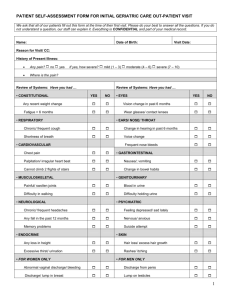
Unpaired t test results
advertisement

1. The data is catergorical since it is split into culture confirmed matching A or B. Any culture flu A or B, ad any culture or serology confirmed influenza A or B. Quantitative Variable A quantitative variable is naturally measured as a number for which meaningful arithmetic operations make sense. Examples: Height, age, crop yield, GPA, salary, temperature, area, air pollution index (measured in parts per million), etc. Categorical Variable Any variable that is not quantitative is categorical. Categorical variables take a value that is one of several possible categories. As naturally measured, categorical variables have no numerical meaning. Examples: Hair color, gender, field of study, college attended, political affiliation, status of disease infection. 2. Take the overall data from VMCCI and the overall data from teh vaccine/placebo. Do a t test. The t-test assesses whether the means of two groups are statistically different from each other. This analysis is appropriate whenever you want to compare the means of two groups. Compare the placebo the control to the vaccine group to the number of affected. a. T-test b. One-sided since only care about how far the control (the placebo) is from the vaccine. In testing this drug, you are only interested in testing if it more effective than the placebo. Null hypothesis: There is no difference in VVMCCI cultures between the placebo or the vaccine shot. Alternative Hypothesis: There is a significant difference between the VMCCI cultures between those who received the placebo or the vaccine 3. Unpaired t test results P value and statistical significance: The two-tailed P value is less than 0.0001 By conventional criteria, this difference is considered to be extremely statistically significant. Confidence interval: The mean of Vaccine minus Placebo equals -22.000 95% confidence interval of this difference: From -22.704 to -21.296 Intermediate values used in calculations: t = 61.3845 df = 7480 standard error of difference = 0.358 Learn more: GraphPad's web site includes portions of the manual for GraphPad Prism that can help you learn statistics. First, review the meaning of P values and confidence intervals. Then learn how to interpret results from an unpaired or paired t test. These links include GraphPad's popular analysis checklists. Review your data: Group Vaccine Placebo Mean 23.000 45.000 SD 15.500 15.500 SEM 0.254 0.253 N 3714 3768 The null hypothesis is rejected the placebo and vaccine group are significantly different. 5. 6. Type I error is the incorrect rejection of a true null hypothesis. It is a false positive. This would be that the fact that the difference we found between the placebo and the drug group actually does not exist and the vaccine actually does not help. Type II is the failure to reject a false null hypothesis. It is a false negative. This would be if we did not find a significance difference between the placebo and the vaccine, but there is. Either way these errors would not be good for the general public. 7. 0.014331 8. P value more convincing. A high efficacy does not suggest a high difference in the rates of flu. It is the p value and SD it is small bc it is saying that 95% sure that the vaccine actually works. The .05 p is saying that there is a 5% chance you cannot reject the null. 9. Yes this vaccine protects against the flu. I am 99.9% sure that the null hypothesis is rejected according to the t-test, therefore there is a significant difference between those who receive the shot and get the flu and those who do not receive the flu shot and get the flu. 10. Use a t-test again.Null hypothesis there is no difference between LCI groups who recieved or did not recieve the vaccine. Alternative: There is a difference in LCI between people who recieved the vaccine or did not recieve the vaccine Cart SEARCH Sign In Scientific Software Data Analysis Resource Center Company Support How to Buy 1. Select category 2. Choose calculator 3. Enter data 4. View results Unpaired t test results P value and statistical significance: The two-tailed P value is less than 0.0001 By conventional criteria, this difference is considered to be extremely statistically significant. Confidence interval: The mean of Vaccine minus Placebo equals -78.0000 95% confidence interval of this difference: From -80.5050 to -75.4950 Intermediate values used in calculations: t = 61.1780 df = 7480 standard error of difference = 1.275 Learn more: GraphPad's web site includes portions of the manual for GraphPad Prism that can help you learn statistics. First, review the meaning of P values and confidence intervals. Then learn how to interpret results from an unpaired or paired t test. These links include GraphPad's popular analysis checklists. Review your data: Group Vaccine Placebo Mean 44.0000 122.0000 SD 55.1400 55.1400 SEM 0.9048 0.8983 N 3714 3768 a. P value less than p<.05 in fact p<.001 like in 3 b. Since LCI confirms the flu and the p is significant meaning there is a difference between people who receive the vaccine and the placebo and their LCI so not does not overestimate.