Sentence Diagram 1 Running head: SENTENCE DIAGRAM
advertisement

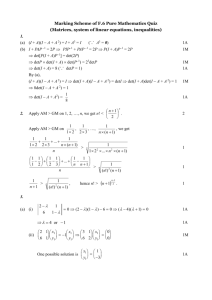
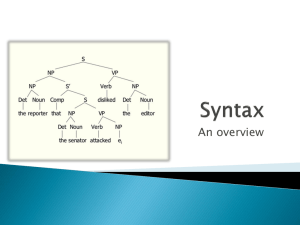
Sentence Diagram Running head: SENTENCE DIAGRAM Sentence Diagram Assignment Chris Giblin ESL 505 University of Phoenix 1 Sentence Diagram 2 INTRODUCTION In teaching English as a second language (ESL), instructors need to have an understanding of how English syntax works, how it can be broken down into constituents (natural groupings of a sentence), and how it can be taught effectively to ESL students. By using tree diagrams as a way of teaching English syntax, English instructors can simplify the students’ learning process. Instead of observing a sentence as a whole, naming the parts of speech, and identifying various constituents (such as noun phrases, verb phrases, and prepositional phrases), instructors can break down the sentence into key components, which can be better understood by L2 learners. SENTENCE DIAGRAMING EXAMPLES One way to introduce sentence diagramming is to simply jump right into some examples. The following are abbreviations that are found under every sentence, phrase, or single word in the example sentences: (S) = sentence, (NP) = noun phrase, (VP) = verb phrase, (V) = verb, (CN) = common noun, (PN) = proper noun, (Adj) = adjective, (Adv) = adverb, (Det) = determiner, (PP) = prepositional phrase, (P) = preposition, and (CS) = coordinate structure. The example sentences are as follows: 1. A scared passenger flew the fast airplane. 2. The cold breeze made my hat blow away. 3. The new car with eight valves sped by the quail on the grassy hill. 4. The teacher saw that the principal arrived. 5. The boat and the ore sank into the water. Sentence Diagram Figure 1. 1. A scared passenger flew the fast airplane. (S) A scared passenger flew the fast airplane (NP) A scared (Det) (Adj) (VP) passenger (CN) flew the fast airplane (V) (NP) the fast (Det) (Adj) airplane (CN) 3 Sentence Diagram Figure 2. 2. The cold breeze made my hat blow away. (S) The cold breeze made my hat blow away (NP) (VP) The cold breeze made my hat (Det) (Adj) (CN) (V) (NP) blow away (VP) my hat (Det) (CN) blow (V) away (Adv) 4 Sentence Diagram Figure 3. 3. The new car with eight valves sped by the quail on the grassy hill. (S) The new car with eight valves sped by the grassy hill (NP) (VP) The new car with eight valves sped (NP) (PP) (V) The new car (Det) (Adj) (CN) by the grassy hill (PP) with eight valves by (P) (Adj) (CN) (P) the grassy hill (NP) the (Det) grassy (Adj) hill (CN) 5 Sentence Diagram Figure 4. 4. The teacher saw that the principal arrived. (S) The teacher saw that the principal arrived (NP) (VP) The teacher (Det) (CN) saw that (V) (C) the (Det) the principal arrived (NP) principal arrived (CN) (V) 6 Sentence Diagram Figure 5. 5. The boat and the ore sank into the water. (S) The boat and the ore sank into the water (NP) The boat (NP) (VP) and the ore sank into the water (CS) (NP) (V) (PP) The boat the ore into (Det) (CN) (Det) (CN) (P) the (Det) water (CN) CONCLUSION After carefully observing the above sentence diagrams, an ESL instructor should have a decent idea of how sentences can be broken down into constituents making them easier to comprehend for L2 learners. Instructors can use sentence diagrams as both part of a lecture as well as for student assignments. 7 Sentence Diagram References Fromkin, V., Hyams, N., & Rodman, R. (2003). An introduction to language (7th ed.) Boston: Thomson, Inc. EBSCOHOST database. 8