Lecture 8 Consumer preferences 1 Basic assumptions
advertisement

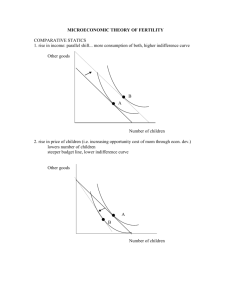
Lecture 8 • Consumer preferences – – – – Basic assumptions Indifference curves Marginal rate of substitution Related issues 1 Basic Assumptions • These are the assumptions for a rational consumer • Preferences are complete: – Consumers can compare and rank all market baskets/options (>, <, ~) – These preferences ignore costs • Preferences are transitive: – If A>B and B>C, then A>C – Necessary for consumer rationality • All goods are desirable (normal): – Consumers always prefer more of any good to less, i.e. no inferior goods 2 Indifference Curves • Definition: An indifference curve represents all combinations of market baskets that provide the same level of satisfaction to a person • Shape of an indifference curve: Downward sloping from left to right • An indifference map: – An indifference map is a set of indifference curves that describes a person’s preferences – An indifference curve to the further right represents a higher utility – Indifference curves for the same person (in an indifference map) never intersects 3 Marginal Rate of Substitution • Purpose: To quantify the amount of one good a consumer will give up to obtain more of another good • Definition: ∆X > 0 – MRS = - ∆Y/∆ – At a particular point, MRS = - dY/dX so that MRS is the negative of the slope of the indifference curve at that point • For a convex indifference curve: – We have implicitly assumed that the MRS is diminishing as quantity increases – Intuition: a consumer would prefer to give up fewer and fewer units of Y to get an additional unit of X 4 Related Issues • Complements and Substitutes: – Indifference curve for perfect substitutes, if MRS is constant – Indifference curve for perfect complements if MRS is zero • Ordinal vs. cardinal: – Ordinal: place market baskets in the order of most preferred to least preferred, but does not specify how much one market basket is preferred to another – Cardinal: provide a quantitative measurement of preference for each market basket in terms of basic units (useful for aggregation) 5