•
advertisement

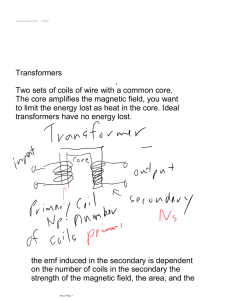
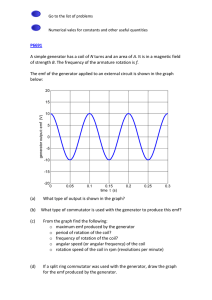
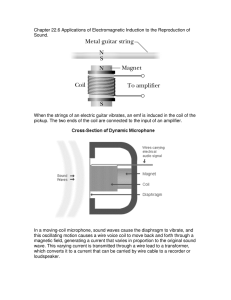
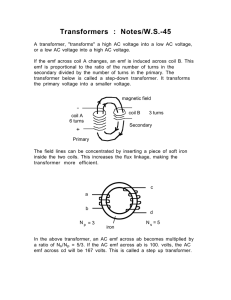
• Targets • describe how mutual induction occurs in circuits • apply the transformer equation to solve problems involving step up and step down transformers • Do Now • staple and turn in Experiment 20.3 report • Homework • read pp. 721, 727-730 • complete Transformer Activity pre-lab Friday, 5 March 2010 Generator • a machine that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy • ac generator: produces alternating current (has slip rings) • dc generator: produces direct current (has split rings) Friday, 5 March 2010 Examples of Generators Friday, 5 March 2010 Examples of Generators • hydroelectric plant • wind turbine • coal-based power plant • gasoline-powered generator • car alternator • hybrid car braking system Friday, 5 March 2010 Motors • convert electrical energy to mechanical energy • almost identical in constructor to a dc generator Friday, 5 March 2010 Transformer • a device that increases or decreases the emf of alternating current • primary coil: connected to emf source • secondary coil: connected to load • coils are electrically isolated but share a magnetic field Friday, 5 March 2010 Transformer Equation • ΔV / ΔV = N / N • ΔV : applied emf in primary • ΔV : induced emf in secondary • N : number of turns in primary • N : number of turns in secondary P S P S P S Friday, 5 March 2010 P S Types of Transformers • step-up transformer • secondary has more turns than primary (N > N ) • induced emf in secondary is greater than applied S P emf to primary (ΔVS > ΔVP) • step-down transformer • primary has more turns than secondary (N > N ) • applied emf to primary is greater than induced emf P in secondary (ΔVP > ΔVS) Friday, 5 March 2010 S Examples of Transformers • power distribution • power bricks for consumer electronics • car ignition coil Friday, 5 March 2010