Transistors Part 1
advertisement

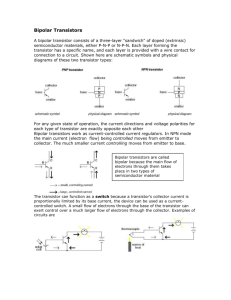
Transistors Part 1 Transistors • Transistors are used for amplification. • They have been referred to as a ThreeTerminal Amplifier with one terminal being common to the other two terminals and is usually grounded. • Transistors behave as a resistor whose ohmic value is varied by the AC input signal. Transistors • A transistor is made up of diodes: NPN type Collector Base Emitter Transistors • There are two types of transistors we will look at; they are the NPN and the PNP. Transistors • Current flows in a transistor from emitter to collector with a small portion flowing into the base. (NPN) Transistors • This also applies to PNP transistors. Transistors • Designation of transistor terminals are the Collector (output), Base (input) and Emitter (common). Transistors THE BASE CURRENT CONTROLS THE COLLECTOR CURRENT The collector current Ic is forced to flow through the base region on its way between emitter and collector. The transistor is so constructed that the base current IB can control the resistance around the base region and thus control Ic. Regardless of the type of transistor (NPN or PNP), an increase in base current reduces the resistance of the transistor, resulting in a larger value of collector current. A reduction in base current increases the transistor resistance, and a smaller value of collector current will flow. Transistors Basics of DC Biasing Transistors Basics of DC Biasing Transistors • Transistor schematic symbols Transistors The transistor as an amplifier The DC bias currents are the solid dark arrows and the mini-sine waves is the AC signal. This is a Common Emitter PNP type as the arrow on the emitter point in to the base. Transistors • The DC bias currents remain constant in the circuit to operate the transistor. Without them the transistor will not function. Thus, the AC signal will ride on top of the DC values. The dashed lines represent DC and the sine wave represents AC. Transistors AC Current Input on Base and Collector Output. Beta (β) is the transistor gain. Equation shown at bottom of chart ↘ Transistors • Amplifying Characteristics of an NPN type Transistors • We have 10-mVp-p as input signal on the base. We develop 20-uAp-p of input signal current and since our Beta is 200 our output signal should be 10-mVp-p x 200 = 4-Vp-p and 20-uAp-p x 200 = 4-mAp-p. • The individual voltage drops and rises are the DC biasing of the circuit to allow the amplifying transistor to operate. Transistors • In Transistors Part 2 we will discuss: – Transistor configurations – Transistor voltage feedback – Transistor current feedback – Two-Stage, Push-Pull, Darlington and other coupling circuits.