electricity
advertisement

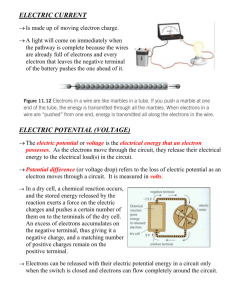
Electricity Electricity Electricity occurs in 2 different forms • Static • Current Current Electricity • Moving electricity • Electrons flow through a conductor - material that allows electrons to flow through • Circuit = continuous loop for electrons to flow • Needs energy supply Electrical components • Wire • Ammeter • Battery • Fuse • Connected wires • Bulb • Switch • Voltmeter • diode • Resistor • Rheostat CIRCUIT TYPES The simplest type of circuit involves electricity going around with no “choices” (electrons don’t really choose). This is called a Series circuit. Draw the path the electrons travel-out the negative toward the positive The other main type of circuit has two or more branches. This is called a Parallel circuit. Draw on the electron flow. What sort of circuit is this? A parallel… but, more importantly… A short circuit. Series circuit • Has a single loop for electrons to travel round • Components are connected one after another • Current has to travel through all components • Current is the same at all points • Voltage is shared between components • It is either all on or all off Series circuit • http://www.ndted.org/EducationResources/High School/Electricity/seriescircuit. htm Parallel circuit • Has two or more paths for electrons to flow down • Current is shared between the branches • Sum of the current in each branch = total current • Voltage loss is the same across all components Practice • http://lgfl.skoool.co.uk/keystage 3.aspx?id=93 Current (I) Current is the flow of electrons around a circuit • DC = direct current like battery • Electrons flow in one direction • AC = Alternating current like mains • Electron flow changes direction 50x per second Ammeter • • • • Measures CURRENT(I) Unit = Amp (A) Current is flow of electrons Connect in series at the point you wish to measure Voltage (V) Gain or loss of energy as it passes through a component • Voltage lost = voltage gained • In series voltage loss is shared between components • In parallel voltage loss is the same across all components Voltmeter • Measures voltage • Unit = Volt (V) • Voltage increases as it passes through energy suppliers • Voltage is decreased as it passes through users • Connect in parallel around a component SUMMARY In Series Current Voltage Always the same Voltage from source = voltage used Voltage is shared between power users In Parallel The branches share electrons and add to the total Voltage is the same in all branches Resistance (R) The amount that a component slows the current •As the electrons are slowed by a resistor, energy is lost in the form of heat. •This means that current, resistance and voltage must be linked. •This is Ohms law •The unit of resistance is the ohm, symbol V I × R Power Energy used by component per second • Unit of power is the Watt, symbol is W • One watt means that 1 joule of electrical energy is being used up per second. • Current, voltage and power are linked P I × V Electricity Generation • Brainstorm ways to generate electricity Fossil Fuels Hydro Dam Hydroelectric power Nuclear power Wind Power Tidal Power Geothermal Solar • Solar water heating • Photovoltaic cells • Solar furnace PROBLEMS 1. Fill in the gaps in the table. a b c d e g i k j f h l