MASTER OF ARTS IN ECONOMICS Degree Requirements
advertisement

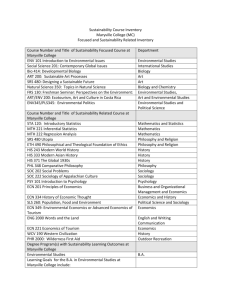
MASTER OF ARTS IN ECONOMICS Chairperson: Dr. Victoria Mantzopoulos Office: Briggs 243, McNichols Campus Telephone: (313) 993-1056 Fax: (313) 993-1166 E-Mail: armstrov@udmercy.edu Website: http://liberalarts.udmercy.edu/programs/depts/econ/econ_p rograms/grad/index.htm A master of Arts degree in Economics offers a student a flexible program satisfying a wide range of needs, and produces graduates capable of applied research and progression to doctoral programs. Students have the ability to learn and apply economics and financial principles to the U.S. and international market and financial systems. Grounded in a liberal arts foundation, the degree program also provides the student with a deeper knowledge of history, institutions and forces at work in the world economy. The flexibility of the program allows the student to pursue or blend an applied concentration which provides for a more academically oriented program, or a theoretical concentration providing a more practical orientation. The Master of Arts degree in Economics program prepares the student for career advancement in the private sector (nonprofit institutions, school systems, industry and financial institutions) as well as in diverse levels of government. With the progression of the globalization process, the demand for more advanced knowledge and abilities in the field of economics correspondingly increases. The Master of Arts degree in Economics will enable the student to achieve a higher level of sophistication that the business world is demanding. The degree helps to prepare the student for managerial advancement in the rapidly emerging international sector of the economy. Admission Requirements In order to be admitted to the Master of Arts degree in Economics, an applicant must meet entrance requirements of UDM. The applicant must also have a baccalaureate or advanced degree from a regionally accredited college or university with a cumulative GPA of 3.0 or better. In certain cases, additional prerequisites may be required. Degree Requirements To obtain a Master of Arts degree in Economics, a degree candidate must successfully complete a minimum of 30 credit hours of required graduate-level Economics courses. (A student completing a B.A. in Economics or Financial Economics from UDM may not repeat an equivalent graduate course without the consent of the advisor or chairperson.) Core Courses ECN 5100 -Economic Analysis of Enterprise ECN 5120 - Analysis of Economic Conditions ECN 5150 - Quantitative Foundations ECN 5400 - Financial Economics ECN 5650 - Theory of International Trade Elective Courses (Must choose 5) ECN 5200 - Economic Policy ECN 5210 - Labor Economics ECN 5220 - Urban Economics and Planning ECN 5300 - Economic Ideas in Perspective ECN 5350 - Contemporary Economic Systems ECN 5450 - Economics of the Public Sector ECN 5460 - Money and Capital Markets ECN 5480 - Business Forecasting ECN 5640 - Practical Issues in Financial Economics ECN 5660 - International Monetary Analysis ECN 5700 - Economic Development ECN 5750 - Resource Economics ECN 5800 - Introduction to Econometrics ECN 5810 - Advanced Money and Capital Markets ECN 5850 - Seminar in Monetary and Fiscal Policy ECN 5950 - Individual Readings and Research ECN 5990 - Master's Thesis For further information, please contact: Dr. Victoria Mantzopoulos, Chair of Economics Email: armstrov@udmercy.edu Phone: (313) 993-1056 Theresa Carson, Graduate Admissions Counselor Email: carsonta@udmercy.edu Phone: (313) 993-3309 International Student Admission Office of Admissions Email: admissions@udmercy.edu Phone: 800-635-5020 University of Detroit Mercy 4001 W. McNichols Rd. Detroit, MI 48221 Economics 2 Overall Course Descriptions ECN 5100 Economic Analysis of Enterprises Cr. 3 Microeconomics concerns itself with analyzing rational decision-making processes by consumers, producers, competitive firms, monopolistic competitors, oligopolists and monopolistic enterprises. Decision-making processes aim at value-maximization by consumers, factor efficiency and costminimization by producers, and profit maximization by sellers. In addition to studying production, distribution and consumer decision, Microeconomics also analyzes rational behavior of factor suppliers whether they be providers of labor, raw materials, parts or services for utility maximization by suppliers and value-product optimization by factor employers. Diverse aspects of buying and selling are then integrated into a general equilibrium model for social optimality. ECN 5120 Analysis of Economic Conditions Cr. 3 The primary function of this course is to delve into economic analysis to describe, explain and predict aggregate measures of economic activities such as product, employment/unemployment, inflation, international trade and the balance of payments. The course constructs macroeconomic models of the economy, based on theory, to explain economic events. The models are then used to apply to and evaluate policy alternatives and actions of governments in their attempt to influence economic outcomes such as keeping inflation in check while achieving fuller employment while trading successfully with economies abroad. ECN 5150 Quantitative Foundations of Economic Analysis Cr. 3 Sets, the axioms of algebra, equations, functions and series. Compound interest. The fundamentals of differential and integral calculus. The elements of linear algebra and linear programming. The structure and reduction of mathematical models in economics. ECN 5200 Economic Policy Cr. 3 An analysis of current economic and social problems, such as the role of government in a market-oriented society, externalities, market structure, regulation, anti-trust, and globalization of business. ECN 5210 Labor Economics Cr. 3 Examines the following topics: determinants of the demand for and supply of labor; the changing labor force; timeallocation models; wage structure; occupational, industrial and geographical wage differentials; the wage-price unemployment problem; the impact of unionism; the implications of wageprice policies; structural unemployment; the problems of maintaining full employment. ECN 5220 Urban Economics and Planning Cr. 3 Application of economic analysis to urban goals, problems and interactions. Course topics include: growth, income levels, income distribution and stability in urban economy; employment, poverty, and local finance; transportation, housing, and land use; interactions and opportunity cost of goals; problems and solution in terms of labor markets; the price system; multipliers, and industrial and occupational mix; interrelationships of physical planning and financial and socioeconomic constraints; patterns of governmental support for urban renewal and development. ECN 5300 Economic Ideas in Perspective Cr. 3 A critical overview of some of the most influential thinkers in the history of economic doctrine. ECN 5350 Contemporary Economic Systems Cr. 3 An examination and comparison of the economic, psychological, and philosophical arguments advanced as the rationale for free enterprise, democratic socialist, fascist, etc. systems of economic order. ECN 5400 Financial Economics Cr. 3 An introduction to the financial system, which precedes courses in finance and economics. It is designed for three groups of graduate students: those who have not had such an introductory course, those who had such a course several years ago and need a review and for those who have had such a course but for one reason or another did not learn the material well enough. Concepts such as financial intermediation, money, credit, interest rates, valuation are covered in depth. Cash and derivative markets as well as domestic and international finance are grist for our mill. The roll of the monetary authority (Federal Reserve) and its relationship to the financial system is covered. Readings written by the author are also supplied to see how problems arise in the system that can seriously impair that system from optimized economic welfare. ECN 5450 Economics of the Public Sector Cr. 3 The role of the public sector in a market-oriented economy. Efficiency criteria in public decision-making, budgeting, setting of priorities. Economic analysis of the incidence and economic effects, particularly on resource allocation and income distribution of major taxes, including their structures. Problems of intergovernmental relations. Prerequisites: ECN 5100 (Minimum Grade of C, May not be taken concurrently) ECN 5460 Money and Capital Markets Cr. 3 A flow of funds approach to the study of financial institutions and markets. Analysis of the nature and role of monetary and non-monetary financial institutions. Effects of cyclical and secular changes in business activity. Federal Reserve policies and treasury operations in the financial markets. Inter-working of financial and non-financial markets. ECN 5480 Business Forecasting Cr. 3 (Formerly ECN 520.) A study of the nature, techniques and problems of business forecasting. Indicators of business activity. Short-run econometric forecasting models and the construction of aggregate forecasts and forecasts for major Economics 3 sectors of the economy. Application of aggregate and sector forecasts to particular industries and firms. Long-run predictions. Prerequisites: ECN 5150 (Minimum Grade of C, May not be taken concurrently) ECN 5850 Seminar in Monetary and Fiscal Policy Cr. 3 A study of monetary and fiscal policies designed to achieve maximum employment, price stability and economic growth. International interrelationships. ECN 5640 Practical Issues in Financial Economics Cr. 3 Acquaints students with various critical issues as applied to present day conditions and economic development. ECN 5950 Individual Readings and Research Cr. 1 An intensive study of some special problems in the general area of financial economics. ECN 5650 Theory of International Trade Cr. 3 An approach to the theory of international trade. Topics examined include the determination of the amount and composition of goods and services traded by nations, the terms of trade and changes in the structure of world trade. The impact of international trade on domestic stability, welfare and development. International factor price equalization, location theory and general methods of international economic relations. Qualitative and quantitative trade barriers are also analyzed. Prerequisites: ECN 5100 (Minimum Grade of C, May not be taken concurrently) AND ECN 5120 (Minimum Grade of C, May not be taken concurrently) ECN 5990 Master's Thesis Cr. 3 Optional Course. An intensive study of some special problems in the general area of financial economics. ECN 5660 International Monetary Analysis Cr. 3 An analysis of monetary and financial problems, adjustment mechanisms and policies of international trade. The foreign exchange market, capital flows, the problem of international liquidity. Particular, cyclical, secular and structural disequilibria in balance of payments are examined as are gold movements and the role of national central banks and international monetary agencies. International Monetary Policy analyzes issues, such as underdeveloped nations, debt forgiveness and funding of Third World projects are discussed and the ethical considerations of the human impact of international economic trends are evaluated. ECN 5700 Economic Development Cr. 3 An examination of the fundamental problems of economic development of nations and an analysis of the process of their economic growth. ECN 5750 Resource Economics A study of the distribution of natural resources. Cr. 3 ECN 5800 Introduction to Econometrics Cr. 3 Ordinary least squares, multicollinearity, dummy variables, specification error, autocorrelation and Durbin-Watson test; heleroscedaticity problem; distribution lag model. ECN 5810 Advanced Money and Capital Markets Cr. 3 Advanced course in money and capital market. This course examines new processes and products in the financial system such as securitization and financial derivatives. Prerequisites: ECN 5460 (Minimum Grade of C, May not be taken concurrently)