger T.Fenner, “ Mechanics of Solids”, ELBS, Oseny Mead, Oxford, 1990 3. Malhotra, D.R. Gupta, H.C., “The Strength of Materials”, Satya Prakashan (Tech. India Publications), New Delhi, 1995 4. Punmia, B.C, Ashok Kumar Jain,, Arun kumar Jain “ Strength of Materials and Theory of Structures” Vol.II, Lakshmi publications, New Delhi, 1998 8 IE9202 OPERATIONS RESEARCH – I L 3 T 1 P 0 C 4 OBJECTIVE To learn the basics of deterministic optimization tools LINEAR PROGRAMMING 10 Introduction - formulation of linear programming model - Graphical solution – solving LPP using simplex algorithm – Revised Simplex Method ADVANCES IN LPP –I 10 Duality theory - Dual simplex method - Sensitivity analysis –- Transportation problems – Assignment problems- Traveling sales man problem -Data Envelopment Analysis ADVANCES IN LPP –II Integer programming – Multi objective optimization - Goal programming 6 NETWORK MODELS 12 Maximal flow problems – Shortest route problem – Minimal spanning tree -. Project network -CPM – PERT – Crashing – project costing and control. DYNAMIC PROGRAMMING 7 Elements of dynamic programming – state –stage-recursive equations – computational procedure – applications Lecture ; 45 hours Tutorial ; 15 hours Total : 60 hours TEXT BOOKS 1. Hillier and Lieberman Introduction to Operations Research, TMH, 2000 2. R.Panneerselvam, Operations Research,PHI,2006 REFERENCES 1. Philips, Ravindran and Solberg, Operations Research, John Wiley,2002 2. Hamdy A Taha, Operations Research – An Introduction, Prentice Hall India,2003 3. Ronald L Rardin, Optimisation in Operations Research, Pearson, 2003 4. David R. Anderson, et al , An Introduction to Management Science – Quantitative approaches to Decision Making, Thomson,2003 9 ME9204 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB-1 L T P C 0 0 3 2 OBJECTIVE Student should have knowledge on common basic machining operations LIST OF EXPERIMENTS Measurement of the Machined Components and Machining time estimation of: 1. Taper Turning 2. External thread cutting 3. Internal thread cutting 4. Eccentric Turning 5. Knurling 6. Square Head Shaping 7. Hexagonal Head Shaping 8. Drilling and Tapping 9. Determination of Cutting forces in Turning and Milling Operations. 10 IE9203 WORK SYSTEM DESIGN LAB LT PC 0 0 2 1 Objective: To understand the theory better and apply in practice, practical training is given in the following areas: 1. Graphic tools for method study 2. Peg board experiment 3. Stop watch time study 4. Performance rating exercise 5. Work sampling 6. MTM practice TOTAL = 20 11 CE9214 STRENGTH OF MATERIALS LABORATORY (Mechanical, Manufacturing, Industrial, Mining, Printing, Material Science & Engineering) LT PC 0 0 3 2 Objective : To study the properties of materials when subjected to different types of loading. 1. Tension test on mild steel / tor steel rod 2. Double shear test on metal 3. Torsion test on mild steel rod 4. Impact test on metal specimen 5. Hardness test on metals 6. Compression test on helical spring 7. Deflection test on carriage spring Reference Relevant Indian Standard Codes 12 MA9261 PROBABILITY AND STATISTICS L P T C 3 0 1 4 9+3 1. RANDOM VARIABLES Discrete and Continuous random variables – Moments – Moment generating functions – Binomial, Poisson, Geometric, Uniform, Exponential, Gamma and Normal distributions Functions of random variable. 2. TWO-DIMENSIONAL RANDOM VARIABLES 9+3 Joint distributions – Marginal and Conditional distributions – Covariance – Correlation and Linear regression – Transformation of random variables-Linberg Levy central limit theorem 3. TESTING OF HYPOTHESIS 9+3 Tests for single mean – Proportion – Difference of means – Tests for single variance and equality of variances – χ2-test for goodness of fit – Independence of attributes. 4. DESIGN OF EXPERIMENTS 9+3 Completely randomized design – Randomized block design – Latin square design - 22 factorial design. 5. STATISTICAL QUALITY CONTROL 9+3 Control charts for measurements ( ¯X¯ and R charts) – Control charts for attributes ( p, c and np charts) – Tolerance limits - Acceptance sampling. L: 45, T: 15, Total : 60 BOOKS FOR STUDY: 1. R.E. Walpole, R.H. Myers, S.L. Myers, and K Ye, “Probability and Statistics for Engineers and Scientists”, Pearson Education, Asia , 8th edition, 2007. 2. R.A. Johnson, C.B. Gupta, “Miller and Freund’s Probability and Statistics for Engineers”, Pearson Education, Asia, 7th edition, 2006, / R.A. Johnson, “Miller and Freund’s Probability and Statistics for Engineers’, Prentice Hall of India, 7th edition, 2007. BOOKS FOR REFERENCE: 1. J.L. Devore, “Probability and Statistics for Engineering and the Sciences”, Thomson Brooks/Cole, International Student Edition, 7th edition, 2008. 2. J. S. Milton, J.C. Arnold, “ Introduction to Probability and Statistics”, Tata McGraw Hill, 4th edition, 2007. 3. S.M. Ross, “Introduction to Probability and Statistics for Engineers and Scientists, 3rd edition, Academic Press, (An imprint of Elsevier), 2004 13 CE9211 FLUID MECHANICS AND MACHINERY 3104 OBJECTIVES: a. The student is introduced to the mechanics of fluids through a thorough understanding of the properties of the fluids. The dynamics of fluids is introduced through the control volume approach which gives an integrated under standing of the transport of mass, momentum and energy. b. The applications of the conservation laws to flow though pipes and hydraulics machines are studied I. INTRODUCTION 12 Units & Dimensions. Properties of fluids – Specific gravity, specific weight, viscosity, compressibility, vapour pressure and gas laws – capillarity and surface tension. Flow characteristics: concepts of system and control volume. Application of control volume to continuity equiation, energy equation, momentum equation and moment of momentum equation. II. FLOW THROUG CIRCULAR CONDUITS 12 Laminar flow though circular conduits and circular annuli. Boundary layer concepts. Boundary layer thickness. Hydraulic and energy gradient. Darcy – Weisbach equaition. Friction factor and Moody diagram. Commercial pipes. Minor losses. Flow though pipes in series and in parallel. III. DIMENSIONAL ANALYSIS 9 Dimension and units: Buckingham’s П theorem. Discussion on dimensionless parameters. Models and similitude. Applications of dimensionless parameters. IV. ROTO DYNAMIC MACHINES 16 Homologus units. Specific speed. Elementary cascade theory. Theory of turbo machines. Euler’s equation. Hydraulic efficiency. Velocity components at the entry and exit of the rotor. Velocity triangle for single stage radial flow and axial flow machines. Centrifugal pumps, turbines, performance curves for pumps and turbines. V. POSITIVE DISPLACEMENT MACHINES 11 Recriprocating pumps, Indicator diagrams, Work saved by air vessels. Rotory pumps. Classification. Working and performance curves. TOTAL : 60 TEXT BOOKS: 1. Streeter. V. L., and Wylie, E.B., Fluid Mechanics, McGraw Hill, 1983. 2. Rathakrishnan. E, Fluid Mechanics, Prentice Hall of India (II Ed.), 2007. REFERENCES: 1. Ramamritham. S, Fluid Mechanics, Hydraulics and Fluid Machines, Dhanpat Rai & Sons, Delhi, 1988. 2. Kumar. K.L., Engineering Fluid Mechanics (VII Ed.) Eurasia Publishing House (P) Ltd., New Delhi, 1995. 3. Bansal, R.K., Fluid Mechanics and Hydraulics Machines, Laxmi Publications (P) Ltd., New Delhi. 14 ME9262 DESIGN OF MACHINE ELEMENTS LTPC 3 003 OBJECTIVE i) To understand the various steps involved in the Design Process. ii) To understand the principles involved in evaluating the shape and dimensions of a component to satisfy functional and strength requirements. iii) To learn to use standard practices and standard data iv) To learn to use catalogues and standard machine components. 1. FUNDAMENTALS OF DESIGN FOR STRENGTH AND STIFFNESS OF MACHINE 15 MEMBERS Introduction to the design process – factors influencing machine design, selection of materials based on mechanical properties – Direct, Bending and torsional stress equations – Impact and shock loading – calculation of principle stresses for various load combinations, eccentric loading _ Design of curved beams – crane hook and `C’ frame – Factor of safety – theories of failure – stress concentration – design for variable loading – Soderberg, Goodman and Gerber relations – Standard preferred numbers. 2. DESIGN OF SHAFTS AND COUPLINGS 12 Design of solid and hollow shafts based on strength, rigidity and critical speed – Design of keys and keys ways – Design of rigid and flexible couplings – Introduction to gear and shock absorbing couplings 3. DESIGN OF FASTENERS AND WELDED JOINTS 12 Threaded fasteners – Design of bolted joints including eccentric loading – Design of welded joints for pressure vessels and structures- Design of Knuckle joints and cotter joints. 9 4. DESIGN OF SPRINGS Design of helical, leaf, disc , torsional, and spiral springs under constant loads and varying load – Concentric springs – Optimum design of Helical Springs- Surge in springs-Belleville springs. 12 5. DESIGN OF ENGINE PARTS BEARINGS AND FLYWHEELS Design of bearings – sliding contact and rolling contact types – Cubic mean load – Design of journal bearings – Mckees equation – Lubrication in journal bearings – calculation of bearing dimensions – Design of flywheels involving stresses in rim and arms – Design of Crank Shaft, Connecting rod. Total 60 Note: (Use of Approved Design Data Book is permitted in the University examination) Design Data Books: 1) PSG Design Data Book ( OR ) 2) Machine Design Data Hand Book, Vol.1 & Vol.2, by Dr. K. Lingaiah. 15 TEXT BOOKS 1. Juvinal R.C. Manshek K.M., Fundamentals of Machine Component Design – John Wiley & Sons Third Edition 2002. 2. Bhandari, V.B., “Design of Machine Elements”, Tata McGraw Hill Book Company Ltd., 2007.. REFERENCE 1. Norton R.L., “Design of Machinery”, Tata McGraw Hill Book Co., 2004. 2. OrthweinW. Machine Component Design, Jaico Publishing Co., 2003 3. UguralA.C. “Machine Design – An Integral Approach, McGraw Hill Book Co., 2004. 4. Spotts M.F.,Shoup T.E. “Design and Machine Elements” Pearson Education, 2004. STANDARDS 1. IS 10260: Part 1: 1982 Terms, definitions and classification of Plain bearings Part 1: Construction. 2. IS 10260: Part 1: 1982 Terms, definitions and classification of Plain bearings Part 2: Friction and Wear. 3. IS 10260: Part 1: Terms, definitions and classification of Plain bearings 16 ME9251 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY – II L T P C 3 0 0 3 OBJECTIVE To understand the concept and basic mechanics of metal cutting, working of standard machine tools such as lathe, shaping and allied machines, milling, drilling and allied machines, grinding and allied machines and broaching. To understand the basic concepts of (CNC) Computer Numerical Control of Machine tools and CNC Programming. 1. THEORY OF METAL CUTTING 8 Mechanics of chip formation, single point cutting tool, forces in machining, thermal aspects of chip formation. orthogonal metal cutting, cutting tool materials, tool wear, tool life, surface finish, cutting fluids and Machinability. 2. CENTRE LATHE AND SPECIAL PURPOSE LATHES 10 Centre lathe, constructional features, specification, cutting tools, nomenclature various operations – taper turning methods, thread cutting methods, special attachments, machining time and power estimation. capstan and turret lathes – tool layout, - automatic lathes: semi automatics – single spindle: swiss type, automatic screw type- multi spindle: 3. RECIPROCATING MACHINES, MILLING MACHINES AND GEAR CUTTING 12 Reciprocating machine tools: shaper, planer, slotter: milling: types, milling cutter attachments, change gear calculations, machining time calculation, operations. hole making: drilling, reaming, boring, tapping, machining time calculations. gear cutting: forming, generations, shaping, planning and hobbing-tool and cutter grinders. 4. ABRASIVE PROCESS, BROACHING 8 Abrasive processes: grinding wheel – specifications and selection, types of grinding process – cylindrical grinding , surface grinding, centreless grinding, internal grindinghoning, lapping, super finishing, polishing and buffing, abrasive jet grindling.broaching machines: broach construction – push, pull, surface and continuous broaching machines. 5. CNC MACHINE TOOLS AND PART PROGRAMMING 7 Numerical control (NC) machine tools – CNC types, constructional details, special features. machining centre, training centre.part programming fundamentals – manual programming. Total : 45 TEXT BOOKS 1. Roy. A. Lindberg, “Process and Materials of Manufacture”, PHI / Pearson Education Fourth Edition 2006. 2. Rao. P.N “ Manufacturing Technology”, Metal Cutting and Machine Tools, Tata Mc Graw–Hill, New Delhi, 2003. REFERENCES 1. Richerd R Kibbe, John E. Neely, Roland O. Merges and Warren J. White. “Machine Tool Practices”, Prentice Hall of India, 1998 2. HMT – Production Technology, Tata Mc Graw Hill, 1998. 3. Hajra Choudhury. Elements of Workshop Technology – Vol.II. Media Promoters. 4. Geofrey Boothroyd, Fundamentals of Metal Machining and Machine Tools, Mc Graw Hill, 1984. 17 ME9263 THERMODYNAMICS L 3 T 0 P C 0 3 1. BASIC CONCEPTS OF THERMODYNAMICS Thermodynamics and Energy – Systems – Types and properties - State and Equilibrium - Processes and Cycles – Forms of Energy – Temperature and Zeroth law of Thermodynamics – Pure substances – Phase change processes of pure substances – Property diagrams – Internal energy – Enthalpy – Energy transfer by Heat, Work and Mass – Applications. 2. FIRST AND SECOND LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS First law of thermodynamics – Energy balance for closed systems and steady flow systems – Applications of First law of Thermodynamics – Energy balance Unsteady flow processes – Second law of Thermodynamics – Entropy – Carnot principles – Change in Entropy – Entropy and irreversibility – Third law of Thermodynamics - Applications. 3. HEAT ENGINES Internal Combustion Engines – C.I and S.I Engines – Four Stroke and Two Stroke Engines – Gas Turbines. Boilers – Fire Tube Boiler & Water Tube Boilers – Boiler Accessories and Components. Turbines – Impulse Turbine and Reaction Turbine – Turbine Components. Refrigeration Cycle – Vapour Compression & Vapour Absorption System – Gas Refrigeration System – Environmental friendly Refrigerants – Air Conditioning. 4. GASES AND VAPOUR MIXTURES Ideal and Real gases – Vander waals equations – Reduced property – Compressibility chart -Properties of mixture of gases – Dalton’s law and Gibbs – Dalton law – Internal energy, Enthalpy and specific heats of gas mixtures. 5. HEAT RANSFER Conduction – Plane Wall, Cylinder system, Composite Walls – Critical insulation thickness – Simple, fins convection – Free convection and forced convection – Flow over Flat plates and Flow through Pipes – Radiation – Black Body, Grey Body Radiation. TEXT BOOKS 1. “Thermodynamics an Engineering Approach” Yunus A. Cenegal and Michael A.Boles, Tata McGraw hill, Fourth edition. REFERENCE BOOKS 1. “A Text book of engineering Thermodynamics” R.K.Rajput ,Laxmi puplication(P) Ltd. ,third Edition 2. “Engineering Thermodynamics” P.K.Nag, Tata McGraw hill, Third edition 3.“A course in Thermal engineering” S.Domkundwar, C.P.Kothandaraman , Dhanpat rai & co (p) Ltd, fifth edition. 18 IE9251 ENGINEERING ECONOMY, COSTING AND ACCOUNTING L T P C 3 1 0 4 OBJECTIVE: (i) To impart knowledge in the areas of cost estimation, pricing of products, cost control methods and principles of accounting. (ii) After undergoing the course, the students will be able to estimate cost of products, analyze product cost and suggest cost reduction measure. 1. INTRODUCTION: 6 Objectives of Managerial Economics, Firm, Cost Estimation, Costing, Cost Accounting, Factors Influencing Managerial Decisions & Theoretical Concepts, Classification and Elements of cost. 2. PRODUCTION ANALYSIS AND PRICING: 9 Production Function-Least Cost Combination of Inputs-Factor Productivities & Return to Scale-Determinants of Price-Pricing under different objectives and Market StructuresPrice Discrimination & Pricing methods in practice. 3. ESTIMATION 10 Estimation of Material, Labor and Overhead Cost, Allocation of Overheads. Estimation for different types of jobs. 4. COSTING 10 Job Costing-Operating Costing-Process Costing- Standard Costing (Variance Analysis) 5. ACCOUNTING 10 Balance Sheet-Profit & Loss Statement-Evaluation of Investment decisions- Average Rate of Return-Payback Period-Net Present Value & IRR. L: 45 T: 15 Total: 45 TEXT BOOKS: 1. Jawaharlal, Cost Accounting, TMH, 1996 2. A. Ramachandran Aryasry & VV.Ramana Murthy, Engg Economics & Financial Accounting, TMH, NewDelhi, 2004. REFERENCE: 1. James.C.Van Home, “Fundamentals of fincancial Management”, PHI, NewDelhi, 2004. 2. V.L.Mote, Samuel Paul & G.S.Gupta, Managerial Economics-Concepts & Cases, TMH, Co, NewDelhi, 1989 3. T.P.Banga & S.C.Sharma, Mechancial Estimating and Costing, Khanna Publishers, 1984. 19 CE9212 FLUIDS MECHANICS AND MACHINERY LABORATORY L T P C 0 0 3 2 1. FLOW MEASUREMENT Calibration of Flow Measuring instruments – venturimeter, orificemeter, rotometer, Calibration of flows in open channels – weirs and notches. Estimation of friction factor in flow through pipes. 2. PUMPS Determination of performance characteristics of pumps – centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps, turbine pumps and positive displacement pumps – reciprocating and gear pumps. 3. TURBINES Determination of performance characteristics of turbines – reaction turbines and impulse turbines. Total : 45 REFERENCE 1. CWR, Hydraulics Laboratory Manual,2004 20 ME9256 MANUFACTURING TECHNOLOGY LAB - II L T P C 0 0 3 2 OBJECTIVE Student should acquire skills on common basic machining operations and press working. LIST OF EXPERIMENTS 1. Contour Milling using vertical milling machine 2. Gear Cutting & Gear Hobbing 3. Hexagonal Machining using Horizontal Milling Machine 4. Gear Cutting – Gear Shaping 5. Spline Broaching 6. Exercise in Surface Grinding 7. Exercise in Cylindrical Grinding 8. Exercise in Tool and Cutter Grinder 9. Spur and helical gear cutting in Milling Machine 10. Determination of cutting forces in Milling Machine 11. Study of Turret and Capstan lathe 12. Forming of Simple Components in Press Working and simple Calculations of sheet metal work 21