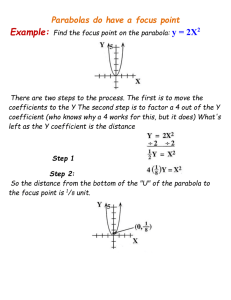
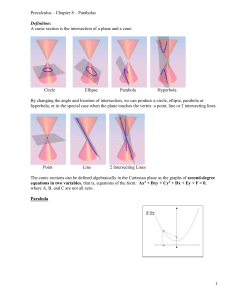
Math 1330 Section 8.1
advertisement

Math 1330 Section 8.1 Section 8.1: The Parabola We already know that a parabola is the graph of a quadratic function ݂ሺݔሻ = ܽ ݔଶ + ܾ ݔ+ ܿ. But there is more to be learned about parabolas. For example, when we studied quadratic functions, we saw that the graphs of the functions could open up or down. As we look at conic sections, we’ll see that the graphs of these second degree equations can also open left or right. So, not every parabola we’ll look at in this section will be a function. A parabola is the set of all points equally distant from a fixed line and a fixed point not on the line. The fixed line is called the directrix. The fixed point is called the focus. The axis, or axis of symmetry, runs through the focus and is perpendicular to the directrix. The vertex is the point halfway between the focus and the directrix. Basic “Vertical” Parabola: Equation: ݔଶ = 4ݕ Focus: ሺ0, ሻ Directrix: = ݕ− Focal Width: |4| p Coordinates of Focal Chord: ሺ±2, ሻ p Basic “Horizontal” Parabola: Equation: ݕଶ = 4ݔ Focus: ሺ, 0ሻ Directrix: = ݔ− Focal Width: |4| -p p 1 Math 1330 Section 8.1 Graphing parabolas with vertex at the origin: • When you have an equation, look for ݔଶ or ݕଶ • If it has ݔଶ , it’s a “vertical” parabola. If it has ݕଶ , it’s a “horizontal” parabola. • Rearrange to look like ݕଶ = 4 ݔor ݔଶ = 4ݕ. In other words, isolate the squared variable. • Determine p. • Determine the direction it opens. o If p is positive, it opens right or up. o If p is negative, it opens left or down. • Starting at the origin, place the focus p units to the inside of the parabola. Place the directrix p units to the outside of the parabola. • Use the focal width 4p (2p on each side) to make the parabola the correct width at the focus. Example 1: Graph ݕଶ = 20ݔ. Vertex: _____________ Focus: ______________ Directrix: ____________ Focal Width: _________ 2 Math 1330 Section 8.1 Example 2: 6 ݔଶ + 24 = ݕ0. Vertex: _____________ Focus: ______________ Directrix: ____________ Focal Width: _________ Graphing parabolas with vertex not at the origin: • • • • Rearrange (complete the square) to look like ሺ ݕ− ݇ሻଶ = 4ሺ ݔ− ℎሻ. Vertex is ሺℎ, ݇ሻ Draw it the same way, except start at this vertex. Focus ሺ, 0ሻ changes to ሺℎ + , ݇ሻ. Directrix: = ݔ− changes to the line = ݔ− + ℎ. • • • Rearrange (complete the square) to look like ሺ ݔ− ℎሻଶ = 4ሺ ݕ− ݇ሻ. Focus ሺ0 ሻ changes to ሺℎ, + ݇ሻ. Directrix: = ݕ− changes to the line = ݕ− + ݇. Example 3: Find the standard form of the equation, the vertex, the focus, and the directrix for each example: a. ݔଶ − 2 ݔ− 8 ݕ+ 25 = 0 3 Math 1330 Section 8.1 b. ݕଶ − 4 ݕ− 2 ݔ+ 8 = 0 Example 4: Suppose you know that the vertex of a parabola is at ሺ−3,5ሻ and its focus is at ሺ1,5ሻ. Write an equation for the parabola in standard form. A line through a point that lies on a parabola is tangent to the parabola at the point if the line intersects the parabola only at one point and the line is not parallel to the axis of the parabola. A tangent line to the point ሺݔ , ݕ ሻwhich lies on the parabola with the equation ܽ ݔଶ + ܾ ݔ+ ܿ will have slope ݉ = 2ܽݔ + ܾ. We can use this information to find the equation of the tangent line. Example 5: Write an equation of the line tangent to the parabola with the equation ݂ሺݔሻ = 2 ݔଶ + 5 ݔ− 3 at = ݔ2 4 Math 1330 Section 8.1 Example 6: Find the point(s) of intersection of the parabola and the line ݂ሺݔሻ = −2 ݔଶ + 8 ݔ− 5 ݃ሺݔሻ = 6 ݔ− 5 5