1 Chapter 16 Chapter 16 Preview Constructing Social Reality
advertisement

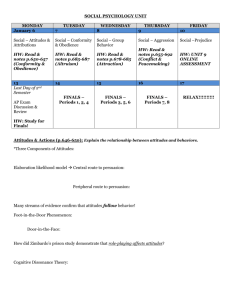
Chapter 16 Social Psychology Chapter 16 Preview Constructing Social Reality The Power of the Situation Attitudes, Attitude Change, and Action Chapter 16 Preview Prejudice Social Relationships Aggression, Altruism, and Prosocial Behavior Recapping Main Points 1 Social Psychology Social Psychology Studies effect of social variables on individual behavior, attitudes, perceptions, and motives also studies group and intergroup phenomena Social Perception Social Cognition Constructing Social Reality Process by which people select, interpret, and remember social information Process by which people come to understand and categorize the behaviors of others Origins of Attribution Theory • Describes ways social Attribution Theory perceiver uses information to generate causal explanations 2 Origins of Attribution Theory • People are Fritz Heider intuitive psychologists • Dispositional causes • Situational causes Origins of Attribution Theory • Covariation Harold Kelly model • Dimensions of information • Distinctiveness • Consistency • Consensus Fundamental Attribution Error • Fundamental Attribution Error (FAE) Lee Ross • Tendency to underestimate impact of situational factors and overestimate influence of dispositional factors • Partially due to cultural sources 3 Ratings of Questioners’ and Contestants’ General Knowledge Self-serving Biases Taking credit for successes and denying responsibility for failures Self-Serving Bias Influenced by culture Expectations and Self-Fulfilling Prophecies Prediction modifies interactions Self-Fulfilling Prophecy so as to produce what is expected People behave in ways that Behavioral Confirmation elicit specific expected reactions and then use those reactions to confirm their beliefs 4 The Power of the Situation Social Role • Social- Rule • Behavioral Social Norms • Expectation defined guideline for group has pattern of acting in for its behavior certain way members at certain time Conformity Conformity Tendency for people to adopt behaviors, attitudes, and values of other members of group Guard and Prisoner Behavior 5 Conformity Influence Information Influence Normative Influence Conformity in the Asch Experiment Conformity Minority Influence and Nonconformity More informational influence and less normative influence Serge Moscovici and colleagues 6 Decision Making in Groups Group Polarization • Tendency of groups to make more extreme decisions then decisions that would be made by members acting alone Two underlying process • Information-influence • Social comparison Groupthink Groupthink Irving Janis Tendency of decision making group to filter out undesirable input so that consensus may be reached Groupthink Factors leading to Groupthink: • High level of group cohesiveness • Isolation of group from outside information or influences • Dynamic, influential leader • High stress from external threats 7 Obedience to Authority Obedience paradigm Why do people To shock or not obey authority? to shock? Obedience in Milgram’s Experiments Attitudes, Attitude Change, and Action Attitude Positive or negative evaluation of people, Predictability of objects, and ideas attitudes influenced by •Cognitive accessibility •Affective •Behavioral 8 Processes of Persuasion • How likely people Elaboration Likelihood Model will focus their cognitive process to elaborate on persuasive message • Central routes • Peripheral routes Persuasion By Your Own Actions Dissonance Theory Cognitive Dissonance • Leon Festinger • Conflict experienced after making decision, taking action, or being exposed to information that is contrary to prior beliefs, feelings, or values Persuasion By Your Own Actions • Daryl Bem Selfperception Theory • People observe themselves to discover why they act as they do 9 Compliance Change in behavior consistent with direct Compliance request Reciprocity Compliance Techniques Commitment Prejudice • How do Prejudice you define prejudice? Origins of Prejudice • Process by which people organize their Social social environment by Categorization and others into groups categorizing themselves • In-group • Out-groups 10 Origins of Prejudice In-group bias • Evaluation of one’s own group as better then others Origins of Prejudice Racism Sexism Effects of Stereotypes Generalizations about group of people in which Stereotypes same characteristics are assigned to all members of group 11 Effects of Stereotypes Expectations encoding Effects Behavior confirmations Stereotype threat (IQ testing) Implicit Prejudice Prejudice that exists outside an individual’s conscious awareness Implicit Prejudice Implicit Association Test (IAT) Reversing Prejudice Reversing Prejudice Muzafer Sherif Elliott Aronson Robbers Cave Experiment Contact hypothesis 12 Social Relationships Liking • Physical Loving • Passion attractiveness • Similarity • Intimacy • Commitment • Reciprocity Factors in Lasting Relationships Close relationship • Feeling that “other” is included in “self” • Individuals differences in ability to sustain lasting, loving relationships • Adult attachment styles Psychology in Your Life In what ways are you like a chameleon? Why do Chartrand and Bargh speculate that mimicry functions as a kind of social glue? For more information, read the study on page 473 of your text. 13 Aggression, Altruism, and Prosocial Behavior Aggression • Behavior that cause psychological or physical harm to another individual Aggression Situational Influences • Frustration-Aggression Individual Differences Hypothesis • Direct Provocation and • Impulsive Aggression Escalation • Instrumental Aggression Altruism Altruism Reciprocal Altruism 14 Bystander Intervention Bystander must • notice emergency • label events as emergency • feel responsibility Roots of Prosocial Behavior Forces that prompt people to act for public good • Altruism • Egoism • Collectivism • Principlism Effects of the Situation on Prosocial Behavior Diffusion of Responsibility Bystander Intervention • Bib Latané and John Darley • Willingness to assist • Larger number of bystanders, less responsibility any one bystander feels to help person in need 15 Recapping Chapter 16 Main Points Constructing Social Reality • Origins of Attribution Theory • Fundamental Attribution Error • Self-Serving Biases • Expectations and Self-Fulfilling Prophecies • Behaviors that Confirm Expectations Recapping Chapter 16 Main Points Constructing Social Reality • Attribution Theory • Fundamental Attribution Error • Self-Serving Bias • Self-Fulfilling Prophecies Recapping Chapter 16 Main Points Attitudes, Attitude Change, and Action • Attitudes and Behaviors • Processes of Persuasion • Persuasion by Your Own Actions • Compliance Prejudice • Origins of Prejudice • Effects of Stereotypes • Reversing Prejudice 16 Recapping Chapter 16 Main Points Social Relationships • Liking • Loving Aggression, Altruism, and Prosocial Behavior • Individual Differences • Situational Influences • Roots of Altruism • Effects of the Situation on Prosocial Behavior 17